McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 1
What is Strategic
Management?
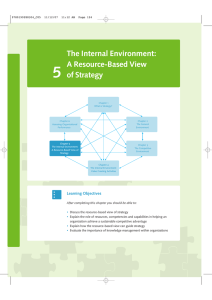
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should have a
good understanding of:
The definition of strategic management and its four
key attributes.
The strategic management process and its three
interrelated and principal activities.
The resource-based view of the firm and the
different types of tangible and intangible
resources, as well as organizational capabilities.
The four attributes that a firm’s resources must
possess to maintain a sustainable advantage
1-3
Two Perspectives of Leadership
Romantic view
Leader is the key force in organization’s success
External control perspective
Focus is on external factors that affect an
organization’s success
Leaders can make a difference
Must be aware of opportunities and threats faced in
external environment
Must have thorough understanding of the firm’s
resources and capabilities
1-4
Example: What’s In a Leader?
Always emphasized the importance of
innovative and flexible leadership that is adept
at adjusting to changing times and
circumstances
In 1989, CEO of Ford Motor received Chief
Executive magazine's CEO of the Year Award
Fred Smith started Federal Express in 1971 on
a premise that was found to be highly
improbable by one of his business school
professors
www.forbes.com/leadership/2007/08/07/ceo-management-personalities-lead-cz_ek_0807topceo.html
1-5
The Nature of Strategic Management
Today must do more than set long-term
strategies and hope for the best
Must go beyond “incremental management”
Making minor changes
Today’s pace of change is accelerating
Manager’s must make major and minor changes in
strategic direction
Leaders must be:
Proactive
Anticipate change
Continually refine and make strategic changes
1-6
Strategic Management
Strategic Management consists of the
analyses, decisions, and actions an
organization undertakes in order to
create and sustain competitive
advantages
1-7
Strategic Management
Analysis
Strategic goals (vision, mission, strategic objectives)
Internal and external environment of the firm
Strategic decisions
What industries should we compete in?
How should we compete in those industries?
Actions
Allocate necessary resources
Design the organization to bring intended strategies
to reality
1-8
Strategic Management
Strategic management is the study of
why some firms outperform others
How to compete in order to create
competitive advantages in the marketplace
How to create competitive advantages in the
market place
Unique and valuable
Difficult for competitors to copy or substitute
1-9
Question
Which of the following is not a key attribute of
strategic management?
a) Recognizes trade-offs between efficiency and
effectiveness
b) Directs management in making proper decisions to
benefit firm
c) Directs the organization toward overall goals and
objectives
d) Needs to incorporate short-term and long-term
perspectives
1-10
Key Attributes
Key Attributes of strategic
management:
Directs the organization toward overall
goals and objectives
Includes multiple stakeholders in
decision making
1-11
Key Attributes
Key Attributes of strategic management:
Needs to incorporate short-term and longterm perspectives
Peter Senge refers to this needs as a “creative
tension”
Must maintain a vision for the future of the
organization and focus on its present operating
needs
Recognizes trade-offs between efficiency and
effectiveness
1-12
Question
The final realized strategy of a firm is a
combination of:
a) Intended and unrealized strategies
b) Unrealized and emergent strategies
c) Emergent and deliberate strategies
d) Deliberate and unrealized strategies
1-13
Strategic Management Process
Henry Mintzberg, management scholar at
McGill University
Business environment far from predictable
Decisions seldom based on optimal rationality
alone
Decisions following analysis constitute
intended strategy
Final realized strategy of any firm is a
combination of deliberate and emergent
strategies
1-14
Strategic Management Process
1-15
Strategic Analysis
Starting point in the strategic management
process
Precedes effective formulation and
implementation of strategies
1-16
Strategic Analysis (cont.)
Frameworks for analyzing a firm’s internal
environment
Strengths
Weaknesses
Analyzing strengths can uncover potential sources
of competitive advantage
Analyzing external environments
Competitors
General environment
Industry environment
1-17
Example: Sony’s Move
Video game leader struggles
Historical industry leader Nintendo had
drifted down to third
Sony Vs. Microsoft and Nintendo
Slashed price of its PlayStation 3 console
Simplest option is to just come up with a
copy-cat version of Nintendo’s Wii controller
www.forbes.com/leadership/2007/08/01/sony-games-innovation-lead-cz_cc_0802christensen.html
1-18
Strategy Formulation
Business level strategy:
Successful firms develop bases for competitive
advantage
Cost leadership
Differentiation
Focusing on narrow or industry-wide market segments
Sustainability
Industry life cycle
1-19
Strategy Formulation (cont.)
Corporate-level strategy addresses:
Firm’s portfolio or group of businesses
What business(es) should we be in?
How can we create synergies among the businesses?
Diversification
Related
Unrelated
1-20
Question
All of the following are key types of resources
except:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Physical
Tangible
Intangible
Organizational capabilities
1-21
Resource-Based View of the Firm
Resource-based view -- helpful perspective for
understanding strategic management and its
activities
Two perspectives
The internal analysis of phenomena within a company
An external analysis of the industry and its competitive
environment
1-22
Resource-Based View of the Firm
Firm’s resources must be evaluated in
terms of how valuable, rare, and hard they
are for competitors to duplicate
Three key types of resources
Tangible resources
Intangible resources
Organizational capabilities
1-23
Resource-Based View of the Firm
1-24
Types of Resources:
Tangible Resources
Relatively easy to identify
Financial resources
Firm’s cash accounts
Firm’s capacity to raise equity
Firm’s borrowing capacity
Physical resources
Modern plant and facilities
Favorable manufacturing locations
State-of-the-art machinery and equipment
1-25
Types of Resources:
Tangible Resources
Technological resources
Trade secrets
Innovative production processes
Patents, copyrights, trademarks
Organizational resources
Effective strategic planning processes
Excellent evaluation and control systems
1-26
Question
Intangible resources are:
a)
b)
c)
d)
The same as capital resources
Easy to attain and keep on hand
Easily substitutable or imitated
Difficult for competitors to account for or imitate
1-27
Types of Resources:
Intangible Resources
Difficult for competitors (and the firm itself) to
account for or imitate
Human
Experience and capabilities of employees
Trust
Managerial skills
Firm-specific practices and procedures
1-28
Types of Resources:
Intangible Resources
Innovation and creativity
Technical and scientific skills
Innovation capacities
Reputation
Brand name
Reputation with customers
Reputation with suppliers
1-29
Example: McDonald’s Innovation
Focus on nonconsumption and a welldesigned innovation process
McDonald's sought to increase sales
during parts of the day when its share of
total food and snack consumption was low
Breakfast – McGriddle products
Snacking occasions – Snack wrap
www.forbes.com/claytonchristensen/2007/08/31/christensen-innovation-mcdonalds-pf-guru_in_cc_0904christensen_inl.html
1-30
Types of Resources:
Organizational Capabilities
Competencies or skills that a firm employs to
transform inputs to outputs, and capacity to
combine tangible and intangible resources to
attain desired end
Outstanding customer service
Excellent product development capabilities
Innovativeness of products and services
Ability to hire, motivate, and retain human capital
1-31
Dell’s Resources and Capabilities
1-32
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Resources alone are not basis for competitive
advantages, nor are advantages sustainable
over time
Resources or capabilities may help firm to
increase revenue or lower costs
Only temporary advantage
1-33
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Is the resource or
capability…
Valuable
Rare
Difficult to imitate or
substitute
Implications
• Neutralize threats and
exploit opportunities
• Not many firms possess
• Physically unique
• Path dependency
• Causal ambiguity
• Social complexity
Organizationally
Activatible?
• Firm has complementary
resources to optimize
capability
1-34
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Is the Resource Valuable?
Resources are valuable when they enable a firm to
formulate and implement strategies that improve its
efficiency or effectiveness
SWOT matrix suggests firms improve performance
only when they exploit opportunities or neutralize
threats
1-35
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Is the Resource Rare?
If competitors possess same valuable resource,
not source of competitive advantage
Common strategies based on a resources is not
an advantage
Some strategies require mix of resources –
tangible assets, intangible assets, and
organizational capabilities
1-36
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Can the Resource Be Imitated Easily?
Inimitability is key to value creation
Constrains competition
Competitors will eventually find a way to copy
valuable resources
Advantage based on inimitability won’t last forever
1-37
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Can the Resource Be Imitated Easily?
Managers can develop strategies around
resources that have one or more of the following
four characteristics:
Physical Uniqueness
Path dependency
Causal ambiguity
Social complexity
1-38
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Are Substitutes Readily Available?
Must be no strategically equivalent valuable
resources that are themselves not rare or inimitable
Substitutability takes two forms:
Substitute similar resource to implement same
strategy (In-person vs. Video Training)
Very different resources can become strategic
substitutes (Internet vs. Brick & Mortar facilities)
1-39
Firm Resources and
Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Is the Capability Organizationally Activatable?
Firm must have access to complementary
resources to maximize capability potential
Types of Complementary Resources Include:
Financial Capital
Production/Manufacturing Facilities
Marketing KSAs
Distribution Networks
1-40
Criteria for Sustainable Competitive
Advantage and Strategic Implications
Is a resource or capability…
Valuable
Rare Inimitable/ Activatable Implications
Substitute
for Competitiveness
No
No
No
No
Competitive disadvantage
Yes
No
No
No
Competitive parity
Yes
Yes
No
No
Temporary competitive
advantage
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Sustainable competitive
advantage
Exhibit 3.7 Criteria for Sustainable Competitive Advantage and Strategic Implications
Source; Adapted from J. Barney, “Firm Resources a Sustained Competitive Advantage, ‘ Journal of
Management 17 (1991), pp. 99-120.
1-41