بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
advertisement

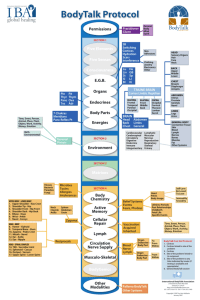
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Shoulder Joint (Gleno-Humeral) & Axilla Objectives How shoulder joint is formed. Name the type of the joint. Explain structures related to the shoulder joint. Name the movements taking place on shoulder joint. Define shoulder joint dislocation and subluxation. Define axilla. Give its boundaries and contents. Shoulder joint Articulation Type Capsule Ligaments Movements Bones forming Shoulder joint Capsule and ligaments of the Shoulder Joint Capsule and ligaments of the Shoulder Joint Movements at the Shoulder Joint Adduction Abduction Flexion Extension Circumduction Rotation Definitions Dislocation: The joint surfaces are completely displaced and are no longer in contact. Subluxation: A lesser degree of displacement, such that the articular surfaces are still partly apposed. Fracture: Fracture is a break in the structural continuity of bone. A. B. C. Subluxation Partial dislocation Complete dislocation Dislocation of shoulder joint Causes of shoulder dislocation Shoulder joint is commonly dislocated due to it’s freedom of movement and instability. Common causes are: A fall on the hand. Excessive extension and lateral rotation of the hummers. Axilla (Armpit) The axilla is the region between the pectoral muscles, the scapula, the arm and the thoracic wall. It is a region through which vessels and nerves pass from the root of the neck into the upper limb. Axilla is a space 4 Sided pyramid Apex connected to the neck Base Arm pit Anterior wall Posterior wall Medial wall Lateral wall Section of Axilla Boundaries of the Axilla • Apex: Clavicle anteriorly, the upper border of the scapula posteriorly and the first rib medially. • Base: Skin and fascia of the arm pit Boundaries of the Axilla • Anterior wall: Pectoralis major muscle, Pectoralis minor muscle, and the clavipectoral fascia • Posterior wall: Posterior axillary fold (teres major and Latissimus dorsi) and the subscapularis. • Medial wall: Upper portion of the thoracic wall and the serratus anterior muscle. • Lateral wall: Intertubercular sulcus of the Humerus. Contents of the Axilla 1. Axillary sheath 2. Brachial plexus :are the nerves which supply the upper limb 3. Axillary vessels and their branches 4. Lymph nodes 5. Lymphatic vessels 6. fat The Axilla . . Thank you