lec4new
advertisement

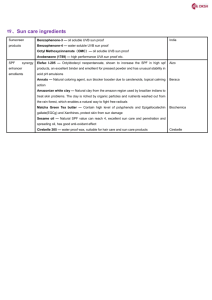
PHT 435 A cream is a topical preparation usually used for application to the skin. Its made of a solid or semisolid emulsion. Water is an important content of skin creams. According to emulsion type: 1. W/O creams Eg: cold cream, cleansing cream, and emollient cream. 2. O/W creams Eg: common misturizers (hands and body) Vanishing cream. According to function: Eg - cleansing, foundation, mousturizing etc. It is an emulsion of water in oil (W/O). Used as moisturizer, makeup remover and cleanser. Normally the following ingredients are used: 1. Meniral oil. 2. White beeswax. 3. Borax (used as emulsifier). responsible for the whiteness of cold cream. 4. Alcohol, glycerin, and lanolin. 5. perfume Cleaning cream used for removal of facial makeup, surface grime and oil from the face and neck. Leaving an emollient residual film on the skin to keep it smooth and soft. Cleansing cream is specifically formulated to dissolve away greasy binding materials holding pigments on the skin. Conveniently applied. Has low irritation factor when used. Will leave an emollient residual film on the skin which is protective in a dry skin condition. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Stable, and have a good appearance. Should soften on application to the skin. Should spread easily. During application It should not feel greasy or oily. A thin emollient film should remain on the skin after use of the cream. It should be effectively be able to remove oilsoluble and water soluble soil and surface oil. Vanishing creams get their name from the fact that they seemed to disappear when spread onto the skin. They are an oil-in-water O/W emulsion consisting of a stearic acid, an alkali, a polyol and water. the continuous phase evaporates leaving thin film on the skin. Produce emollient and moisturizing effect. The traditional formula is based on high quality stearic acid as the oil phase. This provides an oil phase which melts above body temperature and crystallizes in a suitable form so as to be invisible and give non greasy film The emulsifier is a soap which is formed in situ by adding sufficient alkali or base to neutralize a portion of the available fatty acids. Rx Stearic acid Pot. Hydroxide Glycerin Water Perfume, preservative 15 % 0.7 % 5% 79% q.s Moisturizing creams are used for day time , they are intended to help preserve the skin in a soft condition and delay formation of lines and wrinkles. They maintain the moisture content of the skin. Prevent dry skin condition by absorption of moisture. They are used on the skin before applying make up , even before the use of colored foundation cream. Emulsifiers Emulsifying agents, which are surface-active agents (surfactants), are available in a wide range of chemical types. These include nonionic and ionic. 1. Oil-in-Water Emulsions Typically contain 10% to 35% oil phase; a lowerviscosity emulsion may have an oil phase reduced to 5% to 15%. Water in the external phase of the emulsion helps hydrate the stratum corneum of the skin. This is desirable when one desires to incorporate watersoluble active ingredients in the vehicle. Emulsifier blends with HLBs ranging from 7 to 16 are used for forming o/w emulsions. Eg. glycerol monostearate and polyoxyethylene stearate blend and Polysorbates are o/w emulsifiers. Water-in-Oil Emulsions 2. These systems are desirable when greater release of a medicating agent or the perception of greater emolliency is desired. Emulsifiers having an HLB range of 2.5 to 6 are frequently selected. When multiple emulsifiers are used, the predominant one is generally lipophilic with a smaller quantity of a hydrophilic emulsifier. Eg. Sorbitan stearates and oleates are effective emulsifiers when used at 0.5% to 5.0%, sorbitan isostearates, being branched chain materials, give a very uniform particle size for w/o emulsions. Multiple Emulsions 3. Two types of multiple emulsions are encountered in skin care, w/o/w, where the internal and external water phases are separated by oil, and oil-in-water-in-oil (o/w/o), where the water phase separates the two oil phases. Benefits of these types of formulations are the claimed sustained release of entrapped materials in the internal phase and separation of various incompatible ingredients in the same formulation. Emollient Emollients are materials used for the prevention or relief of dryness as well as for the protection of the skin Water soluble emollients: propylene glycol, Glycerol, Sorbitol and PEG. Oil soluble emollients: Hydrocarbon oils and waxes Triglyceride oils Light-to-heavy feel, often used as spreading agents. Humectants Eg. Glycerin, Propylene Glycol, Sorbitol, Polyethylene glycol 0.5–15.0% in formulation Moisture-binding properties help retard evaporation of water from formulation. control viscosity, and impact body and feel of emulsion. Mineral oil Hydrocarbon, stable, inexpensive, not subjected to rancidity and odorless It is a good solvent for oils and greases binding makeup to skin. Increase mineral oil stiffs the cream. Increase water content softens the cream. Petrolatum Petrolatum, help stabilize the cream if a high percentage of oil is used. aids in preventing bleeding of the mineral oil, particularly when a light viscosity oil is used. Thickeners Eg. Carbopol, Veegum Help obtain viscosity, enhance stability, bodying agents. Foundations are available in various forms: liquids, gels, creams, solid creams, cakes (pancakes), mousse, or in sticks (pen stick). There are four basic facial foundation formulations: 1. oil-in-water (for normal- and oily-skin types) 2. water-in-oil (normal- and dry-skin types) 3. oil-free (oily-skin type) 4. water-free (women with facial scarring who require camouflaging) Are applied to the skin to unify the color of the skin, improve a dull and tired complexion, give a matte finish, and mask possible imperfections like dark spots, small wrinkles, and the pores of the skin surface. Their application must be easy and give coverage for a natural complexion. They must have a pleasant texture, a good adhesive property They must be comfortable, and have a consistent color and smooth finish. Pigments Moisturizing agents like glycerin and hyaluronic acid, vegetable oils, which improve the hydration and flexibility of the skin. Vitamins Perfumes Foundation can contain: ceramides,(to strengthen the skin barrier),UV filters (UVA-UVB) giving makeup products a sun protection index (SPF 5–30), Polysolixane as Antifoaming Agent; Emollient, skin conditioning. Fluorocompounds are used as water and oil repellent. Silica is a multi-porous ingredient, which absorbs the oil and sebum UV radiation (UVR) reaching the Earth’s surface can be divided into UVB (290–320 nm) and UVA (320-400 nm). UVB is the principal cause of acute sunburn and tanning (UVA radiation cause only15–24% of sunburn). Therefore, sunscreen efficacy is predominantly directed against UVB radiations. In addition, exposure to UVB radiation is immunosuppressive, mutagenic, and carcinogenic. Definition: it’s a formulations such as creams or lotions, oils, gels, sticks, etc. that Protect the skin against the effects of UVR by ) incorporating sin the specially designed molecules (i.e., UV filters) in the formulation. The protective efficacy of a sunscreen against UVB is expressed as the sun protection factor (SPF). Sunscreens SPF ratings can range from minimal (10 SPF), to moderate (10-30 SPF), to high (30+ SPF). SPF ratings do not actually increase proportionately. In other words, an SPF of 30 is not double the protection of an SPF of 15. In fact, an SPF 30 deflects 97 percent of the sun’s UVB rays; SPF 15 deflects 93 percent of the sun’s UVB rays. UV 1. 2. 3. Filters: UVB: PABA and its derivatives, Cinnamates, Salicylates. UVA: Benzophenones, Avobenzone, Oxybenzone(A&B) Physical Blockers:Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide. Other additives: emusifying agents, emolient, preservatives, ….. Sunscreen ingredient will be determined by the type of product, SPF and UVA efficacy levels, desired 1. 2. 3. 4. It must be non volatile and resistant to water. Must posses suitable solubility characteristics. It must be non toxic non irritant and non sensitizing. Must be stable under conditions of use. The American Cancer Society warns against two types of artificial tanning – tanning beds or sunlamps – and a new product on the market – tanning pills and accelerators. Tanning Beds/Sunlamps: Give both UVA (320 to 400 nm) and UVB (290 to 320 nm) rays which can cause serious, long-term skin damage. Tanning pills: contain color additives similar to beta-carotene, the substance that gives carrots their orange color. The additives are distributed throughout the body, especially the skin, turning it an orange like color. The main ingredient in sunless tanning pills, canthaxanthin, (yellow crystals) its not FDA approved and may cause liver and skin problems. Tanning accelerators: Its in the form of oil or lotion it have the potential to enhance skin pigmentation, while exposing to UV radiation (from the sun or tanning bed) these tan accelerators contain amino acid tyrosine or tyrosine derivatives that broken down by tryosinase enzyme produced by melanocytes. Dopaquinone will be formed which in turn forms the different types of melanin color. This reaction is triggered by UV radiation. Bronzers: made from color additives approved by the FDA Extender:(sunless tanners or self-tanners) for cosmetic use, stain the skin for a short time when applied and can be washed off with soap and water. are applied to the skin as lotions or creams, where they interact with protein on the surface of the skin to produce color. Like a tan, the color tends to wear off after a few days. The only FDA-approved color additive for self tanner is dihydroxyacetone (DHA) 2.5% to 10%. DHA is predominantly formulated in oil-in-water emulsions, DHA will react with amino group supplied by keratin in the is the stratum corneum and pigment will be formed. These products will not protect from UV radiation.