Literary Terms
advertisement

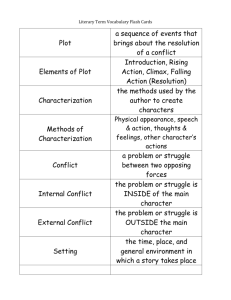
Name: ________________________________________ Date: _________ Literary Terms Personification- an idea, object, or animal is given human characteristics “The starts came out and they danced about and again.” Alliteration- the repeating of beginning consonant sounds “Over the cobbles he clattered and clashed in the dark yard.” Simile- a comparison of two things using "like" or "as" “Her eyes were gray like storm clouds.” Metaphor- a comparison of two related things “His legs were a well-oiled machine.” Flashback- a technique in which a writer interrupts a story to go back and explain an earlier event “When I was a little girl, my father had bought me what would become my favorite shirt.” Allusion- a reference to a well-known person, place, or event from history or literature “Hector rushed in like Superman and rescued the cat from the burning building.” Tone- the author’s attitude toward the subject matter Tone is conveyed through the author’s word choices. Words that can describe tone include doubtful, humorous, gleeful, serious, and questioning. Mood- the feeling the reader gets from a work of literature – atmosphere Authors create mood through word choice, imagery, dialogue, setting, and plot. Mood can be described as calm, creepy, romantic, sad, or tense. Imagery- language that portrays experiences of the five senses: sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch “The gushing brook stole its way down the lush green mountains, dotted with tiny flowers in a riot of colors and trees coming alive with chirping birds.” Hyperbole- extreme exaggeration used for emphasis or effect “I almost died of boredom.” point of view- the perspective from which a story is told first person – the narrator is a character in the story - “I” third person – the narrator is not one of the characters in the story conflict- a struggle between opposing forces - a conflict may be external or internal character vs. character character vs. nature character vs. society character vs. himself/herself dialogue- the words that characters speak aloud between and among each other The dialogue is meaningful and advances the plot. Plot- the series of related events that the author describes from the beginning of a story to the end Exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution setting- the environment in which a story takes place, including time period, the location, and the physical characteristics of the surroundings protagonist- the main or central character of a work of literature, usually involved in a conflict with the antagonist Examples: Percy, Annabeth, and Grover are protagonists in The Lightning Thief. Antagonist- the opponent or enemy of the main character Example: Luke is an antagonist in The Lightning Thief. Irony- a contrast between what is expected and what actually exists or happens situational irony dramatic irony verbal irony static character- a character who does not undergo a significant change over the course of a story Example: Timothy in The Cay Stanza- a grouping of two or more lines within a poem “Oranges” has two stanzas. dynamic character- a character who undergoes a significant internal change over the course of the story Example: Phillip in The Cay Characterization- the means an author reveals a character’s personality Examples: direct – the author or narrator is telling what the character is like, or indirect – the author shows what the character is like Genre- a type or category of writing autobiography, fantasy, poetry, science fiction, historical fiction, news article, etc. climax- the point in a play, novel, short story, or narrative poem at which the conflict reaches its greatest intensity rhyme scheme- the pattern of end rhyme in a poem I quarreled with my brother a I don’t know what about b One thing led to another a And somehow we fell out b figurative language- uses words in some way other than for their literal meanings to make a comparison, add emphasis, or say something in a fresh or creative way Examples: alliteration, hyperbole, idiom, imagery, metaphor, onomatopoeia, personification, and simile narrator or speaker- the teller of a story / the voice that talk to the reader in a poem In “Oranges,” the speaker is a twelve-year-old boy. In The Lightning Thief, the narrator is Percy Jackson. Idiom- an expression that cannot be understood from the meanings of its individual words Example: “It’s raining cats and dogs” means it’s raining really hard.