Chapter Fifteen

Chapter Fifteen
Longer Sectional Forms
Elements of Form
•We have learned that form is manipulated by--
• Repetition
• Contrast
• Variation
Variation
Let’s look closer at variation--
Variation combines repetition with contrast . The variation may be mostly contrast with two or more new melodies. Or, the variation may take the same theme and alter it either melodically, rhythmically, or harmonically.
Altering melodies is referred to as development .
Development is also the term used to refer to sections where variations take place. Development offers a true blend of repetition and contrast .
Types of Sections
• Introductory Sections
• Thematic Sections
• Connecting Sections
• Concluding Sections
Thematic and Introductory
Introduction--
The beginning section to prepare the listener for the thematic material. It may be a very short or an extended section
Thematic--
A section which presents the primary melodic materials (theme) of a composition.
A piece of music may have more than one theme. Thematic material is labeled with capital letters-- A B C
Connecting Sections
Connecting sections provide a sense of movement to or rest from the themes.
Transition
Connecting Section to prepare listener for the theme that follows often by building a sense of anticipation which is resolved by the theme
Interlude
Connecting Section occurring between thematic sections that uses contrasting material to provide rest from previous theme.
Concluding Sections
Coda
Concluding Section that brings a work to a close
Codetta
Internal concluding section that brings a section to a close
Sectional Forms
Binary Form Two-part (A-B)
Ternary Form Three-part (A-B-A)
Compound Binary + Ternary
Theme and Variation A – A’ – A’’ etc.
Rondo A-B-A-C-A (five-part)
A-B-A-C-A-B-A (seven-part)
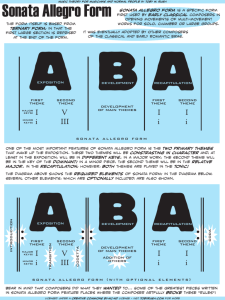
Sonata Form
Sonata form is the form for a single movement within a multi-movement work. It is a sectional work consisting of the exposition , development , and the recapitulation .
Exposition
The opening of a sonata form is the exposition . It presents the thematic material which will be used in the work. The number of themes can vary, but two contrasting themes (with a codetta) is common.
Development
After stating the themes in the exposition section, the piece moves into the section which varies the thematic content through melodic, rhythmic, harmonic or timbral variations.
Recapitulation
The recapitulation is the repetition of the exposition section (with certain modifications). The second theme which was originally stated in a different key from the first theme is now played in the first key.
The development and recap sections may be repeated .
Complete Classical Sonata
Multimovement work, typically 3 or 4 movements, some of which are sonata form. It was used in the late 18th century to the end of the 19th century for most multi-movement instrumental works.
Classical Sonata
Movement Tempo Typical Form(s)
•First Fast Sonata
•Second Slow Sonata
Theme and Var.
•Third (opt.) Mod/Fast Comp. Ternary
•Final Fast Sonata
T and V
Rondo
Performance Venues in Vienna
Chamber Music
Social Music
Parties and Celebrations
Larger Concerts
Gala Occasions
Charity Concerts
Subscription Series
Opera
Franz Joseph Haydn
[1732-1809]
First Viennese
School
Age of Aristocratic
Patronage
Prince(s) Esterházy