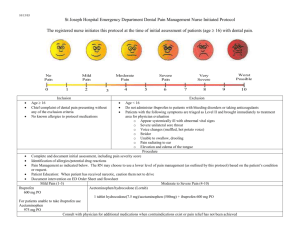
Luis Espinoza-Delgado, Ibuprofen Effect on Prokaryotic Gene
advertisement

Ibuprofen Effect on Prokaryotic Gene Expression Luis Espinoza-Delgado Central Catholic High School Grade 11 β-galactosidase Gene Expression • Cells in different parts of the same organism • • differ in both their structure and physiology, despite containing identical DNA. Cell development- the selective turning on and off of genes with various chemical messengers. Gene expression is used by all known life to generate macromolecules specific to the functions and needs of a given cell. o Products are often proteins. Gene Transcription Jacob-Monod model of prokaryotic gene induction ◦ Production of enzyme depends on the presence of an inducer (transcription factor). ◦ Structural genes specify the amino acid sequence of the enzyme. ◦ Regulator gene controls the transcription of the structural genes by synthesizing a repressor protein. Operon- DNA sequence of the promoter, operator, and immediate structural genes ◦ RNA polymerase- promoter ◦ Repressor protein- operator Lac Operon Lactose inactivates a repressor protein, allowing RNA polymerase to transcribe structural genes β-galactosidase ONPG- similar structure which is broken down into galactose and ortho-nitrophenol (yellow) No lactose present Repressor releases when lactose is present Escherichia coli Escherichia coli is a large and diverse group of gram (-) bacteria. It is found in the intestinal tract of most animals, including humans Most strains of E. coli are harmless, others cause sickness. Estimated to cause infection in more than 70,000 patients a year in the United States. Reported to cause both large outbreaks as well as isolated sporadic infections in small numbers of individuals. Serves as a common prokaryotic cell model. Ibuprofen NSAID used to treat arthritis, primary dysmenorrheal, and fever; also serves as an analgesic. Inhibits cyclooxygenase- produces prostaglandins that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. Non selective of the isoforms of cyclooxygenase it inhibits. ◦ Inhibition of COX-2 enzyme leads to the antiinflammatory properties ◦ COX-1 inhibition affects platelet aggregation and the gastrointestinal tract ◦ Side effects of this drug include: upset stomach, mild heartburn, diarrhea, constipation; bloating, gas; dizziness, headache, nervousness; chest pain, weakness of heart, slurred speech; rapid weight gain; nausea; fever; bruising, muscle weakness; and sensitivity to light. Pharmaceutical Research Citric Acid Generic Dye-Free Infant’s Ibuprofen Active ingredient: ibuprofen ◦ (recommended dosage: 2mL) Sucrose Purpose: Fever reducer/Pain reliever Reduces fever relieves minor aches and pains due to the common cold, flu, sore throat, headaches and toothaches. • Inactive ingredients: anhydrous citric acid, butyleparaben, flavor, glycerin, hypromellose, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, purified water, sodium benzoate, sorbitol solution, sucrose, and xanthan gum. Does ibuprofen affect microbial flora in humans? Purpose: To assess the effect(s) of ibuprofen on the gene expression of E. coli Null Hypothesis: Ibuprofen will not have a significant effect on the gene expression of E. coli. Alternative Hypothesis: Ibuprofen will have a significant effect on the gene expression of E. coli. Materials Escherichia coli Vortex Liquid ibuprofen (C13H18O2) 36 Conical tubes (15mL) 0.22 micron syringe filters + 10mL syringe 400mL lambda broth Sharpie 180 cell culture tubes Latex gloves 400mL Z buffer Incubator (37°C) 80mL ONPG (C12H15NO8) Ice bath 200mL Na2CO3 Sterile pipette tips 1mL lactose (C12H22O11) 15mL glucose (C6H12O6) Two water baths (37°C-concicals, 28°C-cell culture tubes) 9mL SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate NaC12H25SO4) 18mL Chloroform (CHCl3) Spectrophotometer 20 Procedure E. coli was grown overnight in sterile lambda media. A sample of the overnight culture was added to fresh media in a sterile sidearm flask. The culture was placed in a shaking water bath (37°C) until a density of 50 Klett spectrophotometer units was achieved. This represents a cell density of approximately 107 cells/mL. 50mL of lambda broth were extracted from a flask containing 400mL and replaced with 50mL of E. coli. The resulting mixture was swirled and allowed to sit for 5 minutes. The selected experimental variables were diluted with the lambda/ E. coli mixture. 10x x 0x Model/lambda 9mL 9.9mL 10mL Ibuprofen 1mL 0.1mL 0mL Total volume 10mL 10mL 10mL Procedure Fuel 10x (A) X (B) control (0) (-) carb 1 1 1 (+) lactose (15mins) induction 2 2 2 (+) lactose (15mins), 3 (+) glucose (30mins) repression 3 3 • Added 2.0mL ice-cold Z buffer to each culture tube. •Removed 200µL aliquots from all conical tubes. Placed aliquots into their designated time 0 culture tubes in the ice cold bath. •Placed conical tubes into 37°C water bath and removed every 5 minutes to invert 10 times. •After 15 minutes, added 100µL of lactose to conical tubes A2, B2,02,A3, B3, and 03. After an additional 15 minutes, added 1mL of glucose to conical tubes A3, B3, and 03. •Removed 200µL aliquots from conical tubes and added to the appropriate tubes at the indicated time. Returned culture tubes to water bath and inverted every 5 minutes. Repeated this step every 30 minutes until time 120. Procedure Added 50µL aliquots of SDS into each culture tube, followed by 100µL of chloroform. Tubes were mixed thoroughly with vortex. Placed test tube rack into top water bath (28°C). Allowed samples to sit for 5 minutes. Added 400µL aliquots of ONPG into each culture tube. Mixed tubes by hand and then returned to water bath. After 15 minutes, stopped enzyme reaction by adding 1.0mL of Na2CO3 to each culture tube. Took spectrophotometer reading to measure absorbance of each sample with the wavelength set to 420nm. Performed the appropriate statistical analyses to adequately assess the data. 0.2 0.1 0 0.4 0.3 [Ibuprofen] 10x (lactose) 10x (lactose+glucose) 10x (-carb) x (lactose +glucose) x (lactose) x (-carb) control (lactose+glucose) control (lactose) control (-carb) Absorbance (β-gal activity) Ibuprofen Effect on E. coli Gene Expression 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 Time 30 0.5 Time 60 Time 90 Time 120 Ibuprofen Effect on E.coli Gene Induction at Time 30 0.06 P-value= 0.2673580 Absorbance (β-gal activity) 0.05 P-value=0.2311264 P-value= 0.203958 0.04 0.03 (-carb) (lactose) (lactose+glucose) 0.02 0.01 0 control x [Ibuprofen] 10x Ibuprofen Effect on E.coli Gene Repression at Time 120 1 P-value= 4.19E-09 Absorbance (β-gal activity) 0.9 0.8 P-value=3.42E-06 P-value= 8.66E-05 0.7 0.6 0.5 (-carb) 0.4 (lactose) (lactose+glucose) 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 control x [Ibuprofen] 10x Conclusions The null hypothesis can be accepted for all time intervals. Ibuprofen did not significantly alter the ability of E. coli to turn its lac operon on and off. Different energy mechanisms clearly affected gene expression. Limitations Unable to identify ingredient involved in possible genetic disruption Presence of sucrose in liquid ibuprofen as inactive ingredient Extensions Vary pharmaceutical exposure times Explore different mechanisms for testing gene expression (e.g., x-gal) Test different models Use different pharmaceutical drugs and higher concentrations References http://www.americanheart.org http://bio.classes.ucsc.edu http://www.bio.cmu.edu/lacOperon http://www.britannica.com/genetic-expression http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/research http://www.medicinenet.com http://www.mun.ca/biochem http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov http://oregonstate.edu/regulation Freeman, Scott. Biological Science. San Fransicso, CA: Benjamin Cummings, 2011. “Turning Genes On and Off in Bacteria” Dr. Linda Roman Kauffman, Department of Biological Sciences at Carnegie Mellon University ANOVA • Abbreviation for analysis of variance • Statistical test to see variance between and within groups • If the F value is higher than the F crit, then there is significant variation in the data. • P value lower the alpha cutoff gives a high degree of confidence in this interpretation. • Such case warrants the use of Dunnett’s test. ANOVA Statistical Analysis Source of Variation Between Groups Within Groups Total SS df MS 11.98535 5 2.397069 9.8322 24 0.409675 21.81755 29 F P-value 5.851149 0.001137 F>Fcrit-null rejected F crit 2.620654





![Lac Operon AP Biology PhET Simulation[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006805976_1-a15f6d5ce2299a278136113aece5b534-300x300.png)