Chemical Reactions
advertisement

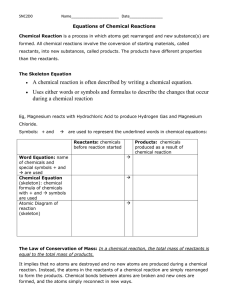
Formula Review • Ionic Formulas • • • • sodium oxide lithium phosphate ammonium sulfide aluminum chloride Formula Review • Covalent formulas • dinitrogen pentoxide • carbon monoxide • triphosphorous tetranitride Chemical Reactions • Examples of Chemical Reactions – Gas stove burner – Rust on a car • How would a chemist describe these reactions? Word Equations • Using the names of the substances, you write a sentence describing the reaction taking place • Reactants (starting substances) are listed first • An action word (reacts, etc) or arrow • Products (ending substances) are listed last Writing Word Equations • Gas stove burner • Iron rusting Chemical Equations • Def’n - representation of a chemical reaction – Reactants on left – Arrow – Products on right • Uses chemical symbols & formulas Chemical Symbols & Fomulas • Most elements are written as just symbols • Exceptions (Br, H, O, N, Cl, I, F) are always diatomic. – Br2, H2, O2, N2, Cl2, I2, F2 • Make sure to correctly write & balance charges on all ionic formulas!! (See flow chart!!) • NH3 = ammonia gas Other Symbols • • • • • • • + - separate reactants or products “yields” used for reversable reactions (s) - designates a solid (l) - designates a liquid (g) - designates a gas (aq) - designates an aqueous solution Symbols (Cont.) • Indicates heat is supplied to the reaction • Indicates a catalyst was used in the reaction – catalyst - speeds up the reaction, but is not involved in the reaction Writing Skeleton Equations • Ethane gas reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor • Solid iron reacts with the oxygen in air to produce solid iron (III) oxide Demo #1 • Dihydrogen dioxide decomposes to form water and oxygen gas Demo #2 • Sodium metal reacts with water to form dissolved sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas