Social Studies - WordPress.com
advertisement

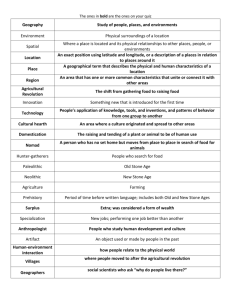
Social Studies Stone age/early civilizations Stone Age Technology • Extinction happens every day, what makes you think humans are any different? • Why was stone age technology so important? • What needs did most technology meet?? Stone Age Tools Hunting Tools Manufacturing Tools Grinding Tools Stone Age Tools • What was one of the hardest, yet one of the most important technologies of the Stone Age? Listen Link Uses Of Fire Summary The Stone Age • The period of time when people used simple stone tools is called the Old Stone Age or Paleolithic Era. • During the Old Stone Age, people also learned to make fire. Use of Fire Early man learned to use fire to adapt to his environment. It was probably discovered from friction, lightning, or accidental hitting two rocks together. Ice Ages Fire was very important during the ice ages. Without fire man would not have been able to survive. Cave Art Man has created art for a very long time. There is some argument as to what this art was for. Was it art as art, or art as a form of religion? “Neo” means new “Lithic” means stone Neolithic means new stone age. The Neolithic Agricultural Revolution was the change from the Paleolithic period to the Neolithic Period. The thing that allowed for this change was the discovery of agriculture. It is thought that women discovered agriculture. Systematic Agriculture was the consistent growing of crops on a continuing basis. Domestication of Animals: In addition to growing crops Neolithic man also tamed animals for hunting (dogs) and other animals for their food such as sheep, cows, etc. . . Developed Agriculture Domesticated Animals Used Advanced Stone Tools Developed Weaving (better clothing) Made Pottery (for food storage) Summary The New Stone Age • The period of time when people began to settle permanently in one location is called the Neolithic Era, or the New Stone Age. • In the Paleolithic age, men were hunters and gathers. In the Neolithic age, people became scavengers, herders, farmers, or producers. Summary The New Stone Age • People were able to live in larger groups. • They learned to domesticate plants and animals. • This meant they also learned which plants provided a higher yield and how to breed animals to better suit their needs. PURPOSE To learn what happened to humanity after the Ice Age To see how technology and urban areas developed Why is this important? How might I check to make sure you understand? 3 The Fertile Crescent The Fertile Crescent is the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The first civilization in the Fertile Crescent was discovered in Mesopotamia, which means land between the rivers The first Sumerian cities emerged in southern Mesopotamia around 3200 B.C. 3 Sumerian Civilization GOVERNMENT City-states with hereditary rulers. Ruler led army in war and enforced laws. Complex government with scribes to collect taxes and keep records. SOCIAL STRUCTURE Each state had distinct social hierarchy, or system of ranks. Most people were peasant farmers. Women had legal rights; some engaged in trade and owned property. RELIGION Worshiped many gods. Believed gods controlled every aspect of life. Saw afterlife as a grim place. Everybody would go into darkness and eat dust. To keep the gods happy, each city built a ziggurat, or pyramid temple. Artifacts of Ancient Mesopotamia Ziggurats The People of the Mesopotamia (start 52:24) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RpspR7Kd9A (end 1:03:26) 4 Invaders, Traders, and Empire Builders A series of strong rulers united the lands of the Fertile Crescent into well organized empires. Again and again, nomadic warriors invaded the rich cities of the Fertile Crescent. Some looted and burned the cities. Others stayed to rule them. 2300 B.C. –Sargon, the ruler of Akkad, conquered Sumer and built the first known empire. 1790 B.C.–Hammurabi, King of Babylon, united the Babylonian empire. Laws http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDALXORbt R4 (Watch from beginning, and stop at 1:56) 4 The Code of Hammurabi Hammurabi’s code was the first attempt by a ruler to codify, or arrange and set down in writing, all of the laws that would govern a state. One section codified criminal law, the branch of law that deals with offenses against others, such as robbery and murder. Another section codified civil law, the branch that deals with private rights and matters, such as business contracts, taxes, and property inheritance. 4 Warfare and the Spread of Ideas • Conquerors brought ideas and technologies to the conquered region. For example, when the Hittites conquered Mesopotamia, they brought the skill of ironworking to that region. • When the conquerors were in turn conquered, they moved elsewhere, spreading their ideas and technologies. For example, when the Hittite empire was itself conquered, Hittite ironworkers migrated to other regions and spread the secret of iron making across Asia, Africa, and Europe. 4 The Persian Empire Cyrus the Great and his successors conquered the largest empire yet seen, from Asia Minor to India. Emperor Darius unified the Persian empire. Drew up single code of laws for empire. Had hundreds of miles of roads built or repaired to aid communication and encourage unity. Introduced a uniform system of coinage and encouraged a money economy. Before it was a Barter economy-exchanging one set of goods or services for another. 4 The Phoenicians Occupied string of cities along the eastern Mediterranean coast. Made glass from sand and purple dye from a tiny sea snail. Called “carriers of civilization” because they spread Middle Eastern civilization around the Mediterranean. Most important contribution: Invented the alphabet. An alphabet contains letters that represent spoken sounds. Cuneiform