68.0 KB - K-10 Outline
advertisement

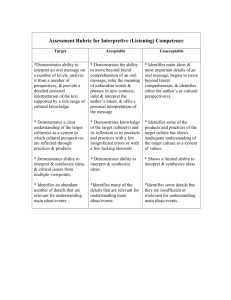
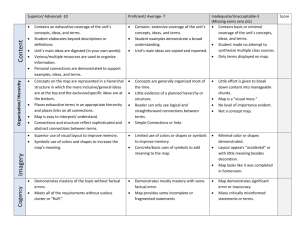
These assessment pointers are for judging standards of student performance in Year 2 Mathematics. They are examples of what students may demonstrate rather than being a checklist of everything they should do. For reporting, they are used to make on-balance judgements about achievement, based on what has been taught and assessed during the reporting period. They can also be used to guide the pitch of assessment tasks, develop marking keys and inform assessment feedback. JUDGING STANDARDS IN YEAR 2 MATHEMATICS Reporting against the Achievement Standard YEAR 2 MATHEMATICS ACHIEVEMENT STANDARD By the end of Year 2, students recognise increasing and decreasing number sequences involving 2s, 3s and 5s. They represent multiplication and division by grouping into sets. They associate collections of Australian coins with their value. Students identify the missing element in a number sequence. Students recognise the features of three-dimensional objects. They interpret simple maps of familiar locations. They explain the effects of one-step transformations. Students make sense of collected information. Students count to and from 1000. They perform simple addition and subtraction calculations using a range of strategies. They divide collections and shapes into halves, quarters and eighths. Students order shapes and objects using informal units. They tell time to the quarter hour and use a calendar to identify the date and the months included in seasons. They draw two-dimensional shapes. They describe outcomes for everyday events. Students collect data from relevant questions to create lists, tables and picture graphs. YEAR 2 MATHEMATICS ASSESSMENT POINTERS A Number and Algebra B C D E The student demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level. Counts, orders and represents numbers to and from 1000, using partitioning and rearranging. Creates, represents and describes a variety of number sequences involving 2s, 3s, 5s and 10s. Creates a rule for number sequences involving 2s, 3s, 5s and 10s. Counts and represents numbers to and from 1000. Identifies increasing and decreasing number sequences involving 2s, 3s, 5s and 10s. Identifies the rule and completes a number sequence involving 2s, 3s, 5s and 10s. Counts to and from 1000. Identifies increasing and decreasing number sequences involving 2s, 3s and 5s. Identifies the missing element in a number sequence. Counts to 1000. Identifies increasing number sequences involving 2s and 5s. Completes number sequences up to 1000. Counts to 100. Identifies a number sequence involving 2s. Completes number sequences up to 100. 2013/37221v7 [PDF: 2013/37666] Published: 20 July, 2015 A Number and Algebra Measurement and Geometry B C D E The student demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level. Applies suitable strategies to solve multi-step problems involving addition and subtraction. Uses repeated addition to solve simple multiplication problems and sorts collections into equal-sized groups to solve simple division problems. Identifies addition and/or subtraction as the operation required to solve a problem. Solves simple multiplication and division problems by sorting collections into equal-sized groups. Solves simple addition and subtraction problems using a range of strategies, e.g. partitioning, arrays, ten-frames and number lines. Arranges collections into equal-sized groups to represent multiplication and division. Solves simple addition and subtraction problems using the ‘+’ or ‘–’ symbols, e.g. ‘7 balls in a box, take out 5, how many are left?’ is the same as 7 – 5 = ? Represents simple addition and subtraction number stories using materials or drawings, e.g. modelling with counters. Converts between fractional values of halves, quarters and eighths, e.g. calculates the number of eighths from given quarters. Partitions collections and shapes in a variety of ways to divide them into halves, quarters and eighths. Divides collections and shapes into halves, quarters and eighths. Identifies half of a small collection and half of a shape. Identifies half of a shape. Counts Australian notes and coins to make up a specific value, e.g. to pay for shopping items. Orders Australian notes and coins according to their value. Identifies different combinations of notes and coins with the same value. Counts and orders small collections of Australian coins according to their value. Identifies the denominations of Australian coins. Identifies the denomination of some Australian coins. Selects an appropriate uniform informal unit to compare shapes and objects for length, area, volume, capacity and mass. Orders different objects by mass from lightest to heaviest. Explains the outcome if the informal units are not uniform, e.g. hands come in different sizes. Orders shapes and objects by their length, area, volume and capacity, and compares mass on balance scales using uniform informal units. Determines whether the mass of one object is greater, less or about the same as that of another. Orders shapes and objects by their length, area, volume and capacity using uniform informal units such as pop sticks, paper clips, hands and blocks. Uses direct comparison to order shapes and objects by length. Uses direct comparison to order two objects by length, e.g. the pencil is longer than the pen. A Measurement and Geometry B C D E The student demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level. Accurately positions hands on an analogue clock face to show passing of time, e.g. identifies the hour hand also moves as the minute hand moves. Reads a clock face to the quarter-hour and predicts an event, e.g. that recess is in 15 minutes. Interprets calendars and applies knowledge of months to identify the dates before and after a given month. Compares analogue and digital times to the quarter-hour. Names and orders the months and seasons. Uses a calendar to identify dates of events. Tells the time to the quarter-hour. Uses a calendar to identify the date and the months included in seasons. Tells the time to the half-hour. Names the months and seasons. Tells the time to the hour on an analogue clock. Matches seasons to pictures. Draws and describes two-dimensional shapes, identifying key features of squares, rectangles, kites, rhombuses and circles. Compares three-dimensional objects based on their geometric features. Draws two-dimensional shapes and identifies the two-dimensional shapes in three-dimensional objects. Identifies three-dimensional objects in two-dimensional representations, e.g. drawings where lines or shading indicates depth. Draws two-dimensional shapes and identifies features of threedimensional objects. Identifies two-dimensional shapes in the environment, e.g. doorframes as rectangular. Names some common three-dimensional objects. Matches two-dimensional shapes to their names. Interprets simple maps and uses directional terms to follow or to give directions to a specific location, e.g. describes the route from the car park to the library. Interprets simple maps of familiar locations to describe the relative position of key features, e.g. identifies the oval is closer to the car park than the library. Interprets simple maps of familiar locations, e.g. locates a specific classroom on the map of the school. Finds major features on simple maps of familiar locations, e.g. identifies the school buildings, oval and car park on a map of the school. Finds a location within a familiar context, e.g. the teacher’s desk on a map of the classroom. Predicts and reproduces a pattern of one-step transformations on a shape. Identifies half and quarter turns of shapes. Visualises one-step transformations of flips, slides and turns, to predict and illustrate an outcome. Explains the effects of one-step transformations of shapes, e.g. flips and slides. Follows directions to flip or slide regular shapes. Arranges shapes to match a picture. A Statistics and Probability B C D E The student demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level. The student demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level. Describes the outcomes for everyday events and practical activities that involve chance and explains why these are likely, unlikely, certain or impossible. Describes the outcomes for everyday events and practical activities that involve chance as being likely, unlikely, certain or impossible, e.g. rolling a nine on a normal six-sided dice is impossible. Describes the outcomes for everyday events as being likely, unlikely, certain or impossible, e.g. the kettle has boiled so the water is likely to be hot; it is certain to be dark at midnight. Classifies the outcomes for everyday events as will happen, might happen or won’t happen. Distinguishes between the chance that something will happen or won’t happen. Generates questions based on one categorical variable and collects data efficiently. Creates, interprets and comments on the usefulness of data displays. Identifies relevant questions to collect data efficiently. Creates and interprets data displays that reflect collected data. Collects data from relevant questions to create simple data displays such as lists, tables and pictographs. Makes sense of collected information, e.g. identifies that more people liked apples than bananas. Collects and records data on prepared simple data displays. Answers simple questions about the display, e.g. identifies that three people liked apples. Records given data on prepared simple data displays.