Chapter_3.251174740
advertisement

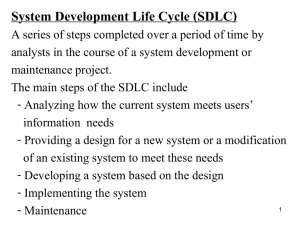
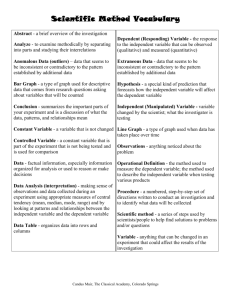
System PlanningPreliminary investigation Information System Strategic Planning Is a set of long term goals that describe the information architecture and major IS initiatives needed to achieve the goals of the org Must be aligned with overall org’s strategic plan Must efficiently allocate resources among competing systems so the projects can be completed on time , within budget and with required functionality Should identify specific areas to be given priority because of resource constraints. Priorities must be set to ensure maximum return is obtained for funds invested in dveloping IS Information System Operational Plan Is a set of projects that will be executed by the IS dept and the functional areas managers in support of the IS strategic planning Is responsible for identifying hardware component and configuration that allow software o operate Typical IS operational plan contains: Mission and objectives of IS function Summary of info needs of the functional areas and org as a whole Constraints of the IS function in terms of technological and personnel limitation Long term plan indicating summary of the system needed by the company to reach org goals Short term listing the current IS projects and a detailed plan of projects to be developed or continued during current year System Request Is a written request from mgt or end users which triggers the start of the SDLC Includes 5 considerations: Project Sponsor Business needs Functionality Expected value Special issues Project sponsor Is the person who usually initiates the proposed system project having an interest in seeing that the new system succeeds Could be the person who work throughout SDLC to ensure project in right direction Business needs Describes why the IS should be developed explaining to the information steering committee why org should fund the project concerned Functionality of the system Describes what the proposed IS will do. Eg. What features and capabilities the IS will need to have Expected values System request will include expected value to be gained from the proposed system Specify rough estimations of tangible and intangible benefits Special issues Include determining the system constraints that must be met for the proposed systems project to be viable Proposed systems project needs to be completed within specific deadline and budget Information System Steering Committee Developing IS must get support from top mgt A good approach is to have IS steering committee that represents top mgt and all functional areas within org Responsible for overall planning and control of system development Existing IS should be reviewed on a regular basis to assess it adequacy The committee may receive request to investigate such as error in payroll , request to design new inventory system etc They will need to review these system requests and determine which one should be considered for further study Other than evaluates system request, they also provide guidance throughout the SDLC Preliminary Investigation The first step in SDLC is to do survey or preliminary investigation of existing system It is important t understand existing system before proposing for changes or modifications It is important to establish relationship with the users because the success of a system depends on users acceptance In order for a system to serves the needs of the org, the development team must: Find out and analyze causes of business problems rather than just deal with symptom Ensure that needs of all affected by new system are considered Consider how the new system will integrate with other system in the org Nature of problem In preliminary stage, the nature of problem must be determined Sometimes what appears to be a problem only a symptom. The problem should be treated and not the symptom Scope Establishing scope is important because problems tends to expand if no firm boundaries are established It is necessary to stay within budget and schedule If scope is too broad , the project will never finished. If the scope is too narrow, user needs may not be met The scope will define: Part of system to be changed Part that is outside its control Restriction on the project if any Resources to be made available Resource limitations Goal Must be developed within practical bounds of the org One way to ensure this is to break down project goal into more detailed sub- goal that consider org constraints These sub- goals will be used in later phases to guide detailed analysis and design Another guideline for goal definition is the identification of deficiencies in the existing system The project goal is to remove such deficiencies The project goal , scope and constraints are also known as term of reference Organization Chart A good starting point to find out who is who and who is doing what Help to determine appropriate individuals to interview during preliminary investigation Should verify that the chart is updated and accurate Obtaining Information When investigating IS, we should gather info. Through some means. Eg.interview Note that preliminary investigation is not designed to learn everything in detail Prepare a Preliminary Investigation Report After conducting preliminary investigation, the findings must be reported to the Information System Committee or top mgt Preliminary investigation is a brief phase and should result in some recommendations suggesting: Drop the matter Fix the problem immediately (if it is simple ) Authorize to go on the next phase for a closer look Typical preliminary investigation report should include: What is found concerning the operation of the system in question The problems that present or appear to present in the system Recommendations for future action