Cnidaria
advertisement

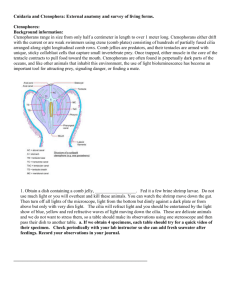
Cnidaria By: Michael Dang Annie Ma David Shia http://scrapetv.com/News/News%20Pages/usa/images-3/Nomura-jellyfish-3.jpg Phylum Phylum: Cnidaria Families: • Hydrozoa- polyp and medusa stages in reproductive cycle (Ex: corals) • Scyphozoa- reduced polyp stage (Ex: jellies) • Cubozoa- box shaped polyps (Ex: box jellies) • Anthozoa- no medusa stage (Ex: corals) Sample Animals • • • • • • • Jellyfish Corals Hydras Box Jellyfish Anemone Sea Wasp Sea Pens • http://www.biology4kids.com/misc/photos/cnidaria1.jpg Body Cavity • Single Body Cavity diploblastic (two membranes: ectoderm/endoderm) used for digestion and respiration • They contain one cavity that operates as both their mouth and anus • Polyp- mouth cavity is on top • Medusa- mouth cavity is on bottom Body Symmetry • Radial Symmetry http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/labs/radial.jpg Nervous System • Cnidaria lack a brain and a central nervous system, but they do have a net of neurons • Ocelli: organs that sense direction of light • Statocysts: means of regulating tilt and acceleration in cnidaria Circulatory System • None Digestive System • All are carnivorous • Absorb nutrients by filtering water • Tentacles put the prey into the mouth where digestive enzymes are used to break prey down into organic substances Excretory System • Present • Anus/ mouth • Diffusion Locomotion/ Musculature • Has muscle, but really weak in most Cnidaria. Strong enough to direct movement in a current • Jet Propulsion: water is squeezed and then released from the cavity using coronal muscles • Some sea anemone can creep along Skeletal Type • Cnidaria bodies are composed of the jelly-like substance called mesoglea • Most can form a hydrostatic skeleton, in which the cavity fills with water, expanding the body of the cnidaria • Coral have exoskeletons composed primarily of calcium http://biology.unm.edu/ccouncil/Biology_203/Images/SimpleAnimals/cnidariaDiagram.jpeg Sensory Structures/ Features • Simple sensory structures • Responds to touch through cnidocytes, stinging cells located on the tentacles • Nematocytes, the stinging capsule of a cnidocyte, releases a poisonous thread when triggered by a chemical or touch http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/16cm05/16labman05/lb5pg2_files/cnidocyte.gif Reproduction • Sexual and asexual reproduction • Cnidaria usually have 2 main forms in their life cycle: the polypoid stage is diploid, and the mature polyp is usually found in colonies. Medusae are produced asexually through budding, which reproduce sexually to form polyps. http://www.palaeos.com/Invertebrates/Cnidaria/Images/obelia_cycle.gif Gas Exchange • Cnidarians lack the organs for gas exchange, so they just let the gas from the water diffuse through their bodies Other • The amount of poison from a sea wasp, a cubozoan, is powerful enough to kill 60 people! • Coral is really a colony of really small polyps! • Many species of jellyfish are bioluminescent! QUIZ TIME 1. What are the two forms of a Cnidaria’s life cycle? a. Polyp and Cnidocyte b. Medusae and Polyp c. Polyp and Hydrozoa d. Cubozoa and Medusae e. None of the above Answer • Medusae and Polyps • Medusae= tentacles facing down. Motile. • Polyp= tentacles facing up. Stationary. QUIZ TIME 2. What mechanism do Medusae use to move through the water? a. Current b. Jet Propulsion c. Latching on to other animals d. A and B are both correct e. All of the above Answer • Current and Jet Propulsion • Medusae have relatively weak muscles, so they must use the current to help them move • Jet Propulsion= uptake and release of water to create the thrust force to make them move forward. QUIZ TIME 3. What is the Mesoglea? a. The excretory waste of the Cnidaria b. The nervous system of the Cnidaria c. The name of the colonies that the polyps form d. The tentacles of the jellyfish e. The substance that the Medusae’s body is composed of Answer • The substance that the Medusae’s body is composed of QUIZ TIME 4. What systems are absent in Cnidaria? a. Skeletal and Nervous b. Excretory and Digestive c. Nervous and Circulatory d. Circulatory and Digestive e. Musculature and Reproductive Answer • Nervous and Circulatory • Cnidaria have no brains, thus no nervous system, but do have a simple sensory network throughout the body. • They do not need a circulatory system and regulate substances through diffusion.