2. Carbohydrates
advertisement
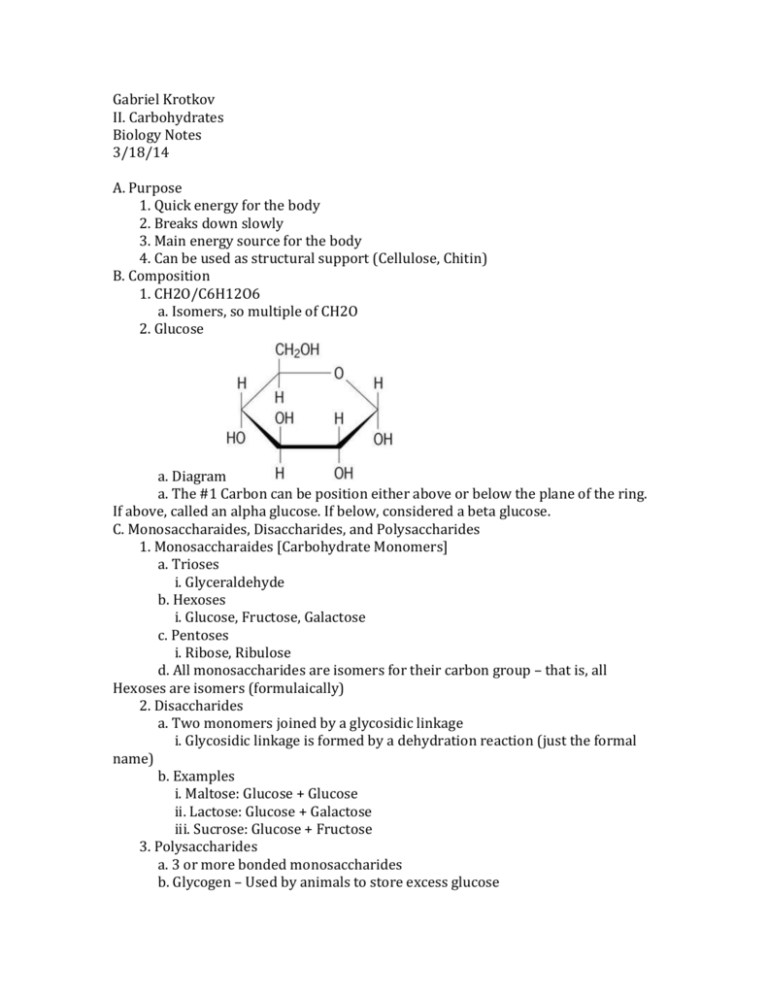
Gabriel Krotkov II. Carbohydrates Biology Notes 3/18/14 A. Purpose 1. Quick energy for the body 2. Breaks down slowly 3. Main energy source for the body 4. Can be used as structural support (Cellulose, Chitin) B. Composition 1. CH2O/C6H12O6 a. Isomers, so multiple of CH2O 2. Glucose a. Diagram a. The #1 Carbon can be position either above or below the plane of the ring. If above, called an alpha glucose. If below, considered a beta glucose. C. Monosaccharaides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides 1. Monosaccharaides [Carbohydrate Monomers] a. Trioses i. Glyceraldehyde b. Hexoses i. Glucose, Fructose, Galactose c. Pentoses i. Ribose, Ribulose d. All monosaccharides are isomers for their carbon group – that is, all Hexoses are isomers (formulaically) 2. Disaccharides a. Two monomers joined by a glycosidic linkage i. Glycosidic linkage is formed by a dehydration reaction (just the formal name) b. Examples i. Maltose: Glucose + Glucose ii. Lactose: Glucose + Galactose iii. Sucrose: Glucose + Fructose 3. Polysaccharides a. 3 or more bonded monosaccharides b. Glycogen – Used by animals to store excess glucose i. Glucose only polysaccharide ii. 1-4 linkage c. Starch – Used by plants to store excess glucose i. Glucose only polysaccharide ii. Alpha glucoses only d. Chitin - Structured materials for invertebrates/cell walls of fungi i. Glucose + NC2OH4 e. Cellulose – Cell walls of plants, indigestible i. All composite glucoses are beta glucoses, meaning that the hydroxyls can hydrogen bond w/hydroxyls in other glucoses – strengthening the polymer. ii. Glucose only polysaccharide D. Carbon Skeleton Classification of Monosaccharides 1. Aldose vs. Ketose a. The location of the carbonyl group in the structure of the sugar determines whether it is an aldose or a ketose b. If the carbonyl is at the end of the carbon skeleton, then it is an aldose. In Ketoses, the carbonyl group in inside the carbon skeleton (attached to a nonterminal carbon) c. Examples i. Glucose is an Aldose, Fructose a Ketose 2. # Carbons a. 6 Carbons like Glucose, Fructose, are called hexoses b. Trioses (3 carbons), pentoses (5 carbons) also common.