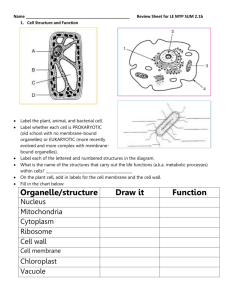
Action Potential

The Action Potential
Objective: To understand how neurones conduct impulses from one part of the body to another.
What is this part of the nervous system called?
What is this part of the nervous system called?
Neurones
(A Motor Neurone)
They have three distinct parts:
• (1) Cell body,
• (2) Dendrites, and
• (3) the Axon
The type of neuron that stimulates muscle tissue is called a motor neuron.
Dendrites receive impulses and conduct them toward the cell body.
Types of Neurons
Relay Neurone
Based on: Mader, S., Inquiry Into Life, McGraw-Hill
• Sensory neurons - carry impulses to the relay of the brain
• Relay neurons - interpret impulses
• Motor neurons - carry impulses to the muscles
Resting Potential
In a resting neuron (one that is not conducting an impulse), there is a difference in electrical charges on the outside and inside of the plasma membrane.
The outside has a positive charge and the inside has a negative charge.
Establishing A Gradient
The sodium-potassium pump creates a concentration and electrical gradient for Na + and
K + .
K + tend to diffuse (‘leak’) out of the cell and Na + tends to diffuse in. BUT, the membrane is much more permeable to K + , so K + diffuses out along its concentration gradient much more slowly. http:// www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/ion_pump/ionpump.html
RESULTS IN:
a net positive charge outside & a net negative charge inside. Such a membrane is considered POLARISED
Nerve Impulse
• Stimulation of neuron, opens channels so that sodium (Na + ) goes in, depolarizing the membrane
• The adjacent section of membrane allows
Na+ to go in, depolarizing it
• This wave of depolarization continues at a rapid rate down the neuron, resulting in a nerve impulse traveling to the brain in milliseconds
+ + + + + + + +
- - - - - - - - - -
Neuron
Nerve Impulse
Polarized membrane of resting neuron
+ + + + + + + +
- - - - - - - - - -
Neuron
Sodium (Na) moves inside to depolarize
0 0 0 0
+ + + + +
- - - - - -
Neuron
Nerve impulse
Nerve impulse is a wave of depolarization moving down neuron http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbg5E9GCNVE
Action Potential
When the cell membranes are stimulated, there is a change in the permeability of the membrane to sodium ions (Na + ).
The membrane becomes more permeable to Na + and K + , therefore sodium ions diffuse into the cell down a concentration gradient. The entry of Na + disturbs the resting potential and causes the inside of the cell to become more positive relative to the outside.
DEPOLARISATION
In order for the neuron to generate an action potential the membrane potential must reach the threshold of excitation.
As the outside of the cell has become more positive than the inside of the cell, the membrane is now
DEPOLARISED.
When enough sodium ions enter the cell to depolarise the membrane to a critical level
(threshold level) an action potential arises which generates an impulse.
Speed of Nerve Impulses
Impulses travel very rapidly along neurones.
• The presence of a myelin sheath greatly increases the velocity at which impulses are conducted along the axon of a neuron.
• Between the sheaths are the Nodes of Ranvier, where sodium channels are concentrated. Action potentials jump from one to the next.
This is called
SALTATORY CONDUCTION
Speed of Nerve Impulses
• Action potentials go faster along axons with bigger diameters, because there’s less electrical resistance.
• They go faster as temperature increases, up to around 40 o C . After that, the proteins begin to denature.
All-or-None Principle
Throughout depolarisation, the Na+ continues to rush inside until the action potential reaches its peak and the sodium gates close.
If the depolarisation is not great enough to reach
threshold, then an action potential and hence an impulse are not produced.
This is called the All-or-None Principle.
A threshold stimulus must be applied to get an action potential.
Refractory Period
Straight after an action potential has been generated, the membrane enters a refractory period when it can’t be stimulated, because sodium channels are recovering and can’t be opened.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x4PPZCLnVkA