Soviet Union
advertisement

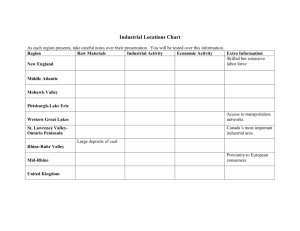
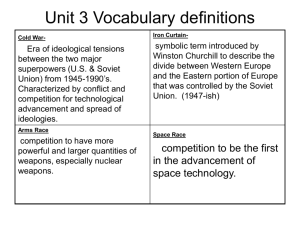
Impact of WWII SS6H7b. Explain the impact of WWII in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers. E.Q. • How did WWII impact the world in terms of the Holocaust, the origins of the Cold War, and the rise of Superpowers? Holocaust Key Facts • Holocaust: systematic killing of 6 million Jews • Key person: Adolph Hitler • Time period: WWII • Genocide: planned killing of a race of people • How: – – – – 1. identified Jews with yellow star 2. took away rights/freedoms 3. gathered/imprisoned Jews in ghettos 4. shipped Jews to concentration camps http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/media_fi.php?ModuleId=10005143&MediaId=183 Concentration Camps Left • Old, weak, young • Sent to “showers” • Gassed to death • cremated • • • • • • Right Workers Sent to showers Heads shaved Given prison clothes Tattooed with number Worked to death Not Just Jews Killed • • • • Political prisoners Mentally ill Disabled Gypsies, Poles, and others Helene Gotthold, a Jehovah's Witness, was beheaded for her religious beliefs on December 8, 1944, in Berlin. She is pictured with her children. Germany, June 25, 1936. After • Survivors – no homes left • United Nations divided Palestine into Arab and Jewish “states” (countries) • Israel became a Jewish nation - 1948 http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/media_fi.php?ModuleId=10005129&M ediaId=177 Page169 CRCT Test Prep #435. What is genocide? The planned killing of a race of people #436. Who created the country of Israel? United Nations #437. Who was spared in the Holocaust? None of the above #438. What actions did the United Nations take as a result of the Holocaust? Created a Jewish state and made genocide a crime Cold War Key Facts • When: end of WWII – 1945 • What: period of distrust and misunderstanding • Who: between Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) & U.S.A. (and former allies) • Why: Soviet Union was communist/command (strong central government controls businesses). U.S.A. believed businesses should be privately owned. Eastern Bloc vs. Western Bloc Eastern (red) • Soviet Union • Most eastern European countries Western (blue) • U.S.A. • Most western European countries Germany • Divided after WWII into 4 parts • 1948: divided into West Germany (free) and East Germany (Soviet controlled) • Capital – Berlin – divided into East Berlin and West Berlin • 1961: Berlin Wall built to separate city Fears • Each side believed the other wanted to rule the world. • People feared a nuclear war would happen. • Countries formed alliances for protection. • 1949 – Western Bloc plus Canada formed North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Eastern Bloc formed Warsaw Pact CRCT Test Prep page 170 439. Which country was the leader of the Eastern Bloc? Soviet Union 440. What 2 terms describe the dividing line between eastern & western, communist & noncommunist areas? Berlin Wall & Iron Curtain 441. Which was 1 of the areas of disagreement between the U.S.S.R. & the U.S. during the Cold War? Best type of economic system 442. When was the Cold War? After WWII 443. The Warsaw Pact was to the U.S.S.R. as NATO was to the U.S. Rise of the Superpowers • • • • • • • • • U.S.A. Constitutional Republic, Free market Permanent seat on U.N. Security Council 4th most populated country in world Powerful military support from NATO Largest navy in world Military bases all over world CIA (spies) Large reserve of nukes Influenced world events Soviet Union • Communist, Command • Permanent seat on U.N. Security Council • Largest country in the world • Military and space technology • World-wide spy network (KGB) • One of largest stockpiles of nukes in world • Influenced world events CRCT Test Prep page 171 444. As a world superpower, the U.S.S.R. had A seat on the UN Security Council 445. As a world superpower, the U.S. had Military bases all over the world 446. Which condition is required to be a world superpower? Influence over world events Collapse of the Soviet Union • Problem: Soviet Union spent $$$$$$$ – Putting down revolts in its countries – protecting its borders – keeping up with the arms race against the U.S.A Collapse of the Soviet Union 1985 • leader Mikhail Gorbachev – reduced government control of business – increased freedom for citizens Result – improved relations with U.S.A. – inspired other Eastern Bloc countries to demand freedom German Reunification • Nov 1989: Berlin Wall torn down • Germany began to reunify • Germany was 1 country again in 1990 • Cold War was over • Soviet republics gained freedom from Soviet Union. • Many new countries were made. Russia is the largest. CRCT Test Prep pages 172 447. Why did Gorbachev reduce government control of the economy? An unstable economy due to increased military spending 448. What marked the end of the Cold War? Destruction of the Berlin Wall 449. What was the largest country created from the former Soviet Union? Russia