project organisation and management
advertisement

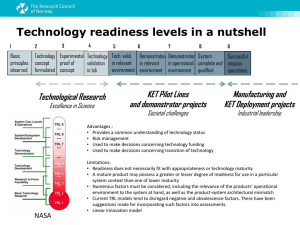
Instructions for completing this form (Delete all instructions in red before submission): The project description should be maximum six pages (Garamond 12pt for all free text and Garamond 10pt for all information in tables) in either Swedish or English. For Mac-users: To check tick-boxes in the table below, please highlight the box and then press spacebar/space key. ELIGIBILITY AND CLASSIFICATION Project partners: Name all project partners. Minimum 2 different sectors required. ☐ Academia Name: ☐ Industry Name: ☐ Healthcare Name: Technical Readiness Level (TRL) at project start TRL definitions available in Appendix 1. A minimum TRL level of 2 is required to be eligible for this application. Marketing activities will not be supported. Technical Readiness Level (TRL) expected at end of project Requested funding from SWElife/VINNOVA (SEK) Co-financing level (SEK and %) Minimum 50% required. Focus Area Please indicate what area is most representative for the project. 1☐ 2☐ 3☐ 4☐ 5☐ 6☐ 7☐ 8☐ 9☐ 1☐ 2☐ 3☐ 4☐ 5☐ 6☐ 7☐ 8☐ 9☐ SEK SEK resulting in a co-financing of % ☐ Imaging method ☐ Early diagnosis ☐ Prognosis ☐ Prediction ☐ Other…………………………………… PROJECT INFORMATION Project title: Coordinator (organisation): Project leader (person): Specify date for project start (151201 - 160301): Specify date for project end (maximum 2 years): Maximum 100 characters (including spaces) (YYYY-MM-DD) (YYYY-MM-DD) 1 PURPOSE AND RESULTS Please specify: Describe the purpose of the project including the impact for the patient and what challenge or difficulty the final innovative solution will overcome Describe the current status of your project proposal including the science behind the project idea, motivate actions/results performed to reach the actual Technical Readiness Level (TRL) and other relevant information. See attachment 1 for definitions of TRL levels. Present expected deliverables at the end of the project CUSTOMER NEED AND BENEFITS The long-term goal is to make a solution available that benefits the patient, healthcare or society in general. The project will thus be evaluated on its potential to become a real-world application i.e. to determine feasibility. Hence please provide information on the following: Who will use the solution and how will it benefit each individual? (Think about patients, healthcare professionals and careers – explain the benefit for each relevant individual.) What would be the benefits of your solution in general healthcare terms? (Think about cost efficiency, reduced time in hospital, more effective treatment etc.) How will this solution be implemented for the benefit of the patient? COMMERCIAL POTENTIAL Who might be interested in taking your verified idea through to the market and why would they be prepared to invest money and time? (Think about private healthcare providers, industrial suppliers, investors etc. and how they might benefit.) To the best of your knowledge, define the size of your first target market for the final solution. (Think about who would use or purchase the product or service and where it would be used.) Describe potential competitors. Describe your Intellectual Property (IP) strategy for your potential solution. (Do you have patents? Have you applied for patents? If not, what is your strategy? Are there patents from others that hinder you? Do you need licenses from others for your final product?) NEXT STEPS AFTER PROJECT COMPLETION After completion of the project, what do you see as the next step in the process (e.g. start a company, license out the technology, sell the idea to someone else, continue product development with a partner or continue in research)? What are the potential sources of new funding, what partners may need to be involved, what would be the roles of current partners in the next step, etc. PROJECT ORGANISATION AND MANAGEMENT Give a brief description of the project leader including earlier experiences and competence relevant to succeed in coordinating the project. Describe how the project partners will add strength to the project Give a brief description of the project team organisation (steering committee? internal and external communication, project meetings, etc.) Describe the working relationship and any previous collaboration between partners. 2 Please indicate if there are any competences or skills needed that would strengthen the project and if you have any plans to include these during the project. Please also present whether any of the partner(s) may contribute to the commercialisation of the concept, and if so, how they will contribute. PROJECT PARTNERS Describe the different partners in the project. Briefly describe each party’s competence and role in the project in the table below. If needed please add more lines. Project partner (organisation) Competence of project partner (for more details, refer to CV) Role in the project PROJECT PLAN The project should define at least three work packages (WPs). For each WP please specify the project activities, deliverables, the scope of the activities and decision point for the project leader to decide how to proceed with the project as well as the contribution from each partner. The deliverables will be the basis for evaluation and should reflect the progress of the project as a whole. Several activities may be run in parallel. One WP must address business development (for example business strategies, bench-marking analysis, reimbursement etc.). If needed you may add more WPs Work package (Title) WP1 Ex Business development WP2 Time (start and end) Detailed description Activities: Ex. 1) Regulatory requirements – Find out the demands for CE marketing for product 2) Market analysis – verify the market including competitors Deliverables (quantifiable where possible): Ex. 1) Report classification and relevant guidelines 2) Report of market analysis Decision point (STOP/GO): Ex. Window in market verified for potential product. Participating partners and their respective contribution: Ex. 1) Partner A via their regulatory experts 2) Consultant – responsible for contact project leader Activities including and the scope of the activity: Ex. 3 Ex. Technical verification of diagnostic product 1) Measure human samples on first prototype of product – confirm research data on a larger number of samples 2) Documentation - write instructions for use of product – to be tested by other technical personnel Deliverable (quantifiable where possible): Ex. 1) 80 % of the samples shall be positive for the diagnostic biomarker 2) A final instruction for handling the product to be used by several technical personnel with same results Decision point (STOP/GO): Ex. Target % of positive samples reached. Participating partners and their respective contribution: Ex. 1) Partner A 2) Partner B Activities including the scope of the activity: WP3 Deliverable (quantifiable where possible): Decision point (STOP/GO): Participating partners and their respective contribution: WP4 Activities including the scope of the activity Deliverable (quantifiable where possible): Decision point (STOP/GO): Participating partners and their respective contribution: WP5 Activities including the scope of the activity: Deliverable (quantifiable where possible): Decision point (STOP/GO): Participating partners and their respective contribution: RISK ANALYSIS Describe the major risks in the project. Please consider the following areas Business/market (market need cannot be verified, new competitive landscape, customer limitations, etc.) Technical (research not mature, uniqueness cannot be verified, etc.) 4 Legal/Regulatory (IPR, dependencies, need for standardisation, etc.) Project execution (lack of necessary competences, need for further financial investments, etc.) Likelihood and Consequence will be ranked on a scale 1-5 (1=none, 2= small, 3=intermediate, 4= high, 5=very high) Risk Likelihood Consequence Action to manage/mitigate risk BUDGET The budget is divided into two steps Step 1. Use the table below and specify the costs of each work package. Step 2. On VINNOVA’S portal, fill in, for each project part: the costs per year and how much that will be cofinanced. Include also the project partners that do not apply for money from VINNOVA: The value of the cofinancing will be in SEK but may well be in-kind resources in practice. BUDGET FOR EACH WORK PACKAGE Cost (SEK) Salary Equipment, land, buildings IPR, cost for consultant etc. Other direct costs incl. travel costs Indirect cost, incl. overhead Sum (SEK) Cost (SEK) Total sum (SEK) WP1 WP2 WP3 WP4 WP5 If relevant If relevant Salary Estimated hours (in total) Equipment Material Other IPR Consultant Other Services Travel costs Other direct costs Indirect cost, incl. overhead 5 Appendix 1. Please use the following definitions to indicate TRL level reached during the project. Please delete this table before submission. Technological Readiness Level (TRL) Definitions TRL General description of TRL Basic principles and research data observed and reported Pharmaceuticals Med Tech including diagnostics e-Health (research based) e-Health (concept based) Scientific research findings are reviewed and assessed, and beginning of translation into applied research. Potential targets and disease mechanisms evaluated. Focus is still on discovery. Scientific research findings are reviewed and assessed, and beginning of translation into applied research and new technologies. TRL2 Technology concept and/or practical application formulated Hypothesis, research ideas, protocols and experimental designs are developed. Potential therapeutic targets for intervention are identified. TRL3 Analytical and experimental Proof of Concept of critical function and /or characteristics Active R&D initiated. Hypothesis testing and target identification and potential candidates characterization, data collection, exploration of alternative approaches and early proof of concept in a limited number of in vitro & in vivo models. Hypothesis, research ideas, protocols and experimental designs are developed. The potential ability of particular technologies, materials, and processes to address certain health problems identified. Active R&D initiated. Hypothesis testing, data collection, identification and evaluation of critical technologies and components and early proof of concept in laboratory models including in vivo studies. Scientific research begins to be translated into applied R&D activities. Concepts evaluated that can be implemented in development of e/mtechnology (software, sensors, devices, infrastructure or process). Invention of potentially practical e/m-technology solutions addressing particular needs. Observed need for either improved treatment procedure (process efficiency) or novel solution where e/mtechnology (software, sensors, devices, infrastructure or process) can be advantageous. Invention of potentially practical e/m-technology or novel setup of existing technology solutions addressing particular needs. Active development initiated. Studies to validate predictions of separate e/m-technology components of the concept that satisfy a need. System application tested in laboratory environment TRL4 Validation of the technology in the laboratory TRL5 Validation of technology in a relevant environment TRL6 Demonstration of technology in relevant environment Preclinical R&D. Optimization of candidates and in vivo demonstration of activity and efficacy. Identification and integration of critical technologies (animal models, biomarkers, assays, etc.) in continued characterization of and development of potential candidates. Initiation of GMP process development and manufacturing of non-GMP material and drug formulations. Evaluation of safety, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetic properties. Formulation of a Target Product Profile initiated. Further characterization of candidate, i.e. absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination. A manufacturing process established amenable to large scale GMP manufacturing and consistent with the intended use of the drug. Development of in process controls and relevant analytical assays. Continued development of animal models for efficacy and dose-ranging studies. Selection of candidate drug. GLP safety studies for IND submission and Phase 1 Clinical development. GMP production, IND submission and Phase I clinical evaluation performed proceeding to Phase II. Appropriate safety evaluations conducted to support further development TRL1 Preclinical R&D. Laboratory testing of critical components and processes. Proof of concept of device demonstrated in relevant laboratory and animal models. Active R&D initiated. Analytical studies to validate predictions of s e/m-technology components of the technology that satisfy a need – forming the system application. System application tested in laboratory environment System components integrated and tested regarding preliminary efficiency and reliability. Software architecture and other system components development to address reliability, scalability, operability, security etc. Other system components development System components integrated and tested preliminary efficiency and reliability. Software architecture, and other system components development to address reliability, scalability, operability, security etc. Further development of device candidates and system solutions. Validation of system components and processes in relevant laboratory environment. Classification of device by appropriate regulatory body and when appropriate an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) prepared and submitted for review. System component architecture established. System tested in relevant testing environment as expected in the operational environment. Verification, validation and accreditation when appropriate initiated. System component architecture established. System tested in relevant testing environment as expected in the operational environment. Verification, validation and accreditation when appropriate initiated. System/device prototype demonstrated in an operational environment. Clinical testing to demonstrate safety may be required. Depending on the classification of the device Representative model or prototype system demonstrated in relevant live or simulated environment. System component releases are “beta” versions and Representative model or prototype system demonstrated in relevant live or simulated environment. System component releases are “beta” versions and 6 TRL7 Technology prototype demonstrated in an operational environment Phase II clinical study is completed. Manufacturing process scale-up and process validation initiated and stability testing ongoing. Continued safety studies to support further clinical testing. The TPP refined when necessary. Phase III clinical plans defined and approved by regulatory authorities. TRL8 Technology system completed and qualified through test and demonstration Manufacturing processes validated. Pivotal clinical Phase III testing and safety studies completed. NDA or BLA prepared and submitted. And approved by appropriate regulatory authorities. TRL9 Technology system in its final form ready for full (commercial) deployment in relevant operating environment Product launched. Post-marketing studies (Phase IV) and surveillance Premarket approval or Premarket notification (510(K)) apply. configuration controlled. Support structure in development and verification and validation and when needed accreditation for safety reasons in progress. Clinical safety and effectiveness trials conducted using a fully integrated prototype version of the medical device in an operational environment. Data evaluated to support further development The final product design validated and final prototype and/or device intended for commercial use produced and tested. Premarket application or premarket notification submitted and approved System tested in an operational environment. Support structure in place and System component releases in distinct versions. Verification, validation and when appropriate accreditation completed. configuration controlled. Support structure in development and verification and validation and when needed accreditation for safety reasons in progress. System tested in an operational environment. Support structure in place and System component releases in distinct versions. Verification, validation and when appropriate accreditation completed. Development completed. System demonstrates to work under real life conditions. Testing of design specifications. System component releases are production versions. Support structure in place to resolve technical issues. Development completed. System demonstrate to work under real life conditions. Testing of design specifications. System component releases are production versions. Support structure in place to resolve technical issues. Product launched. Post-marketing studies and surveillance Product launched. Product launched. 7