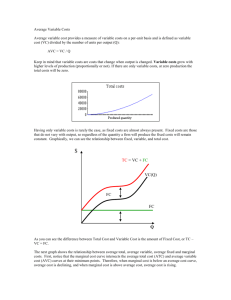
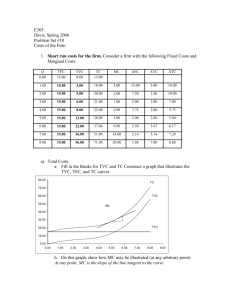
Short-Run Costs of Production
advertisement

COSTS OF PRODUCTION Economic Costs • Equal to opportunity costs • Explicit + implicit costs • Explicit costs • Monetary payments • Implicit costs • Value of next best use • Self-owned resources (rent) • Self-employed resources (labor) 8-2 Profit • Accounting profit • Total revenue less explicit cost • Normal profit • Equal to implicit cost • Economic or pure profit • Total revenue less economic cost 8-3 Profits Compared Economic Implicit Costs (Including a Normal Profit) Explicit Costs Total Revenue Economic (Opportunity) Costs Economic Profit Accounting Accounting Profit Accounting Costs (Explicit Costs Only) 8-4 Definition of the “Short-Run” • We will look at both short-run and long-run production costs. • Short-run is NOT a set specific amount of time. • The short-run is a period in which at least one resource is fixed. – Plant capacity/size is NOT changeable • In the long-run ALL resources are variable – NO fixed resources – Plant capacity/size is changeable Today we will examine short-run costs Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 5 Different Economic Costs Total Costs FC = Total Fixed Costs VC = Total Variable Costs TC = Total Costs Per Unit Costs AFC = Average Fixed Costs AVC = Average Variable Costs ATC = Average Total Costs MC = Marginal Cost Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 6 Fixed Costs: Definitions Costs for fixed resources that DON’T change with the amount produced Ex: Rent, Insurance, Managers Salaries, etc. Average Fixed Costs = Fixed Costs Quantity Variable Costs: Costs for variable resources that DO change as more or less is produced Ex: Raw Materials, Labor, Electricity, etc. Variable Costs Average Variable Costs = Quantity Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 7 Definitions Total Cost: Sum of Fixed and Variable Costs Average Total Cost = Total Costs Quantity Marginal Cost: Additional costs of an additional output. Ex: If the production of two more output increases total cost from $100 to $120, the MC $10 is _____. Change in Total Costs Marginal Cost = Change in Quantity Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 8 Calculating Costs Output Variable Fixed Cost Cost 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 $0 $10 $17 $25 $40 $60 $110 Total Cost $10 $10 $10 $20 $10 $27 $10 $35 $10 $50 $10 $70 $10 $120 Marginal Cost $10 $7 $8 $15 $20 $50 Let’s go column by column… 9 Total Cost Curves TC Costs FC + VC = TC VC Fixed Cost $10 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 FC Quantity 10 Calculating Costs Now Calculate: ATC AFC AVC 11 Calculating Costs Fill in the table 12 Calculating Costs Output Variable Fixed Cost Cost 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 $0 $10 $17 $25 $40 $60 $110 Total Cost $10 $10 $10 $20 $10 $27 $10 $35 $10 $50 $10 $70 $10 $120 Marginal Cost AVC AFC ATC $10 $7 $8 $15 $20 $50 $10 $10 $20 $8.50 $5 $13.50 $8.33 $3.33 $11.66 $10 $2.50 $12.50 $12 $2 $14 $18.33 $1.67 $20 Notice any relationships between average costs? -Shape of curves -AVC + AFC = ATC Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 13 Calculating Costs AVC AFC ATC $10 $10 $20 $8.50 $5 $13.50 $8.33 $3.33 $11.66 $10 $2.50 $12.50 $12 $2 $14 $18.33 $1.67 $20 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 14 MC ATC Costs $20 $18 $16 $14 $12 $10 $8 $6 $4 $2 AVC ATC and AVC get closer and closer but NEVER touch Average Fixed Cost AFC 1 2 3 4 5 6 Quantity 15 MC ATC Costs $20 $18 $16 $14 $12 $10 $8 $6 $4 $2 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 AVC Show TC, VC, and FC of the 5th Unit AFC 1 2 3 4 5 6 Quantity 16 Practice 17 2008 Audit Exam Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 1. 2. Costs Why does marginal cost always go down then up? Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 MC Quantity 20 Relationship between Production and Cost Output As more workers are hired, their marginal product increases and then eventually decreases because of the law of diminishing marginal returns MP Costs Quantity of labor The additional costs (MC) of the units they produce fall when MP MC goes up, but eventually increase as additional workers produce less and less output MP and MC are mirror images of each other Quantity of output Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 21 Graphical Relationships Average Product and Marginal Product Production Curves AP MP Quantity of Labor MC Cost (Dollars) AVC Cost Curves Quantity of Output 8-22 Costs Relationship between Production and Cost Why does ATC go down MC then up? ATC Quantity •When the marginal cost is below the average, it pulls the average down. •When the marginal cost is above the average, it pulls the average up. MC intersects the ATC curve at ATC’s lowest point Example: •The average income in the room is $50,000. •An additional (marginal) person enters the room: Bill Gates. •If the marginal is greater than the average it pulls it up. •Notice that MC can increase but still pull down the average. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 23 2008 Audit Question 23 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 2010 Question 18 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 When in doubt, graph it out Costs MC ATC $12 AVC $10 $8 AFC $2 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 100 Quantity 1. 2. Shifting Cost Curves Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 28 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 3 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 What if Fixed Costs increase to $200 29 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 30 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 31 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 TC 200 210 216 221 226 230 236 246 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 Which Per Unit Cost Curves Change? 32 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 TC 200 210 216 221 226 230 236 246 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 ONLY AFC and ATC Increase! 33 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 TC 200 210 216 221 226 230 236 246 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 200 110 8 100 58 7 66.6 30.3 6.5 50 31.5 6 40 26 6 33.3 22.67 6.6 28.6 20.9 ONLY AFC and ATC Increase! 34 Shifting Costs Curves If fixed costs change ONLY AFC and ATC Change! TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 TC 200 210 216 221 226 230 236 246 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 200 210 8 100 108 7 66.6 73.6 6.5 50 56.5 6 40 46 6 33.3 39.3 6.6 28.6 35.2 MC and AVC DON’T change! 35 Shift from an increase in a Fixed Cost MC Costs (dollars) ATC1 ATC AVC AFC1 AFC Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Quantity 36 Shift from an increase in a Fixed Cost MC Costs (dollars) ATC1 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 AVC AFC1 Quantity 37 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 What if the cost for variable resources increase 38 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 10 16 21 26 30 36 46 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 39 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 11 18 24 30 35 43 55 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 110 116 121 126 130 136 146 MC 10 6 5 5 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 40 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 11 18 24 30 35 43 55 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 111 118 124 130 135 143 155 MC 10 6 5 3 4 6 10 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 Which Per Unit Cost Curves Change? 41 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 11 18 24 30 35 43 55 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 111 118 124 130 135 143 155 MC 11 7 6 6 5 8 12 AVC AFC ATC 10 100 110 8 50 58 7 33.3 30.3 6.5 25 31.5 6 20 26 6 16.67 22.67 6.6 14.3 20.9 MC, AVC, and ATC Change! 42 Shifting Costs Curves TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 11 18 24 30 35 43 55 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 111 118 124 130 135 143 155 MC 11 7 6 6 5 8 12 AVC AFC ATC 11 100 110 9 50 58 8 33.3 30.3 7.5 25 31.5 7 20 26 7.16 16.67 22.67 7.8 14.3 20.9 MC, AVC, and ATC Change! 43 Shifting Costs Curves If variable costs change MC, AVC, and ATC Change! TP 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 VC 0 11 18 24 30 35 43 55 FC 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 TC 100 111 118 124 130 135 143 155 MC 11 7 6 6 5 8 12 AVC AFC ATC 11 100 111 9 50 59 8 33.3 41.3 7.5 25 32.5 7 20 27 7.16 16.67 23.83 7.8 14.3 22.1 44 Shift from an increase in a Variable Costs MC1 Costs (dollars) MC ATC1 AVC1 ATC AVC AFC Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Quantity 45 Shift from an increase in a Variable Costs MC1 Costs (dollars) ATC1 AVC1 AFC Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Quantity 46 Shifts in Cost Curves • Practice: Which curves shift and how? – Decrease in union wage requirements? • AVC, ATC, MC shift DOWN – Increase in rent? • AFC, ATC, shift UP – Increase in cost of materials? • AVC, ATC, MC shift UP – More efficient production technology is discovered? • AVC, ATC, MC shift DOWN