Introduction
advertisement

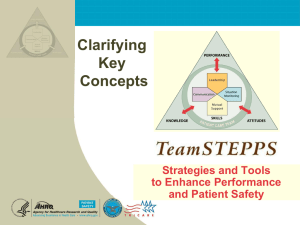
Strategies and Tools to Enhance Performance and Patient Safety Introduction Module 1 Introduction Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 2 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 2 Exercise Instructions Introduction Goal: You have 1 minute to build the tallest tower. Roles: Runners and Builders Rules: Blocks are located at the front and back of the room. Runners retrieve blocks from bins but may only take 5 blocks at a time. Builders build the tower using the pattern of 1 large, 3 small blocks, repeat. No two blocks of the same color may touch. Runners are not allowed to build/ builders are not allowed to run. Any unused blocks that are not replaced in the storage bins before time is called will result in subtraction from the tower height; one block subtracted for each unused block. Report Out: Height of tower in blocks (minus unused blocks). Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 3 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 3 Exercise Instructions Introduction Debrief: • What went well? • What didn’t go well? • What will you do differently? • Same pattern we will follow in simulation − Plan (Brief), Do, Study (Debrief), Repeat Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 4 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 4 Introduction Objectives • Describe the impact of errors and why they occur • Describe the TeamSTEPPS framework • Describe the TeamSTEPPS training initiative • State the outcomes of the TeamSTEPPS framework Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 5 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 5 Introduction Sue Sheridan Video Videos must be saved in the same file as your power point before you can insert them. • Click on insert tab in power point • Click on Video • Click on Video from file • Click on Sue SheridanLg001 • Click on Insert Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 6 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 6 Video Discussion Introduction • Patients are harmed as a result of poor communication and teamwork that results in medical errors − How often do medical errors occur? − Why do medical errors occur? − How can we prevent medical errors? • Applies to non-clinical situations…goals are not achieved …Improved teamwork and communications… Ultimately, a culture of safety Are you ready to be part of the transformation of health care? Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 7 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 7 Introduction How Often do Medical Errors Occur? • 44,000 – 98,000 deaths per year in hospitals due to medical errors IOM (2000). To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System (Photo: Ezra Shaw, Getty Images) • Equal to one jumbo jet crashing EVERY DAY! • Where is CNN? www.foxnews.com Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 8 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 8 Introduction Impact of Medical Errors • From a 2010 analysis of a claims database − 1.8% of hospital admissions experience a medical error (a preventable adverse outcome of medical care) − Medical errors cost the US at least $19.5 billion/year • From a random sample of 780 Medicare beneficiaries discharged Oct. 2008 − 13.5% of hospitalized Medicare beneficiaries experience an adverse event (44% were preventable) − 1.5% experienced an event that contributed to their deaths (projects to 15,000 total patients/month) http://www.soa.org/files/pdf/research-econ-measurement.pdf http://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-06-09-00090.pdf 9 Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 9 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Human Factors Introduction • Study of the interaction between humans and elements of the system in which they live/work • – Physical environment – Tasks – Tools/technology – Organizational conditions Goal: achieve optimal interaction between social, technical, and physical elements of a system. https://www.hfes.org//Web/AboutHFES/about.html 10 Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 10 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction Why Do Errors Occur—Some Human Factors • Workload fluctuations • Excessive professional courtesy • Interruptions • Fatigue • Halo effect • Multi-tasking • Passenger syndrome • Failure to follow up • Rigid Hierarchies • Poor handoffs • High-risk phase • Ineffective communication • Strength of an idea • Task fixation (lack of • Not following protocol situational awareness) • Complacency Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 11 11 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction Task Fixation and Situation Awareness Your Environment Your Team Your Equipment You Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 12 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 12 Human Factors Introduction Turn to your neighbor… 1. Describe a human error that you made. 2. Describe a recent error made at your hospital. CNA had pt use IV pole to walk to bathroom; pt’s legs buckled and she fell. Walker & gait belt were in room. I ran a stop light. Which human factors contribute to this error? Which human factors contributed to this error? 13 Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 13 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction Joint Commission Sentinel Events http://www.jointcommission.org/assets/1/18/Root_Causes_Event_Type_2004_2Q2012.pdf Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 14 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 14 The Problem… Introduction “The problem is not bad people; the problem is that the system needs to be made safer . . .” “People make fewer errors when they who work in teams.” IOM (2000). To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System 15 Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 15 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction Teamwork Is All Around Us Common purpose Performance goals Mutual accountability Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 16 Clear role expectations Complementary skills Interdependent tasks TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 16 Introduction Team Strategies & Tools to Enhance Performance & Patient Safety “Initiative based on evidence derived from team performance…leveraging more than 30 years of research in military, aviation, nuclear power, business and industry…to acquire team competencies” Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 17 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 17 Introduction Evolution of TeamSTEPPS Curriculum Contributors • Department of Defense • Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality • Research Organizations • Hospitals—Military and Civilian, Teaching and Community-Based • Private Companies • Subject Matter Experts in Teamwork, Human Factors, and Crew Resource Management (CRM) • Universities • Medical and Business Schools • Healthcare Foundations Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 18 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 18 Introduction Evolution of TeamSTEPPS: US Army Aviation • Army aviation crew coordination failures in mid-80s contributed to 147 aviation fatalities and cost more than $290 million • The vast majority involved highly experienced aviators • Failures were largely attributed to crew communication, workload management, and task prioritization Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 19 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 19 Introduction Evolution of TeamSTEPPS: US Air Force CRM History • Mid to Late 80s AF bombers and heavy aircraft started CRM training • 1992 Air Combat Command developed Aircrew Attention Management /CRM Training • By 1998, CRM deployed uniformly across the AF • Steady decline in human factors based mishaps since CRM training deployed • AF Medical Service adapted training, rolled out in 2000 Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 20 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 20 The Theory Introduction Mutual Performance Monitoring Team Leadership Team Orientation Back-up Behavior Shared Mental Models Mutual Trust Adaptability Big 5 Coord. Mechanism Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 21 Team Effectiveness Closed Loop Communication TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Salas, Sims, Burke. Is there a “Big Five” in teamwork? Small Group Research. 2005; 36:555-599. 21 Introduction The Framework: What Comprises Team Effectiveness? Knowledge Cognitions “Think” Attitudes Affect “Feel” Skills Behaviors “Do” Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 22 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 …team performance is a science…consequences of errors are great… 22 More Evidence Introduction • Exploding Literature − Patient Care Team + Evidence-Based Practice = 1,128 − Patient Care Team + Evaluation Studies = 843 • Studies in diverse patient populations demonstrate relationship between teamwork and − Improved clinical processes − Reduction in medical errors − Improved surgical team performance − Increased adherence to guidelines − Decreased length of stay − Increased functional status − Decreased mortality Salas et al. What are the critical success factors for team training in health care? Jt Comm Jrnl Qual Safe. 2009;35:398-405. Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 23 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction Your Contribution to the Evidence • Team training can result in transformational change in safety culture when the work environment supports the transfer of learning to new behavior. • Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture conducted in 24 hospitals before training one year after training • To successfully implement and sustain new behaviors − Stay connected to the community via monthly calls − Train supervisors/managers first so they can role model behaviors − Provide multiple follow-up learning opportunities − Job descriptions/performance evaluations include use of team skills Jones KJ, Skinner AM, High R, Reiter-Palmon R. A theory-driven longitudinal evaluation of the impact of team training on safety culture in 24 hospitals. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22:394-404. Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 24 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 24 Introduction Supported by AHRQ Washington -TRC Minnesota -TRC North Shore Long I. TRC 10 18 UNMC 58 5 Duke TRC 1 1 Tulane TRC http://teamstepps.ahrq.gov/aboutnationalIP.htm Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 25 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction HOW DOES TEAMSTEPPS WORK? SHIFT TOWARDS A CULTURE OF SAFETY Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 26 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction HSOPS Teamwork Teamwork Within Departments Positive 1. People support one another in this department. (A1) (Belief/Attitude) Neutral 58% 2. When a lot of work needs to be done quickly, we work together as a team to get the work done. (A3) a 74% 74% 3. In this department, people treat each other with respect. (A4) 63% 4. When one area in this department gets really busy, others help out. (A11) (Behavior) 26% Negative 11% 32% a a Practices/skills that bridge the gap Identify team leaders Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 27 Set team goals Use briefs, huddles, debriefs Cross monitor (“watch each others’ back”) TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 11% 11% a a 32% 16% 16% 16% 21% 42% 32% GAP 27 Introduction Agenda DAY 1 DAY 2 • Module 1—Introduction • Coaching Workshop • Module 2—Team Structure • High Fidelity Simulation • Module 3—Leadership − Practice team skills • Module 4—Situation Monitoring − Coach team skills − Identify team skills • Module 5—Mutual Support • Module 6—Communication • Module 7—Summary— Putting It All Together Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 28 TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Webinars to Complete Requirements for Master Trainer Certification • Wed. Oct. 16 10 - 11 a.m. • Thurs. Nov. 21 2 – 3 p.m. 28 Training BARRIERS to Team Performance • Inconsistency in Team Membership • Lack of Time • Lack of Information Sharing • Hierarchy • Defensiveness • Conventional Thinking • Complacency • Varying Communication Styles • Conflict • Lack of Coordination and Follow-Up with Co-Workers • Distractions • Fatigue • Workload • Misinterpretation of Cues • ModLack Clarity 1 06.2 05.2 of PageRole 29 TOOLS and STRATEGIES Brief Huddle Debrief Situational Monitoring Situational Awareness STEP Cross Monitoring Feedback Advocacy and Assertion Two-Challenge Rule CUS DESC Script Collaboration SBAR Call-Out Check-Back Handoff TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 Introduction OUTCOMES Shared Mental Model Adaptability Team Orientation Mutual Trust Team Performance Patient Safety!! 29 Summary Introduction • Impact of errors…patients are harmed, non-clinical teams do not achieve goals • TeamSTEPPS Framework − Safety net for fallible human beings • TeamSTEPPS training meets a need − Diffuse evidence-based training program nationally and internationally http://teamstepps.ahrq.gov/ • Outcomes of TeamSTEPPS Shared Mental Model Mutual Trust Mod 1 06.2 05.2 Page 30 Adaptability Team Orientation Team Performance Patient Safety!! TEAMSTEPPS 05.2 30