Chapter 5 Quality Food

Chapter 5
Quality Food-
Production Standards
Principles of Food and
Beverage Management
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you should be able to:
• Describe basic concerns in establishing quality standards.
• Explain sustainability and “farm-to-fork” concerns.
• Describe how to determine menu item quantities and labor hours needed for production shifts, and indicate necessary instructions to production staff.
• Explain how food-production methods enhance quality.
Learning Objectives continued:
After completing this chapter, you should be able to:
• Identify food safety concerns that must be addressed as food quality standards are implemented.
• Identify supervision procedures during production that address quality and other concerns.
• Describe quality concerns when considering types of convenience food and when developing production procedures to enhance nutrition.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
ESTABLISHING QUALITY STANDARDS
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
QUALITY AND ENVIRONMENTAL CONCERNS
Sustainability
Water Conservation
Energy Conservation
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Farm-to-Fork Sustainability
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
PRODUCTION PLANNING
Determining Menu Item Quantities
Past Sales Trends
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Current Sales Trends
Future Sales Trends
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Determining Labor Hours
Before-Shift Instructions
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
PRODUCTION METHODS TO ENHANCE QUALITY
Fresh Fruit and Vegetables
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Meat, Fish, and Poultry
Method 1: Moist Heat
Method 2: Dry Heat
Method 3: Combination Method
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Sauces
Thickening Agents
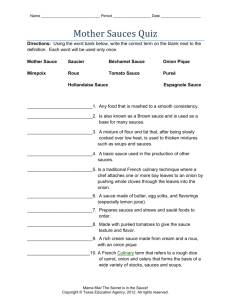
Classic Sauces
Small and Modern Sauces
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Dairy Products
Butter and Cheese
Milk and Cream
Frozen Dairy Product
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Bakery Products
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY STANDARDS
Importance of Food Safety
Food Safety before and during Production
Food Safety after Production
Cleaning and Sanitizing Practices
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Other Food Safety Issues
Chemical Hazards
Physical Hazards
Pest Control Hazards
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
SUPERVISING PRODUCTION STAFF
Supervising for Quality
Supervising for Other Concerns
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
OTHER PRODUCTION QUALITY CONCERNS
Types of Convenience Food
Nutrition and Food Production
Meat , Poultry, and Fish
Fruit and Vegetables
Other Nutritional Preparation Suggestions
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
1. Describe basic concerns in establishing quality standards.
• Managers must establish standards that define the experience that customers will receive.
• Then they must charge a value-driven price that generates a profit for the operation.
• The best managers use planning tools including the menu, standardized recipes, and purchase specifications to help ensure standards will be met.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
2 . Explain sustainability and “farm-to-fork” concerns.
• Managers understand that addressing sustainability will be good for their business as well as the planet.
• They train their employees to conserve water and energy.
• They also consider farm-to-fork concerns that minimize the flow of food from growing to preparation.
• Locally grown food has advantages, and increasingly, customers prefer it.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
3 . Describe how to determine menu item quantities and labor hours needed for production shifts, and indicate necessary instructions to production staff.
• Production forecasts based on past, present, and future sales trends suggest the quantity of each menu item to be sold.
• Required labor hours are determined by considering the number allowed by the operating budget and scheduling based on the number of customers.
• These calculations allow master and crew schedules to be developed.
• Production managers should conduct line-up meetings with employees who must assemble items for preparation.
• Much of this information is included in a prep sheet.
• A production schedule indicating responsibilities may also be distributed.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
4 . Explain how food-production methods enhance quality.
• Basic preparation procedures should be developed for handling fresh fruit and vegetables; meat, fish, and poultry; sauces; and bakery and dairy products.
• Sanitation and other requirements should be addressed in standardized recipes with special attention given to TCS food items: those that need time and temperature control for safety.
• Cooking methods that apply moist heat, dry heat, or a combination of both can be used depending on the product, temperature, and cooking time.
• There are five classic sauces, as well as additional small and modern sauces, that can enhance food.
• Production employees must know quality considerations for butter, cheese, milk, and cream and for ingredients typically used in bakery products.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
5 . Identify food safety concerns that must be addressed as food quality standards are implemented.
• There are numerous procedures that should be used during and after food production to reduce the possibility of foodborne illnesses.
• Facility cleanup practices are also important, as are concerns for chemical, physical, and pest control hazards.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
6 . Identify supervision procedures during production that address quality and other concerns.
• Managers must “manage by walking around” to note activities related to quality.
• These include use of standardized recipes, compliance with the
HACCP program, and work procedures.
• Managers know how to tell if customers are enjoying their food.
• They also establish procedures for transferring food items from production to service staff, and they can identify and correct shortand longer-term problems.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards - Summary
7 . Describe quality concerns when considering types of convenience food and when developing production procedures to enhance nutrition.
• Convenience food items reduce the amount of labor needed to produce menu items on-site, but they must meet quality requirements.
• Numerous food-preparation procedures can address customers’ increasing concerns about nutrition, and many can be incorporated into standardized recipes.
• Examples include substituting nutritional ingredients for less nutritional items and using appropriate cooking methods.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Key Terms:
Aging One of two methods of tenderizing beef: Wet aging involves placing small portions of beef in a plastic bag without air, sealing the bag, and refrigerating for a specific period of time. Dry aging is done in special coolers in which air is circulated at precise temperatures for the time determined by package size and other factors.
Benefits Indirect financial compensation paid to attract and retain employees.
Classic sauce One of five sauces also called “mother sauces,” since other sauces can be made from them. The classic sauces are béchamel sauce, velouté sauce, espagnole (brown) sauce, hollandaise sauce, and tomato sauce.
Crew schedule A chart that shows employees what days and hours they are expected to work during a specific time period, usually a week.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Key Terms continued:
Cross-contamination The transfer of microorganisms from one surface or food to another.
Farm-to-fork The flow of food through the stages of growing, harvesting, storage, processing, packaging, and preparation.
Foodborne illness A disease transmitted to people by food. It can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms, chemicals, or physical hazards.
Labor cost The money and cost of benefits paid for the work employees do.
Leavening The process in which ingredients produce gases that cause dough to rise.
Line-up meeting A meeting that provides specific information for the shift including special events, new ingredients, or discussion about how to resolve an emerging or recurring problem.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Key Terms continued:
Make or buy analysis A procedure to determine whether menu items should be made with raw ingredients or purchased in a convenience form with some labor “built in.”
Marinating A tenderizing method that involves immersing food items from one to several hours in liquid made from oil and vinegar or lemon juice seasoned with herbs and spices.
Master schedule A schedule that shows the number of employees needed in each position and the total number of hours each employee must work.
Mise en place A French term that means “get everything in place.”
Production forecast A determination of the quantity of each menu item that will likely be sold during a specific time period, such as lunch or evening meal.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Key Terms continued:
Production sheet (prep sheet) A document that indicates items that will be needed for the shift.
Roux A thickener made from equal parts flour and butter, cooked on the stove at a low temperature.
Sales forecast report A report that tells the production staff about the overall product needs to meet the sales forecast.
Sustainability Activities including water conservation, energy efficiency, and recycling that can lessen an operation’s impact on the environment.
TCS food Food that needs time and temperature control for safety.
Tenderizing (meat) Breaking down connective tissue in meat.
Thickener Any ingredient added to a liquid to make it thicker.
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter Images
Chapter 5 Quality Food-Production Standards
Chapter Images continued