a rare case of angiomyofibroblastoma of vulva
advertisement
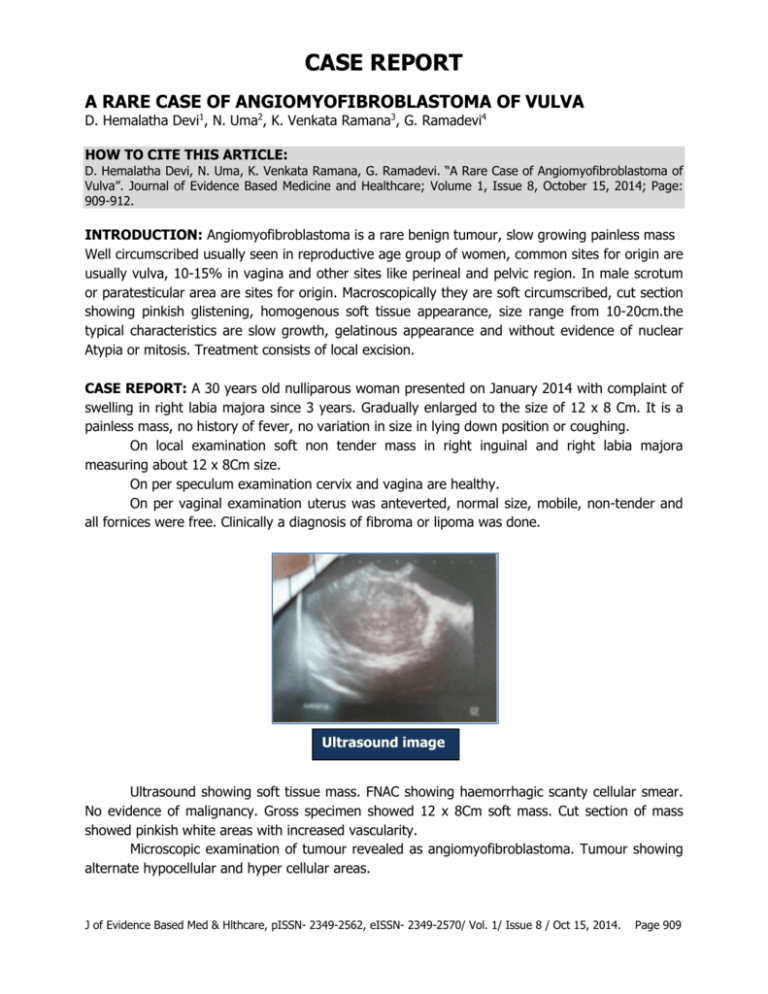
CASE REPORT A RARE CASE OF ANGIOMYOFIBROBLASTOMA OF VULVA D. Hemalatha Devi1, N. Uma2, K. Venkata Ramana3, G. Ramadevi4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D. Hemalatha Devi, N. Uma, K. Venkata Ramana, G. Ramadevi. “A Rare Case of Angiomyofibroblastoma of Vulva”. Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare; Volume 1, Issue 8, October 15, 2014; Page: 909-912. INTRODUCTION: Angiomyofibroblastoma is a rare benign tumour, slow growing painless mass Well circumscribed usually seen in reproductive age group of women, common sites for origin are usually vulva, 10-15% in vagina and other sites like perineal and pelvic region. In male scrotum or paratesticular area are sites for origin. Macroscopically they are soft circumscribed, cut section showing pinkish glistening, homogenous soft tissue appearance, size range from 10-20cm.the typical characteristics are slow growth, gelatinous appearance and without evidence of nuclear Atypia or mitosis. Treatment consists of local excision. CASE REPORT: A 30 years old nulliparous woman presented on January 2014 with complaint of swelling in right labia majora since 3 years. Gradually enlarged to the size of 12 x 8 Cm. It is a painless mass, no history of fever, no variation in size in lying down position or coughing. On local examination soft non tender mass in right inguinal and right labia majora measuring about 12 x 8Cm size. On per speculum examination cervix and vagina are healthy. On per vaginal examination uterus was anteverted, normal size, mobile, non-tender and all fornices were free. Clinically a diagnosis of fibroma or lipoma was done. Ultrasound image Ultrasound showing soft tissue mass. FNAC showing haemorrhagic scanty cellular smear. No evidence of malignancy. Gross specimen showed 12 x 8Cm soft mass. Cut section of mass showed pinkish white areas with increased vascularity. Microscopic examination of tumour revealed as angiomyofibroblastoma. Tumour showing alternate hypocellular and hyper cellular areas. J of Evidence Based Med & Hlthcare, pISSN- 2349-2562, eISSN- 2349-2570/ Vol. 1/ Issue 8 / Oct 15, 2014. Page 909 CASE REPORT Marked proliferation of blood vessels, spindle to ovoid nucleus, scanty cytoplasm, mild pleomorphism, perivascular hyalinization, mitotically active cells. HPE report suggesting angiomyofibroblastoma. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: These tumors have to be differentiated from lipoma, fibroma, neurofibroma and angiomyxoma of vulva. Lipoma is soft non tender mass. Fibroma is firm non tender mass no recurrence seen. Angiomyxoma has much high risk of recurrence than angiomyofibroblastoma. It is cured by simple excision. DISCUSSION: This angiomyofibroblastoma was first described on 1992. Peak incidence is during third decade of life. It generally involves the genital, perenial and pelvi region with vulvar region being the most common site of involvement followed by vagina (10-15%). It is slow growing benign tumor. Investigations necessary are ultrasound, FNAC, CT scan. Our patient was not subjected to CT as its clinical appearance was that of benign. The treatment of choice consists of excisional biopsy, recurrence is rare. CONCLUSION: Angiomyofibroblastoma should be kept in mind when an asymptomatic and slow growing vulvar mass is detected in reproductive age group of women. Treatment is local excisional biopsy. This unusual neoplasm should be distinguished from aggressive angiomyxoma and other myxoid malignant tumors with widespread metastatic potential. REFERENCES: 1. Giannella L, Costantini M, Mfuta K, Cavazza A, Cerami LB, Gardini G et al. Pedunculated angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: case report and review of literature. Case reports in medicine 2011; vol 1: 1-4. 2. Lim KJ, Moon JH, Yoon DY, Cha JH, Lee IJ, Min SJ. Angiomyofibroblastoma arising from the posterior perivesical space: a case report with MR findings. Korean J RADIOL 2008; 9: 382385. 3. Kim SW, Lee JH, Han JK, Jeon S. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva. J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: 1417-1420. 4. Omori M, Toyoda H, Hirai T, Ogino T, Okada S. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: A large pedunculated mass formation. Acta Med Okayama 2006; vol 60(4): 237-242. 5. Hjalmer S, Svennevik MS, Fai CK, Andua KT. Angiomyofibroblastoma and aggressive angiomyxoma.Two rare tumors of the vulva. Journal of pelvic medicine and surgery 2006; vol 12(4): 225-228. 6. McCluggage WG. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vagina. J Clin Pathol 2000; 53: 803-806. 7. Hisoaka M, Kouho H, Aoki T, Daimaru Y, Hashimoto H. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: A clinicopathologic study of seven cases. Pathology International 1995; vol 45(7): 487-492. 8. Fletcher CDM, Tsang W, Fisher C, Lee KC, Chan J.Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: A benign neoplasm distinct from aggressive angiomyxoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1992; vol 16(4): 364-372. J of Evidence Based Med & Hlthcare, pISSN- 2349-2562, eISSN- 2349-2570/ Vol. 1/ Issue 8 / Oct 15, 2014. Page 910 CASE REPORT Photograph of Vulval Angiomyofibroblastoma Cut section of specimen Alternating hypocellular and hypercellular edematous areas Gross specimen of mass Capillary type blood vessels with spindle and plump stromal cells J of Evidence Based Med & Hlthcare, pISSN- 2349-2562, eISSN- 2349-2570/ Vol. 1/ Issue 8 / Oct 15, 2014. Page 911 CASE REPORT AUTHORS: 1. D. Hemalatha Devi 2. N. Uma 3. K. Venkata Ramana 4. G. Ramadevi PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS: 1. Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Government Victoria Hospital, Visakhapatnam. 2. Incharge Professor /Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Government Victoria Hospital, Visakhapatnam. 3. Assistant Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Government Victoria Hospital, Visakhapatnam. 4. Assistant Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Government Victoria Hospital, Visakhapatnam. NAME ADDRESS EMAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. D. Hemalatha Devi, #14, Doctor’s Quarters, Near Zilla Parishad, Maharanipeta P.O, Visakapatnam – 530002, Andhra Pradesh. E-mail: hema.vgh.gyn@gmail.com Date Date Date Date of of of of Submission: 01/09/2014. Peer Review: 02/09/2014. Acceptance: 21/09/2014. Publishing: 07/10/2014. J of Evidence Based Med & Hlthcare, pISSN- 2349-2562, eISSN- 2349-2570/ Vol. 1/ Issue 8 / Oct 15, 2014. Page 912