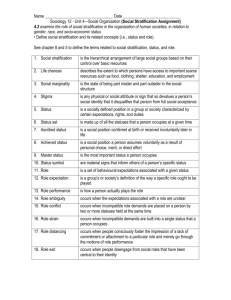
Social Stratification

Stratification
Learning Objectives
Explain the interconnectedness between stratification, economics, politics, subsistence, and kinship.
Demonstrate and understanding of basic concepts in cultural anthropology.
Distinguish between open and closed systems.
Read and critically analyze writing on stratification and gender relations
Distinguish between sex and gender.
Discuss how gender varies across cultures
SOCIAL STRATIFICATION
Social Stratification
_____________________________
Access to _________________
What is a resource? Is it purely economical?
Social Stratification
Points to Note:
1.
Not a reflection of individual differences
2.
3.
Open vs Closed Systems
Stratification systems are either
Closed: _______________________
Open: __________________________
Checkpoint:
What does mobility mean in the context?
Closed Systems
__________________________
__________________
Checkpoint:
What are ascribed characteristics?
Caste Example: Japan’s Feudal
Caste System
Feudalist era
Very complex cast system
Touchable
Untouchable
Caste Example: Japan’s Feudal
Caste System
Nanda’s ‘Arranging a Marriage in
India’
How did Nanda's definition and perceptive of arranged marriages changed as she conducted ethnographic fieldwork?
What fieldwork did she conduct?
How does the social stratification of India play a role in arranged marriages?
Open Systems
________________________________
___________________
Checkpoint:
What are achieved characteristics?
Can you think of a culture with a class system?
Social Mobility
Is there a relationship between ethnicity and social mobility?
Is there a relationship between gender and social mobility?
Remember: think beyond the U.S.
GENDER
AND
GENDER STRATIFICATION
What is Gender?
Sex = biology
_____________________________
Gender
1.
2.
What Does Gender Consist Of?
How males/females perceive and define themselves and each other
1.
2.
KEY POINT:
Terms for Lecture
Gender Roles
1.
[Distinguish between: Prestige systems & Power given in society]
Gender stereotypes
1.
Gender stratification
1.
Gender Stratification
Table 9.1 (p211) – based on 1973 article
Generally ♂ Swing Generally ♀
Generalities not Universals Gathering fuel
What does this mean?
Building boats Body mutilation Fetching water
Preparing soil
Butchering
Planting crops Spinning
Making pottery Dairy products
Gender Stratification
Table 9.1 (p211) – based on 1973 article
Generally ♂ Swing Generally ♀
Hunting Make fire Gathering fuel
Building boats Body mutilation Fetching water
Preparing soil
Butchering
Planting crops Spinning
Making pottery Dairy products
Gender Stratification
Deviations from Table 9.1
Gender Stratification
Deviations from Table 9.1
Gender Stratification
Deviations from Table 9.1
___________ among Mbuti ‘pygmies’
___________________
________________
Today men also hunt but their goal is centered on obtaining bushmeat for market sales
Gender Stratification
Deviations from Table 9.1
Gender Roles & Stratification
Interconnected with subsistence & economics
Generally observed when:
♀ ______________________ than ♂
Example: __________________
Inuit
What happens when _____________?
Gender Roles & Stratification
Domestic and public spheres
_______________________________
Domestic-public dichotomy
________________________________
Examples of these spheres?
Gender Stratification
Increase Gender Stratification
Patrilineral – Patrilocal Complex
Patrilinal descent:
Patriarchy:
Example: Densely populated areas of _________
Gender Stratification
Decrease Gender Stratification
Matrilineal – Matrilocal
Matrilineal descent:
Matriarchy:
Examples:
1. _________________♀ sole inheritance of rice fields, decision making
2. ______________________ – central role socially, economically, and ceremonial life plus village and regional influence
Gender Roles & Worksheet #3
Worksheet #3: Meintjes ’ (2001) ‘Washing Machines
Make Lazy Women’
(Multiple) Symbolic, Gender Roles & Identity
Beyond ♂ & ♀
How males/females perceive and define themselves and each other
Self identity
Social identity
KEY POINT: Gender, in several cultures, is not biologically fixed
Beyond ♂ & ♀
1. __________________________
Preference for the work of the opposite sex and/or for work set aside for their 3 rd or 4 th gender
2. ______________________
________________
Beyond ♂ & ♀
3. __________________________
Calling
4. ___________________
Formation of sexual or emotional bonds
Beyond ♂ & ♀
William’s article:
In your own words, explain the spiritual connection for the acceptance of a Berdache in Native American societies.
Use an example from William's article to support your explanation.