Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases.
advertisement

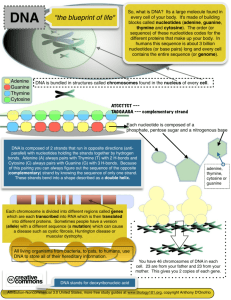
Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Do Now: Compare and contrast the molecules below. How are all of them similar? How does Nucleic Acid differ? Glucose Nucleic Acid Lipid Amino- acid Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Where do you find Nucleic Acids in a cell? Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Where do you find Nucleic Acids in a cell? Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. How is the structure of a Nucleic Acid? What is the pattern? Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. DNA structure of double helix Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Structure of DNA Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugar-phosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) DNA is made up of repeating unit of nucleotides. Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. Watson & Crick Watson and Crick discovered the double helix structure of DNA in 1953 Objective: Understand the structure of DNA Key words: Nucleic Acids, DNA, RNA, nucleotides, nitrogen bases. What is a nucleotide? 1. What kind of molecules is a nucleotide? (Organic or inorganic) Organic molecule _______________________________ 2. How do you know: It is made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen a._______________________________________ Carbon is the main element b. _______________________________________ It is a large and complex molecule c. _______________________________________ 3. What are the THREE common parts of a nucleotide. Deoxyribose or sugar a. _____________________________________________ Phosphate group b. _____________________________________________ Nitrogen base c. ______________________________________________ 4. What is the ONE part of a nucleotide that differs among the four DIFFERENT nucleotides? Nitrogen base ___________________________________________________ 5. List the FOUR different kinds of nitrogen bases. a ____________________________________________ (A) Adenine b____________________________________________ (G) Guanine c _____________________________________________ (C) Cytosine d _____________________________________________ (T) Thymine Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine Do Now: List 3 things you learned about the structure of Nucleic Acids Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine 6. Explain WHERE the nucleotide molecules connect to each other. • Phosphate group connects to _____________________ deoxyribose (sugar) nitrogen base • Nitrogen base connects to_________________________ Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine A real DNA molecule consists of THOUSAND of pairs of nucleotides. 7. What is the pairing arrangement of nitrogen bases? (T) Thymine pairs with ____________________________ (A) Adenine ___________________ (G) Guanine pairs with_____________________________ (C) Cytosine and _______________ Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine 8.Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of adenine and thymine nucleotides in a molecule? Yes Why? Because Adenine always pairs to Thymine Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of Guanine and Cytosine nucleotides in a molecule? Yes Why Because Guanine always pairs to Cytosine Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine 9. Scientists abbreviate the nitrogen bases by using the first letter of each base. So, T Cytosine A always binds to _____________ Guanine always binds to ______________________ C Guanine G always binds to _____________ Cytosine always binds to ______________________ G C always binds to _____________ Thymine always binds to ______________________ Adenine A T always binds to _____________ Adenine always binds to ______________________ Thymine 10. Pair the missing bases on the DNA molecules. a) A – T – A – A – G – C – T – A - G __________________________________ T–A –T –T – C–G– A– T–C b) C – C – G – T – A – A – C – G – A __________________________________ G–G–C–A–T–T–G– C-T c) A – T – A – C – T – A – G – C – A __________________________________ T–A–T–G–A–T–C–G-T d) G – C – T – A – C - A - G – A – C __________________________________ C–G–A–T–G–T–C–T–G DNA replication New strand Original strand DNA polymerase Growth DNA polymerase Growth Replication fork Replication fork New strand Original strand Objective: Understand How Nitrogen Bases pair in DNA Key words: Nitrogen Bases, DNA, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine 10. What is the function of the DNA? To store and transmit the genetic information from one Generation of an organism to the next 11. What is the structure of DNA? Double helix