Cardiovascular System
advertisement

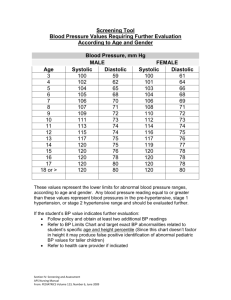
Cardiovascular System • Understand the concept of the heart as a double pump • Identify what are the immediate effect of exercise on the cardiovascular system Our Learning Objectives Write them down so we can tick them off! By the end of the lesson you should be able to: 1.Be able to name at least 2 immediate effects of exercise 2.Be able to explain Heart Rate and Blood Pressure. Task 1 Using your simple diagram of the heart: 1. Label the left and right side 2. Label the atrium 3. Label the ventricles 4. Draw arrows to indicate where blood is pumped in from the body and lungs. 5. Draw arrows to indicate where blood is pumped in to the body and lungs. 6. Use colours or labels to indicate which is side is deoxygenated and oxygenated. 7. Write a brief paragraph summarising how the heart works using the diagram you have labelled. Cardiac system The four chambers of the heart have special names: An upper chamber is called an atrium (plural: atria). right atrium left atrium right ventricle left ventricle A lower chamber is called a ventricle. The circulatory system Immediate effects of exercise Lets give it a go… • Take you Resting Heart rate ………… • Exercise, then take your Working heart rate ………….. Immediate effects of exercise • What happens to your pulse? Why? • When feeling for your pulse was this easier or harder? Why? The Immediate effects of exercise on the Cardiovascular system ***Know These!!!!!! • Increased Heart Rate • Increased Blood Pressure • Systolic/Diastolic Pressure Why/How do these happen……. Immediate Effects of Exercise Increased Heart Rate Increased Blood Pressure Increased Systole/Diastole Why this occurs Heart Rate Definition: The number of times the heart beats per minute. (Write this down!) For a normal person this is approx. 60-80 beats per minute Why this happens: • When the body works harder it requires more oxygen and nutrients to meet the demands of exercise • Oxygen and nutrients are carried to the muscles in blood, therefore the heart has to work faster to pump more blood around the body. • The heart rate is increased by the release of the release of adrenaline (hormone). • The heart rate also needs to increase in order to remove carbon dioxide and lactic acid. Blood Pressure Definition: the force exerted by the circulating blood on the walls of the blood vessels. This increases during exercise because more blood is being pumped around the body increasing the pressure on the blood vessels. A blood pressure meter is used to measure systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure explained…… Systolic/Diastolic pressure Systolic: • where blood pressure is at its maximum (pumping out of the heart). • This rises with activity or excitement as more blood is needed by the body Diastolic • The pressure of the blood during the relaxation phase between heart beats (when the heart is at rest) • This depends mainly on the elasticity of the arteries and quality of the vessels. Blood Pressure • The heart makes 2 beating sounds Systole and Diastole. • Systole: This is made by the lower chambers (ventricles) contracting and pushing the blood at high pressure into the arteries and out of the heart. • Diastole: Is the second sound and this is made by the upper chambers (arterioles) contracting to push the blood into the lower chambers (Ventricles). • The actual sound we hear is the valves opening and closing. Blood Pressure Abnormal blood pressure High Systolic – persistently above 140mmHg Diastolic – persistently above 85mmHg Low Systolic – persistently below 90mmHg Diastolic – persistently below 60mmHg Causes!!! • • • • • • Overweight Alcohol Smoking Too much salt Stress/Anxiety/Worry Not enough exercise Questions 1. • • • • Fill in the blanks using the word arteries or veins. I. ………………………………. Work under high pressure ii. ………………………………. Rarely pulsate iii. ……………………………….have thick walls iv. ……………………………….have elastic walls. 2. Define Heart rate and explain how this changes during exercise 3. Provide 2 reasons why this change occurs. 4. Define blood pressure and explain what happens to this during exercise 5. What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure 6. What causes high blood pressure? HOMEWORK Create a poster highlighting all the IMMEDIATE effects of exercise on each of the bodies systems • Skeletal – doesn’t have any • Muscular • Respiratory • Circulatory *Use notes, GCSE websites and power points on the parent drive to help!