LiM08-Adaptive_Conten - Middleware Systems Research Group
advertisement

MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Adaptive Content-based
Routing In General
Overlay Topologies
Guoli Li, Vinod Muthusamy
Hans-Arno Jacobsen
Middleware Systems Research Group
University of Toronto
http://padres.msrg.toronto.edu
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
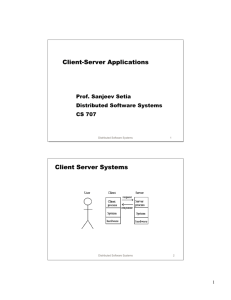
Distributed Publish/Subscribe
Advertisement
Publisher
Subscriber
Publication
Subscriber
Subscription
Applications
Business process execution e.g., BPEL
Business activity monitoring
Service discovery and integration
…
An acyclic overlay is sensitive to:
Congestion
Broker failures
Benefits of a general overlay:
Routing around congestion and failures
Handling imbalanced workloads
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Challenges With General Overlays
Subscriptions are
routed in loops
Brokers receive
duplicate
subscriptions
Subscription copies
exacerbate the
problem
Same problem for
publications
S
Adv 1
X
S
1
2
3
4
S
5
6
Adv 2
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Agenda
Content-based routing protocol for general
overlays
Atomic and composite subscriptions
Optimal publication routing
Evaluation
Dynamic publication routing
Adaptive composite subscription routing
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
TID-based Approach
S
Each advertisement
is assigned to a
unique tree identifier
(TID)
Each subscription
has a TID predicate
with a variable
X
1
2
3
4
5
6
Adv 1
Adv 2
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Subscription Routing
S: [class=stock][symbol=*] [TID=$Z]
S
X
SA1 SA2
At Broker 1:
Adv1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
Adv 1
[class=stock][symbol=IBM] [TID=Adv1]
Adv2:
[class=stock][symbol=HP] [TID=Adv2]
S matching Adv1:
[class=stock][symbol=*][TID=Adv1]
Adv 2
S matching Adv2:
[class=stock][symbol=*] [TID=Adv2]
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Publication Routing
Each publication is assigned the TID of its
matching advertisement
e.g., p [class, stock][symbol,HP][TID, adv_msg_id]
Publications are routed:
Fixed TID routing: a publication is routed to
subscribers along its advertisement tree.
Dynamic publication routing: a publication may be
routed to subscribers across advertisement trees.
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Fixed TID Routing
Adv 1
P
Property
No broker receives
duplicate publication
messages
Adv 2
P
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sub
X
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Dynamic Publication Routing
Adv 1
Publication’s TID is
changeable
Routing heuristic
Adv 2
P
2
3
4
5
6
Util = Routput / Rsending
Property
1
Changing a publication’s
TID while in transit will not
change the set of notified
subscribers.
Sub
X
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Advantages
Retains the publish/subscribe client interface
Speeds up subscription and publication
matching
Avoids duplicate subscriptions and
publications
Routes publications dynamically across
multiple alternatives
Enables routing around failures, congestion
and load imbalances
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
Composite Subscription
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
A composite subscription consists of atomic
subscriptions linked by logical operators (e.g., AND,
OR).
AND
e.g., CS= {[class=stock][symbol=YHOO][price>12]}
AND
{[class=stock][symbol=MSFT][price<20]}
Composite subscription routing
Topology-based routing
Adaptive routing
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
S1
S2
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Topology-based CS Routing
Adv 3
Adv 2
1
2
7
S2A2
3
5
4
CS’ S3A3
Broker 4 and 8
are the joint
point brokers
8
S1A1
6
9
Adv 1
CS
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
CS={{S1 AND S2} ANDS3}
CS’ ={S1 AND S2}
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Adaptive CS Routing
CS’s joint points are determined according
to potential publication traffic, bandwidth,
latency, etc.
Adv 2
Adv 2
2
1
Adv 1
2
3
1
CS={S1 AND S2}
Adv 1
CS={S1 AND S2}
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
3
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Cost Model
Routing cost of CS
Broker
RC(CS)) =
+
Matching
Engine
+
+
Routing
Table
input
queue
Subscription cardinality
|P(S)| : The number of matching
publications per unit of time.
|P(S)|
|P(CS)| =
=
|P(Sl)| + |P(Sr)|
if op = or
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
subscription
dest
symbol=IBM
B1
symbol=HP
B2
output output
queue queue
B1
B2
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Adaptive CS Routing
Adv 3
Adv 2
1
3
Adv 1
2
7
CS’
CS’ S3A3
6
9
4
8
S2A2
5
S1A1
CS
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
CS={{S1 AND S2} ANDS3}
CS’ ={S1 AND S2}
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Evaluation
Setup
Overlays of 32 brokers with different connection
degrees
Cluster (each node:1.86GHz, 4G) and PlanetLab
Workloads:
Yahoo!Finance stock quote traces
http://research.msrg.utoronto.ca/Padres/DataSets
Metrics
End to end notification delay
Network traffic
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Dense vs. Sparser Topologies
4%
20%
Note: The benefit is not proportional to the connection degree.
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Higher Publication Rate
stabilized
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Publication Burst
Burst
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
With Broker Failures
2nd failure
1st failure
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
CS Routing Traffic
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Conclusions
Enables routing around failures, congestion
and load imbalances
Allows publications routing across alternative
paths
Improves the notification delay by 20%
Enables flexible CS routing
Reduces 80% publication traffic
Improves the notification delay by 55%
Simplifies solutions for failure recovery and
load balancing
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Questions?
http://padres.msrg.utoronto.ca
P ADRES
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
More Publishers
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Effect of Subscriber Distance
Distance
Fixed(ms)
Dynamic(ms)
Improvement
6 Hops
47.202
47.568
-0.78%
10 Hops
64.477
52.895
17.96%
12 Hops
74.416
60.598
18.57%
Max Diff
57.65%
27.39%
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
On PlanetLab
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
CS Delay
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Faster Matching with TIDs
Subscriptions are augmented with TIDs only
once at the first broker.
Other brokers can route the subscription
based on the TID alone.
Similar argument applies to publication
routing.
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Advertisement Routing
Each advertisement forms a spanning
advertisement tree
Duplicated advertisements are discarded by
brokers
Each advertisement is assigned a unique tree
identifier (TID)
e.g., a [class,eq,stock]……[TID,eq,adv_msg_id]
Subscription Routing Table (SRT)
A set of [advertisement, last hop]
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium
MIDDLEWARE SYSTEMS
RESEARCH GROUP
Subscription Routing
Each subscription has a TID predicate with a
variable.
e.g., s [class,eq,stock]……[TID,eq,$X]
The variable is bound to the TID of a
matching advertisement
Publication Routing Table (PRT)
A set of [subscription, {TID, last hop of
subscription }]
Middleware 2008 @ Leuven, Belgium