7.3 PPT
advertisement

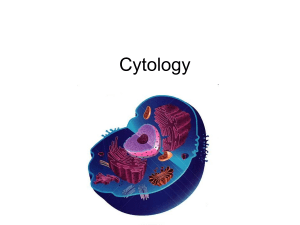
HONORS: Organelle PPT • AT least ONE slide for each organelle – A-j plus plasma membrane • Must have – Cell Type it is found in (ALL, Eukaryote, Plant, and/or Animal) – Location in cell – Function – Picture w/ URL link 7.3 Organelles 7.2 The Plasma Membrane • Cell Type: ALL (pro/eu) • Location: outer boundary or just under cell wall of plant cells. – Flexible boundary between cells & environment – Selectively permeable: ___ – Phospholipid Bilayer – Cholesterol, Protein www.biology.arizona.edu/.../ graphics/bilayer.giff fig.cox.miami.edu/.../ 150/memb/fluidmosaic.jpg nai.arc.nasa.gov/team/ images/2006/ciw/1829/1.jpg Cell Wall • Cell Type:Found in plant cells and some prokaryotes • Location: outside the Plasma membrane • Function: protection and support • In plants: Made of cellulose Nucleus • Cell type: Eukaryotic (plant and animal) • Funtions: Manages and controls all cell functions • Holds genetic information • Nucleolus is found inside – Makes ribosomes iweb.tntech.edu/mcaprio/normalonionskin.jpg www.palaeos.com/.../Lists/Images/nucleolus.jpg Ribosomes • Cell Type: ALL (pro/eu) • Location: in nucleus, on Rough ER, floating in cytoplasm • Produces proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum • Cell Type: Eukaryotic • Location: Rough – just outside the nucleus, Smooth – out in cytoplasm • Function – site of cellular chem. rxns – Rough: helps ribosome build proteins – Smooth: produce and stores lipids HONORS LINK Golgi Apparatus HONORS • Cell Type: Eukaryotic • Location: in Cytoplasm near plasma membrane • Function: sorts and packages proteins/lipids, works closely with ER Vacuoles • Cell Type: Eukaryotes (in Plants they are LARGE! Rare in animal cells, small if so) • Location: • Function: Storage of food, enzymes, waste, etc. Lysosomes • Cell type: Eukaryotes • Location: throughout cell • Function: digests unwanted materials and waste. Can fuse with vacuoles. • Tadpole Tails! HONORS Chloroplast • Cell Type: Plant Cells ONLY • Location: through out cell • Function: carry out photosynthesis – light E is turned into chemical E used by cells. Mitochondria • Cell Type: Eukaryotes • Location: Through out cell, some cells have A LOT (liver cells) • Function: converts food (E from carbs/sugars) into E usable by cell. makes cell batteries • Manufacturing – Nucleus – Ribosomes – ER (both) – Golgi Apparatus • Energy Processing – Chloroplast – Mitochondria • Store/Breakdown • Support – Lysosomes – Vacuolues – Cell wall Honors: Smooth ER • Store Ca+ needed for muscle contraction. • Different types of cells make different lipids • Cells may need little or lots of Smooth ER – Cells of ovaries and testes synthesize steroid sex hormones – Liver cells use SER to help process drugs, etc BACK • More drugs = more enzymes to degrade/ more SER, increasing tolerance causing more drug to get equal “high” • Cannot differentiate between drugs, so tolerance to other drugs also increases BACK Honors: Golgi Apparatus • Receives and modifies substances from the ER. BACK HONORS: Lysosomes 1.) RER packs enzymes into vesicles 2.) Golgi refines enzymes and releases mature lysosomes 3.) Engulf or merge with vacuole to diget substance 4.) IF it can recycle, it will Used extensively in human embryos.