Federalism A system where the power is vested with a strong

Federalism
1.
A system where the power is vested with a strong, sovereign national government.
Britain and France are excellent examples. Unitary
2.
This clause in the final paragraph of Article I of the Constitution, authorizes Congress to pass all laws needed to carry out the enumerated powers: "necessary and proper" clause
3.
Lobbying activities by state and local governments who establish offices in DC and compete for federal funds. Intergovernmental Lobby
4.
The way to amend the constitution, which has been used 26 times: 2/3 Congress, ¾ states
5.
Sovereign in their own spheres: dual federalism
Democracies
1.
The founders feared that people would allow demagogues to make decisions for them if this system was implemented: direct democracy
2.
Also known as a republican form of government: representative democracy
3.
Central Government decides what is in the best interest of its people: Democratic
centralism
4.
Thought of as “mob rule” by the founders: direct democracy
Politicians
1.
Secretary of State: John Kerry
2.
Speaker of the House: John Boehner
3.
Washington’s Democratic Governor: Jay Inslee
4.
Senate Majority leader: Harry Reid
5.
First female speaker of the house and current minority leader: Pelosi
Chaaaaa-ching!
1.
Requirements to receive funds: conditions of aid
2.
These are grants given by the federal government for general purposes. The states love them. Block Grants
3.
Interest groups favorite type of grant: Categorical
4.
The Marshall court argued that this clause gave the federal government the right to have a bank: necessary and proper
The Court of Last Resort!
1.
Established judicial review: Marbury v. Madison
2.
The power to tax is the power to destroy: McCullough v Maryland
3.
Guns in school zones is not interstate commerce: US v. Lopez
4.
Liberal justices sided with the conservative administration in deciding against California’s medical marijuana laws: Gonzales v. Raich
5.
Established the supremacy of the federal government over the states: McCullough
6.
Cities can now take land if it is for economic purposes: Kelo
Convention
1.
The way the founders appeased both large and small states: Great Compromise
2.
Originally elected by state legislatures: senate
3.
Established a balanced delegation of northern and southern representatives: 3/5ths Comp.
4.
Argued that liberty would be safest in a large republic: Madison
5.
The plan that became the agenda at the convention: Virginia
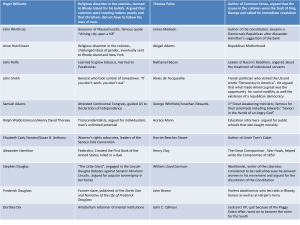
Founding Fathers
1.
Argued that the real revolution was the change of hearts and minds of the colonists: Adams
2.
Presided over the constitutional convention: Washington
3.
Lead the antifederalists: Jefferson
4.
Argued for a president for life: Hamilton
5.
Called the Father of the Constitution: Madison
A system of restraints
1.
A check granted to Congress to limit the power of the president’s veto: override
2.
The body that approves the president’s appointment of Supreme Court justices: Senate
3.
The power given to the Congress and the states to weaken the Supreme Court: amendment
4.
The key way the founders buffered the Supreme Court from political interference: serve for life
5.
The Senate’s ability to legislate is limited by the fact that these types of bills must not originate in the Senate: revenue
6.
An executive’s ability to block a particular provision in a bill passed by the legislature: line item veto
The Constitution
1.
This document established a "league of friendship" among the American states, but proved too weak to survive. Articles of Confederation
2.
This is proposed by 2/3 of both Houses of Congress and ratified by 3/4 of the states:
Constitutional Amendment
3.
The power of one of the branches of government to block the acts of the other two:
checks and balances
4.
Within this essay James Madison argues that factions can be best controlled under a large federal government system: Federalist 10
5.
Forbidden in the Constitution, this law would declare a person guilty of a crime
WITHOUT a trial: Bill of Attainder
Elites
1.
Argued that the bureaucrats were behind the scenes with the real power: Weber
2.
View that the competition between a variety of elites will not allow in one group to have too much power: pluralist
3.
Argued that those who control the money have the power: Marx
4.
C. Write Mills argued that these three small groups have the power: military officials,
Corporate officials, select government officials
5.
Madison seems to agree with the pluralist view when he argued that competing factions would have to form these to get anything done: coalitions