Piaget's Theory - Stage1PsychologyMsGrear
advertisement

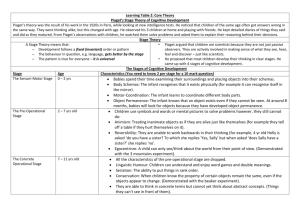
COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Cognitive psychology involves the study of how we acquire, organise, remember and use information. Cognitive development focuses on how and when we develop and use these mental abilities. Jean Piaget (1896-1980) studied the development of children's understanding. He did this through observing them and talking and listening to them while they worked on exercises he set. PIAGET’S THEORY Piaget’s theory of cognitive development proposes that we move through four distinct and sequential stages from birth to adulthood, which develop our cognitive abilities. Each stage is linked to an approximate chronological age range, though these are subject to individual differences. SENSORIMOTOR STAGE Birth – two years. Differentiates self from objects Recognises self as agent of action and begins to act intentionally. For example: pulls a string to set mobile in motion or shakes a rattle to make a noise . Achieves object permanence: realises that things continue to exist even when no longer present to the sense. OBJECT PERMANENCE EXPERIMENT http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKZ9IPRKkkU&feature=related This clip shows a 13 month old child who is beginning to understand the concept of object permanence. PRE-OPERATIONAL STAGE 2 – 7 years Learns to use language and to represent objects by images and words. Thinking is still egocentric: has difficulty taking the viewpoint of others. Classifies objects by a single feature. For example: groups together all the red blocks regardless of shape or all the square blocks regardless of colour. EGOCENTRISM EXPERIMENT http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OinqFgsIbh0 CONCRETE OPERATIONAL STAGE 7 – 12 years Can think logically about objects and events. Achieves conservation of number (age 6), mass (age 7), and weight (age 9) Conservation refers to the idea that an object does not change its weight, mass, volume or area when it changes shape or appearance. Classifies objects according to several features and can order them in series along a single dimension such as size. CONSERVATION EXPERIMENT http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=gnArvcWaH6I&feature=endscreen http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=gA04ew6Oi9M FORMAL OPERATIONAL 12 years and over Focus is on complex, abstract, logical thinking. This evidenced by an individual’s ability to develop plans to solve problems, identify a range of possible solutions to problems, as well as developing hypotheses and systematically testing solutions. Becomes concerned with the hypothetical, the future, and ideological problems FORMAL OPERATIONAL EXPERIMENT http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw36PpYPPZM FORMAL OPERATIONAL So, do all people achieve the formal operational stage? Originally Piaget believed that they did, however, his later research suggested that this may not be the case. Formal operational thinking may depend on education and everyday experiences. Mathematical training has been shown to be effective in enhancing formal operational thinking. STUDENT ACTIVITY: How good is your logical thinking and reasoning ability? Learning activity 10.12 on page 354 of textbook. WAS PIAGET RIGHT?! Strengths of Theory: Great impact on psychology – his theory stimulated considerable interest + led to thousands of studies by other psychologists. Many aspects of Piaget’s theory have been confirmed, whilst others have been challenged. Limitations of Theory: For example: it is now suggested that infants know a lot more, and know it sooner, than Piaget suggested. Some psychologists also disagree with the idea of stage theories – they argue that development results from life experiences rather than biological timing.