File
advertisement

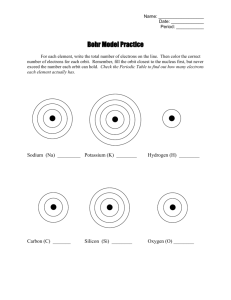
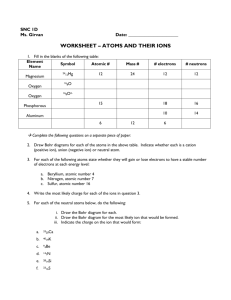
Bohr’s Model of Electron Arrangement Atomic Structure Atomic number = the number of protons Atoms are neutral, so the number of protons = the number of electrons Atomic mass ≈ the number of protons + the number of neutrons Protons and neutrons have the same mass, which is 1800 times bigger than the mass of electrons. Examples: Element Symbol Atomic Mass Atomic Number # of Protons # of Neutrons Oxygen O 16 8 8 8 Lithium Li 7 3 3 4 Bohr Model • 1913 – Bohr explains movement of electrons around the • • • • • nucleus of the atom. Bohr’s model: Electrons orbit around the nucleus Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus Each orbit has a definite energy level Each orbit has a definite number of electrons • 1st orbit • 2nd orbit • 3rd orbit 2 8 8 Examples: Name Symbol Electrons Bohr Diagram Nitrogen 7 Phosphorus 15 •Valence Shell – the outer shell of electrons •Valence electrons – the electrons in the outer shell of an atom •Valence – the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom Do Bohr Diagrams of first 20 elements/atoms Bohr Models and the Periodic Table Most elements in the same family have the same number of valence electrons (an exception is Helium) Elements in the same period have valence electrons in the same shell. The period number indicated the number of shells that have electrons. The number of electrons in a shell corresponds to the number of elements in that period. Valence shells and Stability Atoms become stable when they have a full outer shell of electrons Noble gases are un-reactive because they have a full outer shell of electrons. Atoms in other families will gain or lose electrons to have a full outer shell. Having an uneven number of protons and electrons gives an atom a charge. Charged atoms are called ions. o Atoms protons = electrons o Ions protons ≠ electrons Metals lose electrons to become positive ions. Non-metals gain electrons to become negative ions. Atom 3 electrons and 3 protons Ion 2 electrons and 3 protons The charge of an ion is equal to the sum of the charges of the protons and electrons. Ions are written as the chemical symbol with a superscript of their charge Bohr Models of Ions Ion Atomic Number # of Protons # of Electrons Sulphur Ion 16 16 18 12 12 10 Ion Charge: 2- Magnesium Ion Ion Charge 2+ Bohr Model Do Bohr Diagrams of first 20 ions