CH3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
advertisement

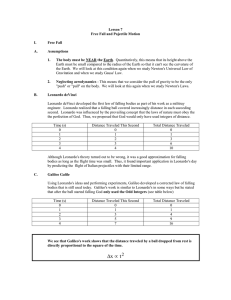
Chapter-3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Overview: Explore how objects move under the influence of gravity close to the surface of the earth. Outline: Acceleration due to gravity Falling object Projectile motion Falling Objects Why objects fall to the ground when released? When you drop objects of different sizes and weights, do they reach the ground at the same time? (Click the link below) http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/phy03.sci.phys.mfw.galmoon/ Measuring the acceleration due to gravity for Earth: 9.8 m/s2 Falling Object: Velocity and Distance t (s) Spread Sheet (Excel) Calculations v=v0 + at d=v0t+1/2 at2 y = 9.8x 250 V (m/s) 200 150 100 50 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (s) 2500 d (m) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 v (m/s) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 0 9.8 19.6 29.4 39.2 49 58.8 68.6 78.4 88.2 98 107.8 117.6 127.4 137.2 147 156.8 166.6 176.4 186.2 196 t (s) Reaction Time Experiment d (m) 0 4.9 19.6 44.1 78.4 122.5 176.4 240.1 313.6 396.9 490 592.9 705.6 828.1 960.4 1102.5 1254.4 1416.1 1587.6 1768.9 1960 Throwing up a ball: Velocity and Distance Q: A ball is thrown straight upward and then returns to the Earth. Does the acceleration change during this motion? Throwing up a ball: Velocity VS. Time graph Projectile Motion: A Cartoon Coyote Falling off a Cliff We need to consider the horizontal and vertical motions separately in projectile motions. Time is the same for both motions. Horizontal and Vertical motions Q: What determines the time of flight? A: Vertical motion Practice Sample Exercise in example box 3.4 Angle for maximum Range http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Projectile_Motion Go to the above website and determine the angle for maximum range by firing at different angles. ______________