Test Cross, Complete,Incomplete Dominance
advertisement

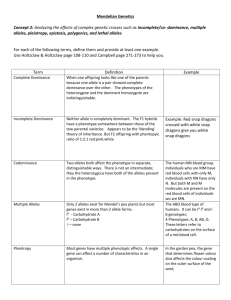
Extending Mendel's Laws A question that breeders often have is "what is the genotype of an organism that displays the dominant phenotype?" For example, in a breed of dog in which the gene for black coat is dominant (B) over the gene for red coat (b) colour, a dog with black coat colour could have either of two possible genotypes: BB or Bb To determine whether the black coat colour is homozygous (BB) or heterozygous (Bb), it is necessary to perform a test cross. TEST CROSS A specific cross to determine the unknown traits in an individual. In other words to determine whether the organism is Homozygous or Heterozygous Lets revisit the example A dog breeder thinks that his dark colour dog is carrying a gene for no red colour coat. Prove it! Possible Genotypes BB or Bb Let B represent black coat colour Let b represent red coat colour Cross his dog with a homozygous recessive red colour coat dog B_ X bb B_ X bb The phenotype of the offspring resulting from the test cross will reveal the genotype of the mystery dog. The homozygous recessive parent can only contribute the recessive allele (b) to the offspring, therefore the phenotypes will indicate the alleles from the other parent (the mystery dog) B B B b Bb Bb b Bb Bb Bb b Bb b Bb b bb bb If the mystery dog is Homozygous (BB) then it can only contribute (B) and all the offspring would have a black coat colour If the mystery dog is Heterozygous (bb) then it can either contribute (B) or (b) and we would expect both colour coats Dominance Complete Dominance a kind of dominance wherein the dominant allele completely masks the effect of the recessive allele in heterozygous conditions this type of dominance resemble Mendel's pea plants eg. What are the chances of two heterozygous tall plants producing a short plant. T t T TT Tt t Tt tt 25% 25% Dominance and recessiveness explain some simple forms of inheritance. For most traits, however inheritance patterns are more complex. Incomplete Dominance one trait is not dominant over another, each allele has some degree of influence eg. Snapdragons, pink flowers occur when red and white flowers are crossed. Let R represent Red Colour Let W represent White In what ratio will red, white and pink flowers occur if 2 pink flowers are crossed? RW X RW Similar to incomplete dominance, codominance is an inheritance pattern in which neither allele is dominant to the other. Both alleles are completely expressed at the same time. Codominance a kind of dominance in which a heterozygote shows the phenotypic effect of both alleles fully and equally. eg. in roan cattle the expression of one allele is not masked by the expression of the other. Homework pg. 134 #2,3 pg. 138 #16 pg. 141 #1 So far we have discussed traits that involve only two alleles per gene. But for most genes, more than 2 alleles exist in a population. The existence of multiple alleles means that there maybe many possible genotypes for a particular gene, and many possible phenotypes. Multiple Alleles three or more forms of a gene eg. Blood type in humans involves three alleles IA - type A allele IB - type B allele i - type O allele A person can have one of four blood types: A, B, AB, or O. The letters refer to the two types of carbohydrates, A and B, that are found on the surface of the red blood cells. There are six possible ways to pair the alleles, six possible genotypes. Blood transfusion: Must be sure the donor's antigens (causing an immune response) will not cause clumping with recipient's antibodies (chemical for defense) If the blood types are incomnpatible, the recipient will have a potentially fatal immune response Blood Type Marker on Antibodie s rbc's Present Can give blood to Can receive blood from A A A B A, AB A, O B B B A B, AB B, O AB A, B, AB, O AB AB AB None Eye Colour Let B - brown eyes Let b - blue eyes Let G - green/hazel eyes Let g - light coloured eyes Lets cross Heterozygous Parents BbGg X BbGg Homework pg. 145 #1, 5, 6, 7, 11