Lec11-Multinatl&Chan.. - Arizona State University
advertisement

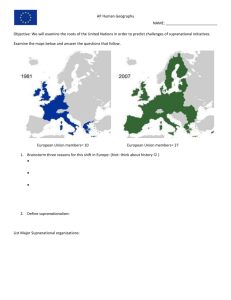
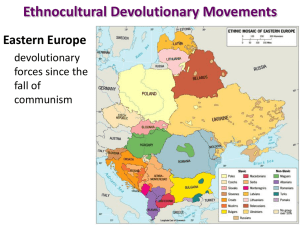
MULTINATIONALISM and the CHANGING POLITICAL LANDSCAPE Supranationalism The efforts of three or more states to forge associations for common advantage and in pursuit of common goals International sanctions From League of Nations to United Nations The United Nations Representation of countries has been more universal than that of the League The United Nations Peacekeeping operations – Internal conflicts – Not always successful – > 40,000 peacekeeping troops serve – The UN peacekeeping function provides major benefits to the international community Unrepresented peoples – UNPO By 2002 had 51 members and 13 applicants The Law of The Sea UN Conference on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), 1982 The Truman Proclamation Widening maritime claims The UNCLOS process – Main provisions of the treaty: The territorial sea—12 nautical miles The exclusive economic zone (EEZ)—200 to 350 nautical miles Median lines – States on opposite coasts divide the waters separating them – The “High Seas”… Regional Multinational Unions The first multinational union – Benelux—Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg – The Marshall Plan First-step of cooperation among European states Toward a European Union The Organization of the European Economic Community (OEEC) France proposed a union with six other states called the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) The ECSC through negotiations and agreement led to the formation of the Common Market (EEC) Expansion created the European Community (EC) In 1992, further expansion led to creation of the European Union (EU) Regional Multinational Unions Toward a European Union – The future of European Supranationalism Difficult The United Kingdom did not allow its citizens to vote on membership in the EU – Expansion May cause strains Progress toward supranational goals tends to be cyclic and flourishes when economic times are good Regional Multinational Unions Supranationalism elsewhere – – – – – NAFTA—the North American Free Trade Agreement CARICOM South America’s MERCOSUR ECOWAS Today, new groups are forming in almost all parts of the world FTAA—Free Trade Area of the Americas Other forms of Supranationalism – NATO – Cultural unions – Political unions THE CHANGING GLOBAL POLITICAL LANDSCAPE A New World Order? Balance of mutual opposition and nuclear terror between two super powers no longer determines destinies of states (supposedly) Shaped by forces that connect nations and states, like the EU – Risks of nuclear war goes away – Negotiation instead of confrontation What happened? Forces of Devolution The counterforce to supranationalism – Today, many states are afflicted by internal centrifugal forces – Time has failed to submerge regionalism in the United Kingdom Ethnonational forces – – – – Fundamental in promoting devolution Devolutionary forces exist in Europe Devolution elsewhere Weakening many states today Forces of Devolution Economic forces Spatial Influences – Along margins of states – Islands – Gateway states The Devolution of the USSR The Devolution of the Soviet Union The Changing Russian periphery – ~ 25 million Russians in former Soviet Republics’ Rimland Devolution of Russia – Five additional “republics” – Internal “republics” – Rise of anti-Russian rebellion in Chechnya – Vastness = less control The State in the New World Order The complexity in today’s world Forces of change – Globalization – Notions of democracy – The growing influence of religion Some see the world in bipolar religious terms— including terrorists The State in the New World Order A New World Order – What factors affect its forming? – Must include a consensus Geopolitics in the Twenty-First Century? Discussion Question The United Nations has managed to control and channel many conflicts that might otherwise have had serious consequences. One of these involved the world’s oceans and seas: a United Nations Law of the Sea now exists. One feature of UNCLOS is the so-called EEZ. – How has the EEZ functioned to expand as well as inhibit states’ maritime activities? – What has been the impact on marine resources?