(1) Supreme Court
advertisement

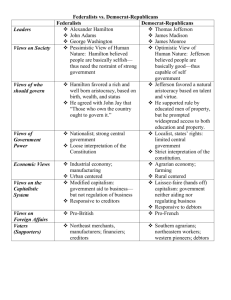
A NEW NATION (1789-1800) CHAPTER 6 SECTIONS 2-4 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION The meeting in Philadelphia resulted in a new Constitution. Moving forward: The task ahead of Washington and Congress was to build a government around the ideas of the Constitution KEY CONCERNS Establish federal laws, courts, & law enforcement officers Solve financial problems, establish a federal treasury, & a method for collecting taxes WASHINGTON George Washington was elected the first U.S. President & served two terms Was their a term limit established by the U.S. Constitution at this time? John Adams became Vice President PRESIDENT Amendment 22 (1951) established the twoterm limit of a president What U.S. President was elected to the most terms prior to this Amendment? Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) INAUGURATION Inauguration ceremonies were held in NYC on April 30th 1789 After this Presidential Inaugurations were held in March Amendment 20 (1933), also known as the “Lame Duck” Amendment changed Presidential Inaugurations to January 20th QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER What is a Lame Duck? Why may the framers of the Constitution have specified a longer lame duck period? Hint: think technology and transportation Transportation and Technology were less advanced causing information to travel slower Political office holder reaching the end of their term either because of a lack of desire to run again, a loss in re-election, term limits, or the termination of their office. They often have less political power at this time. BUREAUCRACY • In 1789, Congress recognized a need for a bureaucracy Congress create the following Departments: The Department of State The Department of the Treasury The Department of War The office of the Attorney General SELECTING LEADERS Washington wanted men who were “disposed to measure matters on a continental scale” rather than their home states to head the departments. What does this quote mean? -Disposition-inclination or a tendency -Washington wanted men who acted in interest of the country rather than their own individual state. THE CABINET Washington chose the following men to lead the Departments: Secretary of State-Thomas Jefferson Secretary of the Treasury-Alexander Hamilton Secretary of war –General Henry Knox Attorney General –Edmund Randolph These department heads became known as the cabinet Cabinet- a group of advisers to the president PRESIDENTIAL CABINET (INCUMBENTS) State Treasury Defense John Kerry Jack Lew Ashton Carter IMPORTANT MEASURES TAKEN BY CONGRESS Other Cabinet Posts: Attorney General – heads the Department of Justice today & the first was Edmund Randolph Edmund Randolph Eric Holder FEDERAL JUDICIARY Congress passed the Judiciary Act of 1789 13 district courts 3 courts of appeal 1 Supreme Court Washington selected five associate judges and one chief justice Appointed John Jay to Chief Justice Stressed the power of Judicial Review (constitutionality of legislation) JUDICIAL STRUCTURE (1) Supreme Court (1) (3) Courts of Appeal (12) (13) District Courts (94) TODAY President appoints Supreme Court justices if one retires or is removed from office However, the Senate must approve the president’s choice How many Supreme Court justices are their today? http://www.supremecourt.gov/about/memb ers.aspx BILL OF RIGHTS • • • James Madison- Pushed for the passage of a Bill of Rights -Drafted the Bill of Rights Congress agreed on 12 amendments -States ratified ten of twelve One through eight protect individuals from certain government actions Nine and ten limit the powers of the federal government Which two rights are the only ones unique to the American Bill of Rights, and why do you think that is? 1789 Problems solved: Federal courts (the Supreme Court, 3 courts of appeal, 13 district courts) Bill of Rights (ten amendments) Cabinet (to advise president) Existing problems: Revenue -a source of income THE PRICE OF FREEDOM The American revolution cost the newly independent U.S. government about 50 million dollars $40 million to American citizens (Bonds) Bonds-a piece of paper/document that promises to repay borrowed money by a certain time with interest $11.7 million to France, Spain, and the Netherlands 21.5 million state debt the federal government agreed to pay (gain trust) Note: There was an annual interest on these debts TARIFF OF 1789 Hamilton suggested taxing imports to raise money & protect American businesses from unfair foreign competition Congress passed the Tariff of 1789 Required • importers to pay a rate/percentage of the total value of goods brought into the United States Shippers paid tonnage –tax on amount their ships carried Also, levied an excise tax on distilled liquors, which led to the Whiskey Rebellion in Pennsylvania SOUTHERN RESPONSE Southern planters were angry because: Tariff= raise prices of European and other goods that Southerners either wanted or needed Tonnage tax= more expensive to ship their rice, tobacco, and other common cash crops FINANCES,1792 HAMILTON’S ECONOMIC PLAN Pay off national debt ($50 million): Incurred by the Revolutionary War & debts owed to private citizens Pay off state debts ($24 million): Compromise between Hamilton & Jefferson Nation’s capital was moved to the banks of the Potomac River Washington, District of Columbia HAMILTON’S ECONOMIC PLAN Create a National Bank Hamilton argued to congress a national bank was necessary to: Manage debts Establish a national currency - Bank notes-paper money Promote trade Encourage investment Stimulate economic growth OPPOSITION Southerners opposed plan Felt Northern merchants would own most of bank’s stock James Madison argued congress could not create a national bank It was not among the enumerated powers Powers specifically mentioned in the Constitution THE NATIONAL BANK Hamilton argued that the elastic clause (AKA necessary and proper clause, art.1 sect.8 ) gave Congress this power Washington knew his choice to veto or sign this bank bill set a precedent Created implied powers THE RISE OF POLITICAL PARTIES Group of people that share the same ideology (platform) Two-party system-two main political parties of today (Democrats and Republicans) Can we name some of today’s political parties? Democratic, Republican, Boston Tea Party, Libertarian, Prohibition Party, many others CHOOSING SIDES Washington’s first term in office Hamilton’s financial plan Congress divided based on view of federal governments role Nation’s first political parties Hamilton’s supporters-Federalists Madison and Jefferson –Democratic-Republicans HAMILTON AND THE FEDERALISTS Favored strong national government “democracy was dangerous to liberty” Distrust of “the people” Wanted government in hands of the elite (“rich, well-born, and able”) Loose construction of Constitution FEDERALISTS (ECONOMICS) Manufacturing and trade = national wealth and power Federalists supporters- often artisans, merchants, manufacturers, and bankers Some urban workers and eastern farmers (trade benefit) JEFFERSON AND THE REPUBLICANS Jefferson led the Democratic-republicans Called Republicans (not the same as today’s republican party) Thought Hamilton’s policies favored the North Became party that protected right of states vs. federal government REPUBLICANS (ECONOMICS) Believed strength of U.S. was independent farmers Most people own land they would fight to keep preserve republic (agrarianism-favored rural farming over urban industry) Believed North’s industries= sharply divide rich and poor And wealthy would corrupt government and threaten ordinary people’s liberties Thought Hamilton’s policies favored the North A GEOGRAPHIC DIVIDE Rural South & West supported the Republicans More Urban Northeast typically supported the Federalists Conflict between France and Britain would widen the divide DEVELOPING THE NATION’S FOREIGN POLICY FRENCH REVOLUTION – FRANCE OR GREAT BRITAIN? REVOLUTION 1789, the French Revolution began At first most Americans supported the cause 1793, more radical group seized power Took property from wealthy, executed 1000’s(including king and queen ) Federalist-horrified by chaos and violence Republicans-many still supported revolutionaries because it seemed to be for freedom and liberty FRANCE VS. ENGLAND In 1789, the French people revolted against their King, England attacked France, and France asked for assistance from the United States. What is Britain concerned about? At this time, Britain and France were both monarchs and the British Crown hoped to prevent any future rebellions within their own borders. North (Hamilton) favored England because both were industrial and had strong economic ties South (Jefferson and Madison) favored France because both were agricultural, and also to repay the help they lent during the American Revolution (Yorktown) NEUTRALITY Washington issued the Proclamation of Neutrality of 1793. -Impartial to Britain and France Why would someone (in this case Washington) choose to be neutral? Both Britain and France traded with the United States (economic interests) JAY’S TREATY (BACKGROUND) Congress almost declared war because of British aggression at sea and at home (“inciting Native Americans”) Britain was at war with France but knew U.S. relied on Britain for trade In an effort to avoid war Washington sent John Jay to negotiate with Britain JAY’S TREATY (CONTINUED) Cons: Jay had to agree that Britain had the right to seize American Ships bound for France Britain did not have to compensate U.S. Merchants whose goods were seized Pros: Britain gave up forts in American territory Granted U.S. most-favored nation status Meant American merchants could trade without being subjected to British discrimination Note: Many Americans were angered by the conditions PINCKNEY’S TREATY Prior to Jay’s treaty Spain allied with France Spain feared U.S. would join Britain in order to obtain Spain’s North American territories (Florida) 1795 Spain signed Treaty of San Lorenzo (Pinckney’s Treaty) Americans happy-gained access to the Mississippi River Washington refused to serve a third term, retired at Mount Vernon, and warned against foreign alliances & political parties in the future. ELECTION OF 1796 The 1st contested election (Feds vs. Reps) The Federalists nominate John Adams despite Alexander Hamilton trying to gain the nomination for Thomas Pinckney The Dem-Reps nominate Thomas Jefferson Adams wins! But his Vice President is Thomas Jefferson QUASI-WAR France began seizing American Ships as a result of the U.S. unwillingness to support them in their war against Britain. Charles Pinckney, John Marshall, & Elbridge Gerry were sent by Adams to secure a treaty with France VS. “XYZ” AFFAIR 3 French agents (X, Y, Z) representing French Foreign Minister Charles Talleyrand requested a bribe of $250,000 and a 10 million dollar loan to initiate talks to end the war. Americans called for war with the rallying cry of “Millions for defense but not 1 cent for tribute”. In retaliation, U.S. Congress banned trade with France & the U.S. Navy began capturing French ships. QUASI-WAR WITH FRANCE U.S. & France began QuasiWar (undeclared) as a result of France undermining U.S. neutrality. This war lasted from 17981800 A pro-war faction within the Federalist Party led by Alexander Hamilton that called for a full-scale war was resisted by Adams who instead favored diplomacy. CONVENTION OF 1800 Napoleon seized power in France and quickly reached an agreement with Adams. The Convention of 1800 released the U.S. from its 1778 defensive alliance with France & in return the U.S. gave up its claims to French seizures of ships & cargo ALIEN & SEDITION ACTS 4 laws passed in 1798 by a Federalist (dominated) Congress for the purpose of reducing the power of the DemocraticRepublicans. 1st – Naturalization Act – extended the # of years required to become a citizen. 2nd – Alien Act – Gave the President the power to kick out of the country any alien regarded as dangerous to public peace & safety. 3rd – Alien Enemies Act - made it a crime to attack the government with "false, scandalous, or malicious" statements or writings. 4th – Sedition Act – made it illegal print anything “false, scandalous, or malicious” about the federal government. Many immigrants were French and Irish (both anti-British and voted for the Republicans) OBJECTIONS TO THE ALIEN & SEDITION ACTS Democratic-Republicans responded with the Kentucky and Virginia resolutions Both secretly written by Jefferson and Madison Both said that since the states formed the Constitution they had the right to declare federal laws unconstitutional (introduced the idea of nullification & states right theory of government) The states threatened secession if the Acts were not revoked. KEY TERMS The Virginia Resolutions The Kentucky Resolution interposition ; if the federal government did something unconstitutional the state could intervene for the people and stop the illegal action nullification; if the federal government passes an unconstitutional law the states could declare the law invalid Neither resolution is successful in 1800, however, states used both of these to “defend regional interests” in the future (i.e. Civil War) ELECTION OF 1800 In 1800, Federalists controlled the army, presidency, and the Congress For Adams, the Alien and Sedition Acts angered too many Americans With a tie vote in the Electoral College (Jefferson & Burr), the House of Representatives with help from Alexander Hamilton(Federalist), chose Jefferson over Burr on the thirty-sixth ballot 12th amendment (1804) – directed electors to vote separately for pres and vice pres rather than the same ballot. This solved the problems that resulted from the elections of 1796 & 1800. What made the election of 1800 so significant in American political history & referred to as a revolution? The second contested election in U.S. history went through a peaceful transition of power: the losing party accepted the choice of the people despite often strongly opposing ideologies (views) between the Democratic-Republicans and Federalists. WEBSITE http://www.glencoe.com/video_library/index_ with_mods.php?PROGRAM=9780078745218& VIDEO=2839&CHAPTER=4 FIRST POLITICAL PARTIES