Lec 6 Nafta P 1 and 2
advertisement

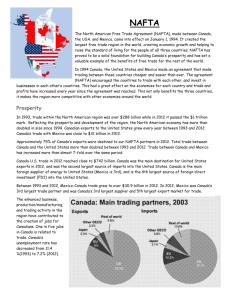
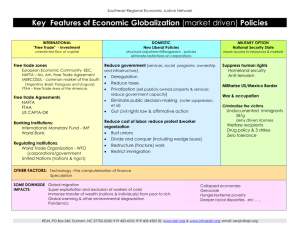
Topic: 4: NAFTA & US hegemony: Canada and Mexico (Kit: Quintero-Ramírez; Mize, R.L.; Pantaleo, K; Wise, C. ; Wise. T.A.; Abboushi, S.) WST • Financial Meltdown (2008) • Trade liberalization (Neoliberalism) • Continental Commodification The Wonderful World of NAFTA (Part 1, 2) - 2007 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZnVL0d9fwkY 7min p1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XxQQael1ueE 7 min p2 NEED TO KNOW | After NAFTA | PBS 13.57 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mSXmB_my0ls 0c1 2011 Thesis: Under U.S. hegemony, NAFTA has integrated Canada and Mexico into a continental free-trade system. As a result, Canada’ s raw materials are exploited for reconstructing the declining U.S. global hegemony. As a result of US-led 2008 financial meltdown, workers face a sharply depressed job market in a deindustrialized Canada barely buffeted by the welfare system. In contrast, Mexican cheap, but skilled and surplus labour is exploited for restructuring the industrial sector in the U.S. The failure of the US financial system has worsened the unemployment of the Mexican workers intensifying their poverty as they have no welfare system. Both, Mexican and Canadian economies, have become dependent on the U.S. through the commodity chain of exploitation. Peripheries: NAFTA Periphery: Mexico Semi-periphery: Canada Arguments you need to integrate in the essay: 1. Wise T. A.(2011): Hegemony and dumping NAFTA + U.S. Farm Subsidies Devastates Mexican Agriculture 2010 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N4KRd7Qjyys 8 min 1. Abboushi, S (2010): • US trading power, US disregard for agreements, land-ownership structure vs. strategy of acquisition; and Managed (not Free) trade 3. Quintero Ramirez (2002) • NAFTA deindustrialized & depressed labour conditions in Canada and exploits workers in Mexico 4. Susan George: WTO is ineffective http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NQ952ba75Yk you tube uploaded May 5, 2011) 5. Wise, R.D & Cypher, J.M (2007). Cheap-labor embodied Mexican exports but not achieving new high-value added production or specialization. 1 Source: The Strategic Role of Mexican Labor under NAFTA: Critical Perspectives on Current Economic Integration, THE ANNALS OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY, March 2007 6. Carol Wise (2009): Regional market integration of US, Canada and Mexico has been superseded by China’s use of NAFTA to facilitate its entry into US through Mexico 7. Gandasegui, M.A (2006) Kit #17: Using its hegemony, US wants to gain advantages over 4 areas in making trade agreements with each country in LAm : Government contracts Pharmaceutical markets Agricultural markets Intellectual property (GRAIN 2004). 8. Katherine Pantaleo (2010). The murders as gendered sexual serial killings primarily perpetuated and caused by:NAFTA, Gender issues & Corruption of the criminal justice system. NAFTA's Ultimate Effect on Mexico P1 of 2 2010 april 9.29 min murder city Charles bowden http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WSrOAfMylAs NAFTA's Ultimate Effect on Mexico P2 of 2 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nokmc36jnOI 7 min 9. Cormier & Targ (2001) • Globalization led to workers’ poverty & global income inequality (Cormier , D & Targ, H, (2001) Globalization And The North American Worker. Labor Studies Journal, Spring 2001 v26 i1 p42 ) How does NAFTA de-industrialize & depress labour conditions in Canada and exploit workers in Mexico? (Quintero Ramirez: 2002) By: • Reducing the number of full-time jobs • Subcontracting work outside the plant • Increase of part-time workers • Piecework outsourced to home work Core: NAFTA & US (as Core): • Power of the US: Neoliberalism is imposed on Mexico and Canada • Impact of US financial boom-bust cycles affect their trade balances. Semi periphery and Periphery: • Continental commodification of Canada’s (semi periphery) and Mexico’s (Periphery) raw materials • http://www.slideshare.net/MariaRey/nafta-may-18-2011-rey 1-40 slides 2 Driving force of Global market integration: (Cormier & Targ: 2001) • Neoliberalism (NL) deregulate commercial activity. Liberalize trade, open for foreign investments. Deregulate finance/currency, privatize the economy, ensure private property protection Why should Canada and Mexico adopt NL? • US’s enforcement: How? • By integrating Canada and Mexico through NAFTA • As requirements of loans: WB, IMF & SAP Feb 2010: UNCTAD’s new economic report shows that neoliberal policies have negatively affected the countries that were forced to follow them Why does Mexico as a peripheral country bow to American hegemony IMF requires each country to balance export vs. import payment in trade. It lends money to bridge the gap (imports minus exports) and imposes the rules of neoliberalism (LAPDoGS) on the borrowing country. Core: NAFTA & US (as Core): • Power of the US: Neoliberalism is imposed on Mexico and Canada • Impact of US financial boom-bust cycles affect their trade balances. Semi periphery and Periphery: • Continental commodification of Canada’s (semi periphery) and Mexico’s (Periphery) raw materials WST: US’s commodification of Canadian and Mexican raw materials: How? 1. Continentalization of the 3 economies • Corporatization of production in NAFTA countries • Continental expansion of US’s MNCs • Continental enforcement of neoliberalism 2. FT • FT-terms favourable to the US • GCC & Continental commodity chain 3 Global Integration by trade agreements in Table 1 • US vs. European Union (EU). • European U: Sovereign states may resist global integration because it would mean surrendering national control on economic policies • CU allows greater bargaining power between trading nations • FTA may appeal to small states as exporters need to adjust only to block standards not to global standards. WST: Continentalization of the three economies & US (Core’s)hegemony: Mexico (periphery) and Canada (semi-periphery) are integrated through NAFTA • Favourable terms of trade for the US (unequal exchange) • US disregards WTO’s decisions FT: Continental commodification of Canada’s (semi periphery) and Mexico’s (Periphery) raw materials • US power within NAFTA leads to the continental commodification Under the US hegemonic power Mexico and Canada abide by the US strategies. How does a hegemon in a trade block make gains? • Political influence • Terms-of-trade (TOT) 4 • • Discrimination against non-members Greater influence over multilateral trade negotiations Impact of Neoliberal Trade Policies: UNDP Human Development Report 2004 : • 46 countries’ people are poorer today than in 1990 • Liberalization and privatization restrict countries’ supply of basic services • WB conditionality undermines local service industries that cannot compete with trans-national service corporations http://www.un-ngls.org/cso/cso5/cfmm2004statement.pdf UN • • • • Economic and Social Council, 2000: committee on human rights reports: Most global trade is controlled by multinational enterprises Trade and commerce have serious human rights implications WTO: gender insensitive Patents for genetically engineered species – economic high-jacking. http://www.unhchr.ch/Huridocda/Huridoca.nsf/(Symbol)/E.CN.4.Sub.2.2000.1 3.En?Opendocument . 5 6 WST: US’s commodification of Canadian and Mexican raw materials: How? 1. Continentalization of the 3 economies • Corporatization of production in NAFTA countries • Continental expansion of US’s MNCs • Continental enforcement of neoliberalism 2. FT • FT-terms favourable to the US • GCC & Continental commodity chain Ciccantell (2001): NAFTA: an institutional framework of integrating raw materials Why was U.S. interested in NAFTA? • US raw materials supply systems were declining • To access cheap labour and to gain new markets Name a resource that is expensive today: oil & gas e.g.: oil price increases of 1973-74 led to 1979-80 decline of U.S. economic competitiveness 7 Core: NAFTA & US : 1. Problems of U.S. & its MNCs: How did they solve insecure supplies of the raw materials ? Canada’s & Mexico’s oil, natural gas, and other natural resources 2. Why was US interested in these supplies? To reduce for U.S. MNCs’ cost of production to advance their profit & competitiveness. Core: NAFTA & US (cont’d): 3. Core-Periphery unequal exchange continues under hegemonic FT rules: FT ensures: • Cheap access to heaviest, bulkiest, and largest volume raw materials • Monopolistic (MNCs) extraction peripheries’ raw materials at low costs What is ‘Direct foreign investment’? branch plants -- central mechanisms of core economies' control over their raw materials in peripheries Limit processing to certain refineries: physical relationship tightly links many extractive peripheries to particular core firms 8 h p://revista.amec.com.mx/num_7_2004/Peter_Kresl.htm 9 10 Quintero Ramirez (2002): How does NAFTA de-industrialize & depress labour conditions in Canada and exploit workers in Mexico? In Canada: by • Reducing the number of full-time jobs • Subcontracting work outside the plant –affects jobs: - increase of part-time workers - piecework - outsourced to home work Quintero Ramirez (cont’d) In Mexico: • average of 70 hrs. per week without overtime pay - no health insurance, no benefits • violation of the Employment Standards by employers – workers received no compensation under the Workplace Safety Act • no welfare or UI (unemployment insurance) 11 12 NAFTA benefits the capital investors but workers lose jobs: Source: G & M Feb. 15, 2008, p.A18.(editorial) • Trade Area 440 mil people • 1993-2006: $15 Trillion (value of goods and services produced) • Economies grew by : U.S. 50% Canada 54% Mexico 46% • NAFTA partners’ total trade /a minute $1.7 million (worth) Source: G & M Feb. 15, 2008, p.A18.(editorial) The Wonderful World of Nafta http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZnVL0d9fwkY 7 min (the wonderful World of Nafta 1/2) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XxQQael1ueE (2/2) 13 Does Canada control its own sovereignty, taxation and borrowing? Yes, but: • U.S. hegemony It ensures that its huge sunk capital in raw materials, overpowers Canada’s claims to sovereignty Pre 9/11: What % of Canadians were ‘continentalists’? Two thirds What is hegemony? Arrighi (2004): When a state uses its economic, political, military and cultural power to control a group of sovereign states. Core: NAFTA & US :Ciccantell, P. (2001) 1. Problems of U.S. & its MNCs: How did they solve insecure supplies of the raw materials ? Ciccantell, P. (2001). Canada’s & Mexico’s oil, natural gas, and other natural resources 2. Why was US interested in these supplies? To reduce MNCs’ cost of production for U.S. to advance their competitiveness. (Ciccantell, P (2001). NAFTA and the Reconstruction of U.S. Hegemony: The Raw Materials Foundations of Economic competitiveness. (Statistical Data Included) , Canadian Journal of Sociology, Winter 2001 v26: 1, p57) Core: NAFTA & US (cont’d): 3. What does US as a hegemon want to monopolize trade in the world? 14 Cheap access to heaviest, bulkiest, and largest volume of raw materials • Maintain its hegemony to extract raw materials at low costs from the peripheries. WST explains Core’s Globalization agenda & its consequences to the peripheries Expansion of US Hegemony: (read: Ciccantell, P: 2001) • Enforced uniformity in development • Hegemonic control over technologies • Unsuitable, costly & centralized solutions • Lack of locally effective problem solving • 15 Peripheries: NAFTA Periphery: Mexico Semi-periphery: Canada 1. Wise T. A.(2011): Hegemony and dumping 2. Abboushi, S (2010): • US trading power, US disregard for agreements, land-ownership structure vs. strategy of acquisition; and Managed (not Free) trade 3. Quintero Ramirez (2002) • NAFTA deindustrialized & depressed labour conditions in Canada and exploits workers in Mexico 16