OSI model review

DISCLAIMER:
If you think you know it all, don’t shout out the answers! Go here:
http://www.gocertify.com/games/osigame.shtml
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz26
96101ede0b8.html
http://www.purposegames.com/game/osi
-model-layers-and-darpa-layers-quiz/info
Review:
List the 7 layers of the OSI model on your paper. Don’t cheat, don’t tell your neighbor. NO LAPTOPS (2 minutes)
List the 4 layers of the TCP/IP model on your paper. Don’t cheat, don’t tell your neighbor. NO LAPTOPS (1 minute)
All together now
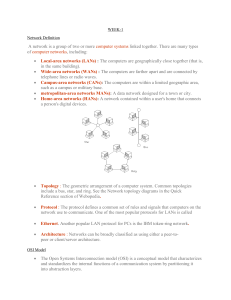
A
P
S
T
N
D
P
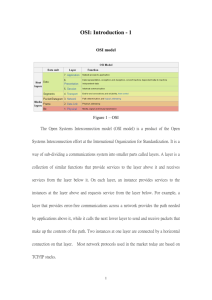
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Mnemonics
All People Seem To Need Data
Processing (7 to 1)
Please Do Not Take Sausage Pizzas
Away (1 to 7)
Pew! Dead Ninja Turtles Smell
Particularly Awful! (1 to 7)
Layer 1: Physical
Physical transmission of bits. This layer generally defines the transmission medium, such as the standard of cabling used, pins, electrical currents, light modulation, etc.
Devices:
-hubs, repeater, cabling
Protocols:
-RJ-45, IEEE 802.3
Layer 2: Data Link
Defines the rules (protocols) that determine when a device can send data over a particular medium. Data link protocols also define the format of a header and trailer that allows devices attached to the medium to send and receive data successfully. (FCS field, etc)
Devices:
-switches, wireless access points
Protocols:
-ARP, CDP, 802.11,
Frame Relay, PPP,
STP, etc.
Layer 3: Network
Logical addressing, routing (forwarding), and path determination. Define how devices forward packets to their final destination. Logical addressing defines how each device can have an address that can be used in routing. Choosing best path.
Devices:
-routers
Protocols:
-IP
Pop Quiz:
How is a router different from a switch?
How is a router different from a bridge?
How is a switch different from a bridge?
How is a hub different from a switch?
Hub: dummy device-forwards any incoming traffic out all ports (except the one it came in)
Bridge: acts as a bridge in a network. If traffic attempts to cross that does not have a proper destination, YOU SHALL
NOT PASS!
Pop Quiz:
How is a router different from a switch?
How is a router different from a bridge?
How is a switch different from a bridge?
How is a hub different from a switch?
Layer 4: Transport
Data delivery to another computer, data ensurance (error recovery, flow control)
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
•3-way Handshake
•Ordered Transmission of Bits
•Used for: anything where order and accuracy matter
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
•No error-checking
•Used for: streaming data (VoIP, video)
•Reserved ports for protocols
Note: Layers 5-7 generally share the same protocols, but most often are referenced in Layer 7
Layer 5: Session
Defines how to start, control, and end conversations (called sessions). Includes the control and management of multiple bidirectional messages so that the application can be notified if only some of a series of messages are completed.
This allows the presentation layer to have a seamless view of an incoming stream of data.
Function:
Starts, stops, maintains order
Layer 6: Presentation
Define and negotiate data formats, such as ASCII text, EBCDIC text, binary, BCD, and JPEG. Encryption also is defined by
OSI as a presentation layer service.
Function:
Encryption, data conversion, ASCII to
EBCDIC, BCD to binary, establishing file formats, etc
Layer 7: Application
Provides interface between the communications software and any applications that need to communicate outside the computer on which the application resides. Also defines processes for user authentication.
Devices:
-firewall, intrusion detection system
Protocols:
-Telnet, HTTP, FTP,
SMTP, POP3, VoIP,
SNMP
TCP/IP
For next week:
Know the layers of the OSI and TCP/IP models.
Be able to describe the functions and/or basic protocols of each layer
Name the devices that operate at each layer
Know the cabling standards discussed: speed, IEEE standard name, cable type, etc.