3OverHere--theUSAinWWI
advertisement

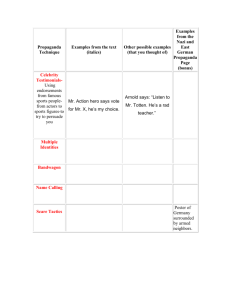
“Over Here” The Homefront During World War I “Over Here” ■To win over there, the U.S. had to effectively mobilize over here –Wilson consolidated federal authority to organize U.S. war production & distribution –Wilson began a massive propaganda campaign aimed at winning over the American public to support the war effort Homefront Propaganda ■Wilson formed the Committee on We Are Fighting” & Public “Why Information (CPI) & hired “The Meaning of America” muckraker George Creel to Sauerkraut was renamed “Liberty Cabbage” The Prussian Cur & & pretzels were no longer served in bars publicize the U.S. war effort: The Kaiser, the Beast of Berlin Bach, Beethoven, & Brahms –Voluntary censorship in press were not played in symphonies –75,000 “4-minute men” gave speeches (facts or emotions?) –Propaganda motion picture films ■Led to sweeping anti-German sentiment & some vigilantism “The Flag of Liberty represents us all” Which groups are these posters targeting? “Emotional” Wartime Propaganda Murder Pillaging & Kidnapping Rape A “Creel Commission” Film IWW anti-war critic "It's allimage right, of vigilantism Find Frank Little was pal; just tell dragged through the them he was a streets of Butte, traitor" Montana & lynched Anti-German Vigilantism Homefront Censorship ■Wilson encouraged censorship: –Espionage Act—aiding the enemy, obstructing troop recruitment, or encouraging Wilson set out to encourage U.S. unity “disloyalty” were declared illegal (like Lincoln during the Civil War, Wilson –Trading-with-the-Enemy Act— was willing to use force if needed) censored the foreign press –Sedition Act—made it illegal to speak “disloyally” towards the U.S. gov’t, the flag, or U.S. troops Schenk Eugene was sentenced conspiracy to circulate Homefront Censorship V. Debsfor was jailed when his pamphlets encouraging soldierstotoReason mutiny Socialist newsletter Appeal ■First Amendment restrictions were encouraged Americans to resist enlisting in upheld by tothe Supreme Court: the military fight a “capitalists’ war” –3 cases were decided in 1919: Schenk v US, Debs v US, Socialism in thev U.S. Abrams US never that supported recovered WWI attacks gov’tfrom convictions under the Espionage Act of 1917 Defendants passed out documents that denounced 1st–The Amendment rights can be restricted gov’t usedtothe wartime thewhen sending of U.S. troops Russia resist the it presents a “clear & present(to danger” Bolshevik Revolution) that called for a climate to undermine radical (Like “yelling ‘fire’ in a & crowded theater”) general strikeunions & other “revolutionary actions” labor (IWW) & socialism Homefront: The Red Scare ■A “red scare” hit America as a result of the Russian Revolution –Americans feared Lenin’s anticapitalist revolution & were angry over Russia’s pullout on the Eastern Front –Wilson sent troops to the USSR, refused to recognize the new gov’t, & did not allow Russia to attend the post-war conference The Red Scare “What a year has brought forth” NY World The Red Scare “Put Them Out & Keep Them Out” Philadelphia Inquirer Palmer used this act of violence as an opportunity to invoke the Alien Act ofThe 1918 & arrested or deported ~6,000 suspected Redradicals Scare: (some were innocent U.S. citizens) Palmer Raids U.S. Attorney Police arrested General “suspected Mitchell Reds’ in Palmer’s Chicago, 1920 Home was bombed A Bureaucratic War A Bureaucratic War ■To coordinate the war effort, 5,000 new gov’t agencies were created: –War Industries Board (WIB) Imposed “gasless” days & shut down oversaw all factories, determined factories for days to divert or conserve fuel priorities, fixed consumer prices –Food Admin supplied food to WIB director Bernard Baruch became soldiers by appealing to civilians the “dictator of the American economy” –Fuel Admin rationed coal & oil Asked for a spirit of self-sacrifice, imposed –RR & Admin, War Shipping Board, “meatless” “wheat-less” days & encouraged Americans to plantBoard “victoryhelped gardens”move & War Trade resources to troops U.S. Food Administration U.S. Food Administration U.S. Fuel Administration U.S. Shipping Board A Bureaucratic War ■WWI was expensive, costing the U.S. $32 billion, but was paid for by –Liberty Bonds (raised $23 billion) An unprecedented alliance –A boost in personal & corporate income taxes (led to $10 billion) ■The partnership between business & the gov’t met the war demand & increased business profits 300% The American War Workforce Workers in the War ■WWI led to a new alliance between the gov’t & labor unions: –AFL headman Gompers was named to the Council of Nat’l Defense to help enlist union support for the war effort –War Labor Board (WLB) was formed to standardize wages & hours, protect union rights, & give equal pay for women But the WLB seized companies during strikes (national interests come first!) Coal Miner’s Strike 1919 “Keeping Warm” Los Angeles Times Workers in the War ■The war called for more laborers: –8 million women found new, better-paying jobs in war industry (but few housewives entered the workforce, unlike WW2) –450,000 Southern blacks moved north for new industrial jobs & better pay (led to race riots) –100,000 Mexican laborers Women Helped Recruit & Sell War Bonds Women Joined the Red Cross The True Sons of Freedom Du Bois’ New Negro: “We return. We return from fighting. We return fighting.” Returning black soldiers: “I’m glad I went. I done my part & I’m going to fight right here until Uncle Sam does his.” “Rescuing a Negro during“Migration” the race riots The African American in Chicago, 1919” Northward, 1910-1920 At the beginning of the war, the United Conclusions States owed $3 billion to foreign nations ■World War At 1 thechanged end of the America: war, foreign nations owed the U.S. $13 billion –The U.S. emerged as the world’s strongest economic power & ushered in the “Roaring 20s” –But the U.S. gov’t intervened in American lives as never before: draft, censorship, propaganda, war bonds, partnering with big business & unions