G8C16-20 Jeopardy revised

Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter 16 Reconstruction (1865-1877)
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Chapter 16 Key Terms and People
1. Reconstruction
2. Ten Percent Plan
3. Thirteenth Amendment
4. Freedmen
’ s Bureau
5. Andrew Johnson
6. Black Codes
7. Radical Republicans
8. Civil Rights Act of 1866
9. Fourteenth Amendment
10. Reconstruction Acts
11. impeachment
12. Fifteenth Amendment
13. Hiram Revels
14. Ku Klux Klan
15. Compromise of 1877
16. poll tax
17. segregation
18. Jim Crow laws
19. Plessy v. Ferguson
20. sharecropping
Academic
Vocabulary
1. procedure
2. principle
Thirteenth Amendment (1865)
Banned slavery throughout the United States
Fourteenth Amendment (1868)
Overturned the Dred Scott case by granting citizenship to all people born in the United States
(except for Native Americans)
Fifteenth Amendment (1870)
Gave African American men the right to vote
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
Laws passed in the southern states during
Reconstruction that greatly limited the freedom and rights of African Americans.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
(1865
–
77) The period following the Civil
War during which the U.S. government worked to reunite the nation and to rebuild the southern states.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
African Americans were free but now faced segregation and Jim Crow laws to impede their freedom progress in America
(free but restricted).
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
Members of Congress who felt that southern states needed to make great social changes before they could be readmitted to the Union.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
(1865) a constitutional amendment that outlawed slavery
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
The new South had to rebuild everything and now they involved industry instead of relying just on agriculture; Atlanta became the new center of Southern industry.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
(1896) U.S. Supreme Court case that established the separate-but-equal doctrine for public facilities
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
(1867
–
68) The laws that put the southern states under U.S. military control and required them to draft new constitutions upholding the Fourteenth Amendment.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
In 1865 Congress established the
Freedmen
’ s Bureau, an agency providing relief not only for _____________ and certain poor people, but white refugees as well.
1.
Reconstruction
2.
13th Amendment
3.
Helping the Freedpeople
4.
Black codes
5.
Radical Republicans
6.
Reconstruction Acts
7. Reconstruction Amendments
8. African American Representation in the South
9. The Ku Klux Klan
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
12. The New South
Chapter 17 Americans Move West (1850-1890)
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Chapter 17 Key Terms and People
1.
frontier
2.
Comstock Lode
3.
boomtowns
4.
Cattle Kingdom
5.
cattle drive
6.
Chisholm Trail
7.
Pony Express
8.
transcontinental railroad
9.
Treaty of Fort
Laramie
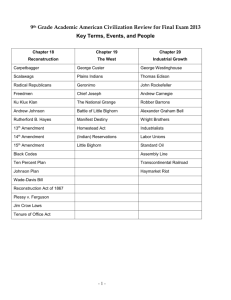
10. reservations
11. Crazy Horse
12. Treaty of Medicine
Lodge
13. Buffalo soldiers
14. George Armstrong
Custer
15. Sitting Bull
16. Battle of the Little
Bighorn
17. Massacre at
Wounded Knee
18. Long Walk
19. Geronimo
20. Ghost Dance
21. Sarah Winnemucca
22. Dawes General
Allotment Act
23. Homestead Act
24. Morrill Act
25. Exodusters
26. sodbusters
27. dry farming
28. Annie Bidwell
29. National Grange
30. deflation
31. William Jennings
Bryan
32. Populist Party
a railroad system that crossed the continental United States; construction began in 1863; The federal government, therefore, passed the Pacific Railway Acts in 1862 and in 1864. These acts gave railroad companies loans and large land grants that could be sold to pay for construction costs. Congress had granted more than 131 million acres of public land to railroad companies. In exchange, the government asked the railroads to carry U.S. mail and troops at a lower cost. Many railroad companies were inspired to begin laying miles of tracks.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward 7. Native Americans Land
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
(1860
–
1925) American lawyer and
Populist politician, he favored free silver coinage, an economic policy expected to help farmers. He was a Democratic nominee for president in 1896 and was defeated by William McKinley.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
From 1860 to 1900, the U.S. population more than doubled. To feed this growing population, the number of farms tripled. With modern machines, farmers in 1900 could harvest a bushel of wheat almost 20 times faster than they could in 1830; in return, farm product prices decreased and farmers lost a lot of money; to protect their interests, the populist party came to power
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
Supply is the amount of a good that is available. Demand is the amount of a good that people want to buy. When supply exceeds demand, prices fall.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
Settlers desired new land to the west. Miners wanted to find mineral resources. Ranchers wanted more land to raise their cattle. Businesses began to support settlers, ranchers, and miners.
So , new towns and cattle kingdoms developed in the west. Also, railroads crossed the continent to connect towns.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
(1862) A law passed by Congress to encourage settlement in the West by giving government-owned land to small farmers.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
(1862) A federal law passed by Congress that gave land to western states to encourage them to build colleges.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
From 1850 to 1890, these people lost almost all of their land and were placed on reservations set aside by the government.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
The Central Pacific and Union Pacific connected their tracks at Promontory, Utah, in 1869, completing the transcontinental railroad; the _____________ was the last one driven into the ground
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
As a result, it increased settlement of the
West, increased business activity and eastwest trade, and helped make the railroad industry one of the most powerful in the country.
1.
Causes and Effects of Westward
Expansion
2.
Myth and Reality in the Wild West
3.
Transcontinental Railroad
4.
Golden Spike
5.
Effects of the Transcontinental
Railroad
6. Plains Indians
7. Native Americans Land
Loss in the West
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
11. William Jennings Bryan
12. Oklahoma Land Rush
Chapter 18 An Industrial Nation
QuickTime™ and a
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
(1876-1900)
QuickTime™ and a
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Chapter 18 Key Terms and People
1.
Second Industrial
Revolution
2.
Bessmer process
3.
Thomas Edison
4.
patents
5.
Alexander Graham Bell
6.
Henry Ford
7.
Wilbur and Orville
Wright
8.
Corporations
9.
Andrew Carnegie
10. vertical integration
11. John D. Rockefeller
12. horizontal integration
13. Trust
14. Leland Stanford
15. social Darwinism
16. monopoly
17. Sherman Antitrust Act
18.
Frederick W. Taylor
19. Knights of Labor
20. Terence V. Powderly
21. Samuel Gompers
22. American Federation of
Labor
23. Labor
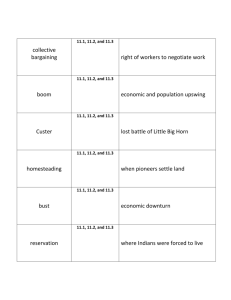
24. collective bargaining
25. Mary Harris Jones
26. Haymarket Riot
27. Homestead Strike
28. Pullman Strike
29. old immigrants
29. new immigrants
30. Steerage
31. Benevolent societies
32. Chinese
Exclusion Act
33. Immigration
Restriction
League
34. mass transit
35. suburbs
36. mass culture
37. department houses
38. settlement houses
39. Hull House
40. Jane Addams
This is the survival of the fittest; the smartest ones make the most money.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
Investors purchased stock in corporations in record numbers in the late 1800s. They received stock certificates to document their part ownership in corporations.
Corporations used the money raised by selling stocks to expand.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
an exclusive right to make or sell an invention
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
Too many people with a lack of sufficient housing led to tenement lifes, disease, and infested cities because of a lack of running, clean water and plumbing.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
a business that sells portions of ownership called stock shares
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
a period of rapid growth in manufacturing and industry in the late 1800s
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
public transportation by subway and railways to accommodate huge city populations
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
(July 8, 1839 – May 23, 1937) _________________ was an American industrialist and philanthropist. ____________ revolutionized the petroleum industry and defined the structure of modern philanthropy.
In 1870, he founded the Standard Oil Company and ran it until he officially retired in 1897.[1] Standard Oil began as an Ohio partnership formed by John D. ___________, his brother William __________, Henry
Flagler, chemist Samuel Andrews, and a silent partner Stephen V.
Harkness. ______________ kept his stock and as gasoline grew in importance, his wealth soared and he became the world's richest man and first American billionaire, and is often regarded as the richest person in history.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
He was a Scottish-born American industrialist, businessman, and a major philanthropist. He was an immigrant as a child with his parents. He built Pittsburgh's __________ Steel Company, which was later merged with Elbert H. Gary's Federal Steel Company and several smaller companies to create U.S. Steel. With the fortune he made from business, he turned to philanthropy and interests in education, founding the ____________ Corporation of New York, __________
Endowment for International Peace, and ________________ Mellon
University in Pittsburgh.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
California entrepreneur and politician who amassed a fortune in the railroad industry during the mid 1800
’ s. He started a famous California University in Northern
California.
1.
Second Industrial Revolution
2.
Patents
3.
Corporations
4.
The Rise of Investing
5.
Antitrust
6a. Carnegie
6b. Rockefeller
6c. Stanford
7. Social Darwinism
8. Labor Strikes
9. Coming to America
10. Symbol of Freedom
11. Coming to America
12. Steel Framed Buildings
13a. Mass transit 13b. Mass Culture
14a. Urban Problems 14b. Settlement Houses
Chapter 19 The Spirit of Reform
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Chapter 19 Key Terms and People
1.
Political machines
2.
William Marcy Tweed
3.
Rutherford B. Hayes
4.
James A. Garfield
5.
Chester A. Arthur
6.
Grover Cleveland
7.
Benjamin Harrison
8.
William McKinley
9.
Spoils system
10. Pendleton Civil Service
Act
11. progressives
12. muckrakers
13. John Dewey
14. Joseph McCormack
15. direct primary
16. Seventeenth Amendment
17. recall
18. initiative
19. referendum
20. Robert M. La Follette
21. Wisconsin idea
22. Florence Kelley
23. Triangle Shirtwaist Fire
24. workers
’ compensation
25. laws
26. capitalism
27. socialism
28. William
“
Big Bill
”
Haywood
29. Industrial Workers of the
World
30. Woman
’ s
Christian
31. Temperance
Union
32. Eighteenth
Amendment
33. National
American
Women
34. Suffrage
Association
35. Alice Paul
36. National
Women
’ s Party
Chapter 19 Key Terms and People
37. Nineteenth Amendment
38. Booker T. Washington
39. Ida B. Wells
40. W.E.B. Du Bois
41. National Association for the
Advancement of Colored People
42. Theodore Roosevelt
43. Arbitration
44. Pure Food and Drug Act
45. Conservation
46. William Howard Taft
47. Progressive Party
48. Woodrow Wilson
49. Sixteenth Amendment
50. Federal Reserve Act
51. Clayton Antitrust Act
52. Federal Trade
Commission
an economic system in which government owns and operates a country
’ s means of production.
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
a group of reformers who worked to improve social and political problems in the late 1800s
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
Wilson wins the election in a landslide is his case against the huge monopolies controlling
American politics and government.
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
life was terrible; no regulations; 16 hour days in unhealthy air quality conditions
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
Rutherford B. Hayes (Republican In office 1877
–
1881)
James A. Garfield (Republican In office 1881)
Chester A. Arthur (Republican In office 1881
–
1885)
Grover Cleveland (Democrat In office 1885
–
1889, 1893
–
1897)
Benjamin Harrison (Rep.) 1889-189
William McKinley (Rep.) 1897-1901
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
The goal was to get children out of the factories and into the classrooms.
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
Direct Primaries -Voters choose candidates
Recall - Voters can remove an official from office
Initiatives -Voters can propose laws by petition
Referendum - Voters can overrule a law
17th Amendment -Senators are elected directly by voters.
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
16 th –
Federal income tax (1913)
17 th –
Senators elected by people rather than state legislatures (1913)
18 th – manufacture, sale, and transport of alcohol prohibited (1919)
19 th – women
’ s suffrage (1920)
1.
Political Machines 9. Working Conditions in Factories
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
5.
Tenement Life
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
12. Left Behind
6.
The Other Half
7.
Expanding Democracy
13. The National Park System
14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
Eighteenth Amendment (1919) a constitutional amendment that outlawed the production and sale of alcoholic beverages in the United States; repealed in 1933; women could vote in the west in the late 1800
’ s but not in the east; The Nineteenth Amendment was declared ratified by the U.S. Congress in 1920 and gave American women the right to vote.
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
a powerful organization that influenced city and county politics in the late 1800s
1.
Political Machines
2.
Spoils System
3.
Gilded Age Presidents
4.
Progressives
9. Working Conditions in Factories
10a. Capitalism
10b. Socialism
11. Women Fight for Rights
5.
Tenement Life
6.
The Other Half
12. Left Behind
13. The National Park System
7.
Expanding Democracy 14. Election of 1912
8.
Improving Conditions for Children 15. Wilson and Big Business
16. The Progressive Amendments
Chapter 20 America Becomes a World Power (1867-1910)
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Chapter 20 Key Terms and People
1.
Imperialism
2.
isolationism
3.
William H. Seward
4.
subsidy
5.
Liliuokalani
6.
consul general
7.
spheres of influence
8.
John Hay
9.
Open Door Policy
10. Boxer Rebellion
11. Joseph Pulitzer
12. William Randolph Hearst
13. yellow journalism
14. Teller Amendment
15. Emilio Aguinaldo
16. Theodore Roosevelt
17. Anti-Imperialist
League
18. Platt Amendment
19. Hay-Herran Treaty
20. Phillippe Bunau-
Varilla
21. Panama Canal
22. Roosevelt Corollary
23. dollar diplomacy
24. Porfirio Diaz
25. Francisco Madero
26. Mexican Revolution
27. Victoriano Huerta
28. Venustiano Carranza
29. Franciso
“
Pancho
”
Villa
30. Emiliano
Zapata
31. ABC Powers
32. John J.
Pershing
an artificial waterway across the Isthmus of
Panama; completed by the United States in
1914
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
The U.S. acquired several new territories to expand its empire.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
By 1900 most of the current boundaries of the United
States had been established. But the world had become a much smaller place. American inventions were spreading, changing daily life in countries around the world. In addition, U.S. troops stationed in Asia were displaying the increasing importance of the United States in global affairs.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
( 1858
1919) He was born into a wealthy family from New York City. He suffered from poor health as a child but became involved in many sports as he grew older. He spent two years on his ranch in the Dakota Territory, where he served as deputy sheriff. While in the West, he became an avid hunter and conservationist. When he returned to the East, he returned to his political career as an important reformer. A strong supporter of imperialism and the Spanish-American War, he recruited a cavalry division called the
Rough Riders. As President McKinley
’ s vice president, he became president upon McKinley
’ s assassination.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
Departing from the example set by the nation
’ s first president, George Washington, later presidents increased U.S. involvement around the world, particularly in Latin
America.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
the reporting of exaggerated stories in newspapers to increase sales
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
the practice of extending a nation
’ s power by gaining territories for a colonial empire
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
In the late 1890
’ s, Japan defeated China, other countries quickly took advantage of China
’ s weakness.
These nations seized ___________________
— areas where foreign nations controlled trade and natural resources. Germany, Great Britain, France, Japan, and Russia all took control of areas of China.
.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
War with Spain
6.
War in the Phillippines
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
The U.S. would intervene in Latin
American issues if it had to. The U.S. would act as
“ police officer
” of the Western
Hemisphere.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
Filipino rebels, however, had helped U.S. forces to capture Manila. They had expected to gain independence after the war. When the United
States decided instead to keep the islands,
Auginaldo
’ s rebels started a guerrilla war against the American forces.
1.
Imperialism 9. Revolt in the Philippines
2.
U.S. Territories in the Pacific10. Building the Panama Canal
3.
Spheres of Influence
4.
Yellow Journalism
5.
6.
War with Spain
War in the Phillippines
11. The Panama Canal
12. Theodore Roosevelt
13. Roosevelt’s Imperialism
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
7.
Fighting in Cuba
8.
War in the Caribbean
15. Mexican Revolutionaries
16. U.S. in Latin America
17. America’s Growth by 1900
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
Chapter
100 - 7 100 - 3 100 - 7 100 - 10b 100 - 11
200 - 4 200 - 11 200 - 4 200 - 4 200 - 2
300 - 1 300 - 9 300 - 2 300 - 14 300 - 17
400 - 11 400 - 10 400 - 14a 400 - 9 400 - 12
500 - 5 500 - 1 500 - 3 500 - 3 500 - 14
600 - 2 600 - 8a 600 - 1 600 - 8 600 - 4
700 - 12 700 - 8b 700 - 13a 700 - 7 700 - 1
800 - 10 800 - 7 800 - 6b 800 - 16 800 - 3
900 - 6 900 - 4 900 - 6a 900 - 11 900 - 13
1000 - 3 1000 - 5 1000 - 6c 1000 - 1 1000 - 9
7. The Reconstruction Amendments
4. Black Codes
1. Reconstruction
11. Hopes Raised and Denied
5. Radical Republicans
2. 13
th
Amendment
12. The New South
10. Plessy v. Ferguson
6. Reconstruction Acts
3. Helping the Freedpeople
3. Transcontinental Railroad
11. William Jennings Bryan, Populist
Party
9. Farming and Rise of Populism
10. Agricultural Supply and Demand
1. Causes and Effects of Westward Expansion
8a. Homestead Act
8b. Morrill Act
7. Native American Land Loss in the West
4. Golden Spike
5. Effects of the Transcontinental Railroad
7. Social Darwinism
4. The Rise of Investing
2. Patents
14a. Urban Problems
3. Corporations
1. Second Industrial Revolution
13a. Mass Transit
6b. Rockefeller
6a. Carnegie
6c. Stanford
10b. Socialism
4. Progressives
14. Election of 1912
9. Working Conditions in Factories
3. Gilded Age Presidents
8. Improving Conditions for Children
7. Expanding Democracy
16. The Progressive Amendments,
1909-1920
11. Women Fight Rights
1. Political Machines
11. The Panama Canal
2. U. S. Territories in the Pacific
17. America
’
s Growth by 1900
12 Theodore Roosevelt
14. U.S. Foreign Policy
4. Yellow Journalism
1. Imperialism
3. Spheres of Influence
13. Roosevelt
’