Blood cells morphology
advertisement

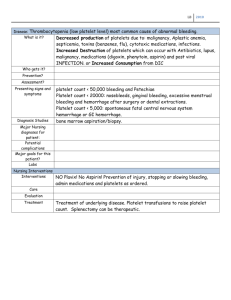
The morphology of Blood cells Composition of the blood The circulating blood is composed of plasma and cells. The cells are red cells (or erythrocytes), white cells (or leucocytes) and platelets. Blood cells can be identified in blood films stained with a mixture of basic and acidic dyes. Normal white cells are divided into polymorphonuclear leucocytes (or granulocytes) and mononuclear cells. White blood cells There are three types of granulocyte named according to their staining characteristics in blood films. They are neutrophils,eosinophils and basophils. Mononuclear cells are divided into lymphocytes and monocytes. Neutrophils The neutrophils in the circulating blood are mainly mature segmented neutrophils. Band form Neutrophils There are smaller numbers of cells of neutrophil lineage with non-segmented nuclei. They are referred to as neutrophil band cells or band forms. They are less mature than segmented neutrophils. An increased number of band cells is referred to as a'left shift'. Eosinophil One eosinophil mature. Normal blood - 100X. Orange colour granules. Bi-lobed nucleus. Basophil One mature basophil. Blackish granules overlying the nucleus. Normal lumphocytes Lymphocytes are the smallest WBC. They have large condensed nucleus, with a scanty bluish cytoplasm. Normal monocyte Monocytes are the largest WBC. The nucleus is slightly indented . The cytoplasm is abundant, sky blue in colour. Some have vacuoles in the cytoplasm. Red cells Normal red cells or erythrocytes show only slight variation in size and shape. The blood film should be examined in the area where the red cells are touching but not often overlapping. Red cells . In this area many red cells have an area of central pallor which may be up to a third of the diameter of the cell. This is consequent on the shape of a normal red cell, which resembles a disc that is thinner in the centre. Platelets Normal platelets are also apparent. They are small anuclear fragments between the red cells containing small purple-staining granules. Platelet ribbon A string of platelets or Platelet Ribbon. This is the appearance of normal platelets when being shed by a megakaryocyte into the marrow sinus. The ribbon then breaks up into numerous small platelet fragments. Normal blood - 100X Platelet aggregates Platelet aggregates may be composed of apparently intact platelets, degranulated pale grey platelets or a mixture of both, as in this example. If the platelet count is low it is essential to examine the blood film carefully for platelet aggregates. Platelet satellitism Platelet satellitism describes the phenomenon of adherence of platelets to white cells. It is an in vitro phenomenon of no clinical significance. However it is important that it is detected since the platelet count will be factitiously low. Nucleated epithelial cells Extraneous nonhaemopoietic cells are sometimes seen in blood films. These include epithelial cells which are readily identified from their abundant sky-blue cytoplasm and small central nucleus. They are more often seen if capillary blood is obtained by percutaneous puncture than when a film is Endothelial cells Endothelial cells are very occasionally seen in films prepared from venous blood samples. They have rather pleomorphic oval nuclei with a grooved surface. The cytoplasm is scanty and the cell outline is irregular. They tend to occur in clumps. It is important not to confuse normal endothelial cells with carcinoma cells which are also very occasionally seen in the Artefacts Fixation artefact is the term used for the artefact that occurs when there is water in the methanol used for fixation of the blood film.This leads to refractile rings in red cells and makes it quite impossible to assess red cell morphology. Heat artefact Inadvertent heating of a blood sample, for example during transport in a hot car, can lead to a heat artefact. Red cells bud off vesicles and microspherocytes seen. White cells disintegrate and proteins coagulate, producing weakly Storage artefact Prolonged storage of blood before making the blood film, particularly storage at room temperature,leads to storage artefact. White cells become fragile and may form smear cells [deep red arrow]. Neutrophil nuclei round up and form homogeneous round masses or a single mass [blue arrow].These cells have a resemblance to NRBC. Red cells undergo an echinocytic change or crenation.