The French Revolution - Spokane Public Schools
advertisement

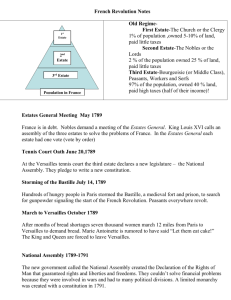
The French Revolution 3 estates – 1% Church (owned 15% of land) – 2% Nobility – 97% (top were the bourgeoisie) Problems – Paying taxes and tithes – Bourgeoisie wanted power and position Financial Crisis – Debt from war and expensive habits – Pay from taxing – Called the meeting of the Estates General to approve new taxes The 3rd Estate Carrying the others The Beginning Recall of the Estates General May 4, 1789; Opened in Versailles 3rd Estate wasn’t allowed in – Met at the Tennis Courts – Would Stay and make a constitution – National Assembly created; Replaces Estates General *Commoners Meet at the Bastille *Wanted release of the political prisoners *Took the Bastille and destroyed it *Start of the Revolution on July 14th 1789 -National Guard created -New flag of the people National Assembly began reform Outlawed the tithe Canceled Feudal Dues Removed privileges of the first two estates August 4, 1789 Feudalism is gone A movement of Emigration Begins Nobles Kings Family Clergy Declaration of the Rights of Man August 27, 1789 Fundamental Natural Rights Freedom of Speech, press, religion, right to a fair trial All MEN could take part in Government Bread Riots Women played a leading role Marched on Versailles Goal was to bring it to the attention of the king King and his family return to Paris National Assembly National Assembly passed many laws Divided country into 83 Departments Elections of all officials Seized lands owned by the church Sold it to the public Proceeds used for paying down the debt Changes in the Church Catholic Clergy had to take an oath Oath backed up the constitution Called Civil Constitution of Clergy People in parishes would now elect own clergy In return for seizing church land Government would pay for salaries of Priests and Bishops Creates Uproar in Rome Breach of the Church Can’t be under French Government control End of the National Assembly 1791: Constitutional Monarchy Created Legislative Assembly Replaces National Assembly Created three branches of Government Judicial, Executive, legislative Limits power of the Monarchy King could no longer make or block laws on his own Tax paying MEN could Vote for Electors Continued Economic Problems Paid off old bonds with new bonds Continued to make more and more Finally forced to accept as money The King King Louis XVI tries to escape France Felt he could regroup and take over from abroad Makes it to Varennes Forced to return to Paris As a prisoner Emigration of Nobles increases Since king tried to leave; oath to him no longer mattered The King’s Arrest at Varennes The Constitution Not everyone happy with the new constitution Lasted less than a year Breaks into three groups Conservatives Moderates Radicals Frequent deadlocks on domestic issues between groups Until foreign threat of war Even King Louis XVI wants war Hoped for French defeat WAR April 1792: France Declares war on Austria Prussia and Sardinia join Austria Every city they hit surrendered September Massacres Prussians kill thousands that were in prisons Prussia warns for no harm to come to the king and his family In response the Commune calls for the abolition of the Monarchy AUGUST 10, 1792: Abolition of the Monarchy Republic declared and Arrested the King and Family The National Convention Delegates elected through Universal Manhood suffrage Any male could now vote Divided into three groups Girondins (moderates) Jacobins (some more radical) Those with no definitive view Wrote a new constitution Declared end to monarchy Beginning of a Republic Brought King Louis XVI to trial Charged with plotting against security of the nation January 1793: Majority votes for immediate death of the King January 21, 1793: Guillotine The War French were doing very well pushed armies out of France So they decided to attack the Netherlands This scares other nations Great Britain, Netherlands, and Spain join forces with Austria, Prussia and Sardinia push France out of the Netherlands and the fighting is back in France The Draft begins Any man with proven abilities could become an officer The creation of the Committee of Public Safety Created to meet the threat of invaders Led by Robespierre Wanted to stop counter-revolutionaries Many Girondin’s arrested Start of …THE REIGN OF TERROR The Reign of Terror… The guillotine is named for Dr. Joseph Ignace Guillotin, who endeavored to commission a device that would deliver a swift and honorable death to people of all classes. Before the French Revolution, only nobles were executed by decapitation -- other lower-class capital criminals were subjected to burning, drowning and maiming. THE REIGN OF TERROR September 1793-July 1794 Rational: Kill all those who oppose the revolution; whether at home or abroad Beginning of Totalitarian Government Leaders were Robespierre and Danton Had 300,000 arrested Just needed suspicion Either not guilty or guilty and beheaded Trials could end as soon as juries heard enough Most that died were Bourgeoisie and peasants The peasants in greater numbers When France was out of danger in the war Danton called for the end of the killings Robespierre calls him a traitor and had him and his followers killed Now his friends are nervous July 1794 Robespierre was arrested He tries to commit suicide They had him beheaded Mass executions end Pendulum swings back to the right Jacobins lose power Judges go on trial Some people favoring return of the monarchy Act of Justice THE NATIONAL CONVENTION (Again) Republic of Virtue Creates Schools Universal elementary education Wage and price controls Abolished slavery in colonies Encouraged religious tolerance Replaced weights and measures with metric system Created new calendar ANOTHER NEW CONSTITUTION Had a two House Legislative 500 members proposed laws 250 more powerful members accepted or rejected these laws Also had the power to pick executive leaders called the DIRECTORY Eliminated manhood suffrage Now only male property owners could vote The DIRECTORY leads for four years Corruption within the members and suffering from the peasants and workers makes it very unpopular