COMMON MISTAKES ON THE AP MACRO EXAM
advertisement

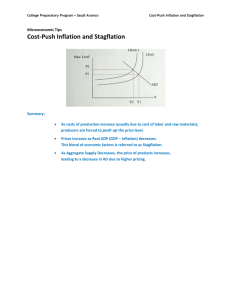
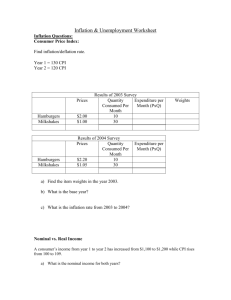
The difference between a change in demand and a change in quantity demanded GRAPHING DEMAND Price of Corn P CORN P $5 4 3 2 1 QD 10 20 35 55 80 $5 4 3 2 What if Demand Increases? 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity of Corn Q GRAPHING DEMAND Price of Corn Increase in Quantity Demanded P CORN P $5 4 3 2 1 QD 10 30 20 40 35 60 55 80 80 + $5 4 3 2 1 o Increase in Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity of Corn D’ D Q The difference between a change in supply and a change in quantity demanded GRAPHING SUPPLY Price of Corn P $5 4 3 2 S What if Supply Increases? 1 o 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity of Corn CORN P QS $5 4 3 2 1 Q 60 50 35 20 5 GRAPHING SUPPLY Price of Corn P $5 4 3 2 1 Increase in Supply S S’ CORN P QS $5 4 3 Increase 2 in Quantity 1 Supplied o 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity of Corn Q 60 80 50 70 35 60 20 45 5 30 Mislabeling or NOT labeling graphs correctly EQUILIBRIUM AND CHANGES IN EQUILIBRIUM Price Level P LRAS AS Equilibrium Real Output P AD Y Real Domestic Output, GDP Q GROWTH IN THE AD-AS MODEL ASLR1 ASLR2 C Price Level Capital Goods A B D Consumer Goods Q1 Q2 Real GDP THE MONEY MARKET Nominal Interest Rate Sm1 Sm Use this graph when the FED changes the money supply to change interest rates. 10 7.5 ie 5 Dm 2.5 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Amount of money demanded (billions of dollars) Net effects of Monetary Policy and/or Fiscal Policy on Interest Rate Expansionary Fiscal Policy = Interest Rate INCREASE • Exp. Fiscal Policy (Gov’t deficit) Increase Demand for Money Increase Interest Rate. • Higher Price Level Increase Demand for Money Increase Interest Rate. Expansionary Monetary Policy Interest Rate DECREASE MONETARY POLICY AND EQUILIBRIUM GDP Nominal interest rate Sm1 S m2 10 10 8 8 6 6 Investment Demand Dm 0 0 Quantity of money Amount of investment, I Price level AS P2 P1 AD1 AD2 Real domestic output, GDP Money Supply Increases If the money Interest Rate Decreases supply increases Investment Increases to stimulate the economy... AD & GDP Increases with slight inflation MONETARY POLICY AND EQUILIBRIUM GDP Real rate of interest, i Sm1 S S m2 m3 10 10 8 8 6 6 Dm 0 Quantity of money demanded and supplied AS Price level Investment Demand P3 P2 P1 0 Amount of investment, i More Money Supply If theInterest moneyRates Lower supply increases More Investment again… AD1 AD2 AD3 Real domestic output, GDP Still higher AD & GDP with significant inflation MULTIPLIER(S) CONFUSION THE MULTIPLIER EFFECT Multiplier Change in GDP 1 1 or 1 - MPC MPS = = Multiplier x initial change in spending MPC and the Multiplier MPC Multiplier .9 10 .8 5 .75 4 .67 .5 3 2 MONEY MULTIPLIER • 1 / Required Reserve Ratio • Maximum Multiple $$$ Money Expansion MULTIPLE DEPOSIT EXPANSION PROCESS Bank Acquired reserves Required and deposits reserves Excess reserves Amount bank can lend - New money created $80.00 64.00 51.20 40.96 32.77 26.22 20.98 16.78 13.42 10.74 8.59 6.87 5.50 4.40 17.57 Total amount of money created by the banking system $400.00 A $100.00 B 80.00 C 64.00 D 51.20 E 40.96 F 32.77 G 26.22 H 20.98 I 16.78 J 13.42 K 10.74 L 8.59 M 6.87 N 5.50 Other banks 21.97 $20.00 16.00 12.80 10.24 8.19 6.55 5.24 4.20 3.36 2.68 2.15 1.72 1.37 1.10 4.40 $80.00 64.00 51.20 40.96 32.77 26.22 20.98 16.78 13.42 10.74 8.59 6.87 5.50 4.40 17.57 Balanced Budget Multiplier= 1 (Net Result on GDP) FEDERAL RESERVE PURCHASE OF BONDS FROM PUBLIC Purchase of a $1000 bond from public... New reserves $800 Excess Reserves $4000 Bank System Lending $200 Required reserves $1000 Initial Deposit Total Increase in Money Supply ($5000) Someone deposits $1000 in new Reserves at a bank. New reserves $800 Excess Reserves $4000 Bank System Lending $200 Required reserves $1000 Initial Deposit Total Increase in Money Supply ($4000) Fed Buys A $1,000 Bond From Joe’s Bank New reserves $1,000 20% RR Excess Reserves $5,000 PMC thru Bank Lending TMS is $5000 OUTCOME OF MONEY EXPANSION $100 New reserves $80 Excess reserves $20 Required reserves Leakages exist...(Savings) Currency Drains $100 $400 Initial Bank system lending Deposit Excess Reserves Money Created $100 New reserves Injections: $80 Excess reserves $20 Required reserves Additional Spending into Income – Expenditures stream: Investment, $100 G, or Xn $400 Bank system lending Money Created Initial Deposit UNEMPLOYMENT Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment Structural Unemployment Cyclical Unemployment Natural rate of Unemployment = Structural + Frictional (Around 4-5%) LOANABLE FUNDS MARKET real interest rate S This graph shows how the supply and demand for loanable funds affects real interest rates r D Q Quantity of Loanable Funds Loanable Funds Market Graph (Long-Term Interest Rates) What changes Supply: 1. Increase in Household savings 2. Increase in Gov’t savings 3. Increase in Business savings 4. Increase in Business savings 5. Increase in Foreigners’ savings What changes Demand: 1. Increase in Household borrowing 2. Increase in business Investment 3. Increase in Foreign borrowing 4. Increase in Government borrowing (When the gov’t has a budget deficit!) = (the crowding out effect) Price Index Price Index Price of market basket in specific year in a given = --------------------------------------------X 100 Year Price of same market basket in base year Real GDP = Nominal GDP ------------------------------Price Index X 100 Remembering the difference between Real and Nominal Nominal: with Inflation Real: Adjusted for Inflation Nominal vs. Real 11% = + 5% Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate 6% Inflation Premium Real Interest Rate [Nominal I.R. – inflation rate = Real I.R.] 16% - 6 % Nominal Inflation Interest Premium Rate = 10 % Real Interest Rate Demand-Pull Inflation vs. Cost-Push Inflation DEMAND-PULL INFLATION ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 c P3 b P2 a P1 AD2 AD1 o Q1 Real domestic output COST-PUSH INFLATION Occurs when short-run AS shifts left ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 b P2 a P1 AD1 o Q2 Q1 Real domestic output COST-PUSH INFLATION Government response with increased AD ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 c P3 b P2 a P1 Even higher price levels AD2 AD1 o Q2 Q1 Real domestic output COST-PUSH INFLATION ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 b P2 a P1 AD1 o Q2 Q1 Real domestic output COST-PUSH INFLATION If government allows a recession to occur ASLR AS2 Price Level AS1 b P2 a P1 Nominal wages fall (which increases AS & AS returns to its original location AD1 o Q2 Q1 Real domestic output People must believe Fed is serious about stopping inflation. Higher expectations decreases Aggregate Supply. THE PHILLIPS CURVE CONCEPT Annual rate of inflation (percent) 7 As inflation declines... 6 5 Unemployment increases 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Unemployment rate (percent) THE PHILLIPS CURVE CONCEPT LRPC = Natural Rate of Unemployment Annual rate of inflation (percent) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Unemployment rate (percent) GENERAL EXAM ADVICE Free Response: • Do not restate question • Use correct terminology • Even if a graph is not required, draw one anyway and explain. • Use same outline as question • Use Good Handwriting GENERAL EXAM ADVICE • Draw graphs large enough for the reader to tell what’s going on. • Explain your reasoning: “the price increased”, why? • No Calculators