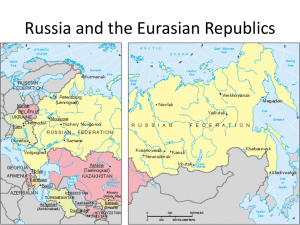
Russian and Eurasian Republics
advertisement

Russia and Eurasian Republics ©2012, TESCCC Grade 6 Unit 6, Lesson 2 Review from the last lesson: • Russia had a king (Czar) • Russia had a revolution and replaced the Czar with a different form of government. • Leader: Lenin; Communism (totalitarian government) • Name change: Russia to U.S.S.R. • Size change: small to big to bigger (many small countries around the Soviet Union soon became forcefully part of the Soviet Union. • Their ethnicity was different but the people did not have the means or power to “take on” the powerful Soviet Union. • They were forced to follow the Soviet Unions way of life, and some people felt like they lost their identity. • Change would soon follow after 1991, when ethnic groups in some of the Russian Republics (states) broke away from Russia. ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC What is an ethnic group? • Ethnicity: belonging to a group that has a common language, religion, same cultural traditions. ©2012, TESCCC Russia and Eurasian Republics (Relative Location to the rest of Asia) ©2012, TESCCC Caspian Sea Black Sea ©2012, TESCCC Russian Topography ©2012, TESCCC Ethnic Map of Russia Light Brown: Russian, Green: Turkic, Yellow: Caucasian, Blue: Iranian, Beige: Mongolian ©2012, TESCCC Outline of Russia and Eurasian Republics ©2012, TESCCC Russian Republics 1. Adygea 2. Altai 3. Bashkortostan 4. Buryatia 5. Dagestan 6. Ingushetia 7. Kabardino-Balkaria 8. Kalmykia 9. Karachay–Cherkessia 10. Karelia 11. Komi 12. Mari El 13. Mordovia 14. Sakha (Yakutia) 15. North Ossetia–Alania 16. Tatarstan 17. Tuva 18. Udmurtia 19. Khakassia 20. Chechnya 21. Chuvashia ©2012, TESCCC Resources Natural Resources Department of Defense (manufacture, distribution, etc.) Petroleum Deposits Oil and Gas Pipelines ©2012, TESCCC CULTURE: RUSSIA AND EURASIAN REPUBLICS ©2012, TESCCC Russian Culture ©2012, TESCCC ©2012, TESCCC