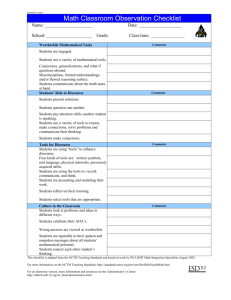
Grade 3 Second Trimester
advertisement
Symphony Math The Importance of a Focused Math Curriculum Hungary Latvia Netherlands Canada France Germany Japan Korea Poland Austria Finland Australia Norway Hong Kong-China Belgium Iceland Denmark New Zealand Liechtenstein Czech Republic Spain Luxembourg Macao-China Ireland Slovak Republic Sweden Switzerland Source: OECD PISA 2003 database The Nation’s Report Card ‣ Less than one-third of US students are at or above the proficient level for math -- National Center for Educational Statistics, 2005 US Congress Protecting America’s Competitive Edge Act ‣ Designed to raise the number of math and science teachers ‣ Seeks to build interest in math and science National Center on Education & the Economy “A world in which routine work is largely done by machines is a world in which mathematical reasoning will be no less important than math facts” Math Now Similar to Reading First: ‣ Students must receive a “firm grounding in math and science.” ‣ Courses must be “rigorous enough to compete with other nations.” ‣ Pledges “early help to students who struggle with math.” ‣ Creation of National Math Panel 1989 NCTM Topics by Grade Center for Research in Math & Science Education, Michigan State University Topics Covered by Top Achieving Countries Center for Research in Math & Science Education, Michigan State University 1989 NCTM Topics by Grade Center for Research in Math & Science Education, Michigan State University NCTM vs Top Achieving Countries Number of Topics Grade TIMMS Test Item 4th Grade “There are 600 balls in a box, and 1/3 of the balls are red. How many red balls are in the box?” Changing Course “Teachers face long lists of learning expectations to address at each grade level, with many topics repeating from year to year. Lacking clear, consistent priorities and focus, teachers stretch to find the time to present important mathematical topics effectively and in depth.” -- NCTM Curriculum Focal Points “A Mile Wide and an Inch Thick” NCTM Standards create two problems: 1. A long list of objectives suggests the objectives are the end points -- instead of foundational components of an integrated and hierarchical system. 2. The NCTM standards treat all objectives on the list as if they are of equal importance . . . which is not true. Learning Descriptors by State 2006 Grade Four -- Math # LE’s Negative Outcomes NCTM argues that a checklist approach produces the following outcomes: ‣The need to repeat instruction of key topics throughout the grades ‣Poor performance in Algebra ‣Poor math understanding by low-income students Grade 3 Benchmarks Grade 3 Benchmarks Grade 3 Second Trimester Add and subtract multi-digit numbers Solve problems based on practical situations Immediate recall of # facts to 81 (+,-,x) Recall division facts through 9’s Divide a two digit number by a one digit number Select appropriate units of measurement Measure length, area, volume, weight & temp. Identify perimeter and area Use coins and bills to equal given $ amounts Grade 3 Second Trimester Round numbers to tens and hundreds Immediately recall addition and subtraction facts “ItModel is acknowledged that with and explain multiplication individual differences, some students Model and explain division will be repeating ready and to go beyond a Create increasing patterns particular benchmark, and others Use patterns to solve problems may be in need of additional Identify missing terms and numbers in sentences instructional support or remediation.” Complete number sentences with (+,-,<,>,=) Read time to the nearest minute NCTM Recommends ‣ Instruction should devote “the vast majority of attention” to the most significant mathematical concepts. ‣ Focus on developing problem solving, reasoning, and critical thinking skills. ‣ Develop deep understanding, mathematical fluency, and an ability to generalize. Florida’s Revised Standards Grade Four -- Math # LE’s Symphony Math