TOPIC 7 and 8
advertisement

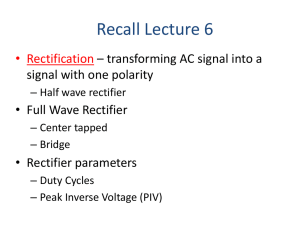
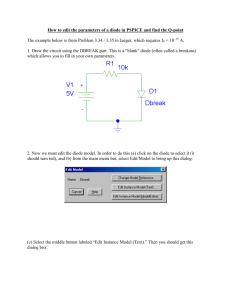
Diodes 1. Basic diode concept. 2. Load-line analysis of diode circuit. 3. Zener-diode voltage regulator circuit. 4. Ideal-diode model. 5. Applications of diodes. BASIC DIODE CONCEPTS A pn junction Drift and diffusion currents in a pn junction Forward- and reverse-biased pn junctions Figure 9.7 Semiconductor diode i-v characteristic Figure 9.8, 9.9 Semiconductor diode circuit symbol The i-v characteristic of the semiconductor diode Figure 9.10 Shockley Equation vD iD I s exp nVT 1 kT VT q k = 1.38 × 10–23 J/K is Boltzmann’s constant and q = 1.60 × 10–19 C is the magnitude of the electrical charge of an electron. At a temperature of 300 K, we haveV 26 mV T Exercise 10.1 At a temperature of 300K, a certain junction diode has iD = 0.1mA for vD = 0.6V. Assume that n is unity and use VT = 0.026V. find the value of the saturation current Is. vD iD I s exp nVT 1 iD Is exp( vD / nVT ) 1 4 10 exp( 0.6 / 0.026 ) 1 9.502 10 15 A LOAD-LINE ANASYSIS OF DIODE CIRCUITS LOAD-LINE ANALYSIS OF DIODE CIRCUITS By applying KVL, we get VSS Ri D v D But two unknowns, we need one more equation relating iD and vD to solve the problem. Example 10.1 If the circuit of Figure 10.5 has Vss = 2V, R = 1kW, and a diode with the characteristic shown in Figure 10.7, find the diode voltage and current at the operating point. Example 10.2 Repeat Example 10.1 if Vss = 10V, R = 10kW Vss = i R + VD Vss = 2, R = 1k Vss=10, R=10k ZENER-DIODE VOLTAGEREGULATOR CIRCUITS What is a Zener diode? Zener Diodes Diodes that are intended to operate in the breakdown region are called Zener diodes. Breakdown region ZENER-DIODE VOLTAGEREGULATOR CIRCUITS A voltage regulator circuit provides a nearly constant voltage to a load from a variable source. VSS Ri D vD 0 Example 10.3 The voltage-regulator circuit of Figure 10.9 has R = 1kW and use a Zener diode having the characteristic shown in Figure 10.10. Find the output voltage for Vss = 15V. Repeat for Vss = 20V. R = 1k Vss + i R +VD = 0 i = 0, VD = -Vss VD = 0, i = Vss/R IDEAL-DIODE MODEL IDEAL-DIODE MODEL The ideal diode acts as a short circuit for forward currents and as an open circuit with reverse voltage applied. Large-signal on/off diode model Figure 9.11 Circuit containing ideal diode Circuit of Figure 9.12, assuming that the ideal diode conducts Figure 9.13 Figure 9.12, 9.13, 9.14 Circuit of Figure 9.12, assuming that the ideal diode does not conduct Figure 9.14 Figure 9.16 Figure 9.15, 9.16, 9.17 Figure 9.17 Summary of Guidelines to analysis ideal-diode circuits APPLICATION OF DIODES DC power supply Figure 9.45 RECTIFIER CIRCUITS Half-Wave Rectifier Circuits Ideal diode rectifier input and output voltages Figure 9.20, 9.21 As Vs reaches VB, then diode starts to conduct Vr/ 2 I LT C Vr Vr V L Vm 2 Full-Wave Rectifier Circuits Full-wave rectifier Operation of bridge rectifier Figure 9.42 (a) A Zener diode voltage regulator; (b) (b) simplified circuit for Zener regulator Figure 9.49