PPT #1 Roots of America
advertisement

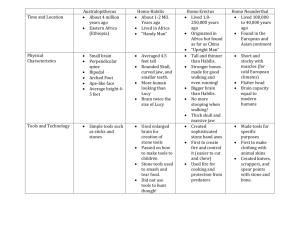
The Roots of America Objectives • Understand how people may have first reached the Americas. • Find out how people learned to farm. • Explore the civilizations of the Mayas, Aztecs, and Incas. Terms and People • glacier – thick sheet of ice • irrigate – to water crops by channeling water from rivers or streams • surplus – excess; quantity that is left over • civilization – an advanced culture in which people have developed cities, science, and industries How did early civilizations develop in the Americas? Scientists have several theories about how people first came to the Americas. One theory says people migrated over a land bridge. One theory says people came by boat. Between 10,000 and 100,000 years ago, much of the world was covered by glaciers. As more of the world’s water froze, the level of the oceans dropped, and a land bridge appeared between Siberia and Alaska. Today, that land bridge lies under a narrow waterway called the Bering Strait. Many scientists think people first came to North America between 20,000 and 30,000 years ago. They believe that hunters crossed the land bridge in pursuit of animals such as the woolly mammoth. Over thousands of years, people spread across North and South America. The coastal-route theory says that people crossed the arctic waters by boat and traveled southward along the Pacific coast. Many Native American groups dismiss both theories in favor of their own creation stories. For centuries, early humans could fill most of their needs by hunting, but then many of the larger animals began to disappear. Hunters became gatherers, traveling around and searching for wild plants and small game. gatherers hunters About 8,000 years ago, gatherers in Mexico began growing food, including squash and lima beans. This discovery of farming meant that families no longer had to wander in search of food. Farmers began to irrigate and learned to raise animals. The population grew rapidly, and once they began to produce surplus food, Native Americans started trading with others. Some farming communities grew into cities, which became centers of government and religious life. With the development of cities came the beginnings of civilization. Ways of Life Hunting and Gathering • In many culture areas, women gathered plants and roots, and men hunted and fished. Farming • In other culture areas, Native Americans grew crops suited to the climate in which they lived. • Populations were much larger in farming areas than in non-farming areas. Trading • Trade was common in all culture areas. • Seashells or beads were used as currency in some areas. Many Native Americans felt a close relationship to the natural world. They believed that spirits dwelled in nature and that these spirits were part of their daily lives. Native American storytellers passed down their beliefs and history from generation to generation. Well before 10,000 B.C., Native Americans had spread across the North American continent. Native American tribes built different kinds of homes. The types of houses they built depended on the climate and the geography in the region where they lived. People of the Arctic, Subarctic, and Pacific Northwest People of the Arctic • They lived in a bitterly cold land. People of the Subarctic • They lived in dense forests in a land too cold for farming. People of the Pacific Northwest • There were plenty of animals and plants where they lived, so they could live in permanent settlements even though they were not farmers. • They ate fish, shellfish, and birds and hunted marine mammals from kayaks. • They hunted caribou, moose, and bear. People of the Far West and the Southwest People of the Far West • They lived in different geographic regions, ranging from cold northern forests and grasslands to hot southern deserts. • Housing types ranged from pit houses to bark houses to wooden houses. People of the Southwest • The climate in their region was dry most of the year but wet in July and August. • Some people farmed; others hunted. The Pueblo people, such as the Hopis and Zunis, had stable towns with houses made of adobe. The towns lasted for hundreds of years. In the eastern Plains, the people farmed and lived in earth lodges. Much of the western Plains was too dry to farm, so the people hunted buffalo, which provided them with most of the things they needed to live. People in the western Plains lived in tepees or round pits in the ground. People of the Eastern Woodlands Early People of the Eastern Woodlands • The earliest woodlands people hunted, fished, and gathered nuts and berries. • By about A.D. 1000, some woodlands people had begun farming. Algonquian • These people spoke Algonquian languages People and lived in southern Canada, the Great Lakes area, and along the Atlantic coast to Virginia. Iroquois People • These groups of people spoke Iroquoian languages and lived in what is now New York. People of the Southeast Cherokees and Creeks • The land and the climate of the southeast supported farming. • The Cherokees and the Creeks built wooden-frame houses covered with straw mats and plastered with mud clay. Natchez People • These people lived on the Gulf Coast. • They created a complex society with a ruler, nobles, and commoners. Over the centuries, several civilizations rose and declined in the Americas: • the Mayas • the Aztecs • the Incas The Mayas Time Period • Between A.D. 250 and A.D. 900 Location • Present-day Mexico and Central America Achievements • Built splendid cities • Developed arts, a system of government, and a written language • Created the most accurate calendar known until modern times Around A.D. 900, the Mayas began to abandon their cities, perhaps because of disease or overpopulation. The Aztecs Time Period • Between 1325 and 1521 Location • Present-day Mexico Achievements • Built the city Tenochtitlán, which may have been the biggest city in the world at the time • Built Tenochtitlán on islands in a large lake and connected them by stone roadways On a series of islands in a large lake, the Aztecs built a great capital city, Tenochtitlán, on the site of present-day Mexico City. Tenochtitlán Population • More than 200,000 people lived there at the city’s height. Farming • Many farmers raised crops on floating platforms. Religion • Religion dominated Aztec life. • The center of the city had dozens of temples that honored Aztec gods. • The Aztecs practiced human sacrifice as an offering to their gods. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F3QA2J 9UxJE&feature=related During the 1400s, Aztec armies brought half of modern-day Mexico under their control. The Aztecs were harsh rulers, and their subjects would eventually turn on them when Europeans came to conquer the region. Aztecs Europeans subjects The Incas Time Period • Between the early 1400s and 1533 Location • Down the coast of South America along the Andes, across the Atacama desert, and to the fringes of the Amazon rain forest Achievements • Built the largest empire in the world in the 1400s • Buildings of huge stones shaped to fit together • Roads, walls, canals, and bridges • Fine weavings and metalwork Encounter of 1492 1492 A. Columbus leads a Spanish fleet to the Bahamas- changed history forever. B. Tainos were Native Americans he met there. Within 100 years, the entire Taino population was destroyed. Encounter of 1492 Columbian Exchange The encounter started a a worldwide exchange of good and ideas. Food, technology, arts, language, medicine, Government. The Columbian Exchange Positive Changes • The Europeans introduced new food plants and domestic animals to the Western hemisphere. • The Americas introduced new food plants and animals to the rest of the world, which now account for nearly one-third of the world’s food supply. Negative Changes • Europeans enslaved Native Americans as they mined for gold. • Contagious diseases brought by Europeans killed Native Americans by the thousands. KNOW IT SHOW GAME Take out a Piece of Paper. Number 1-10 Write down the letter of the answer for each question. Read, Set Go…. Objectives • Learn about the earliest peoples of North America. • Discover what different groups of Native Americans had in common. • Explore the impact of geography on Native American cultures. Terms and People • culture – way of life • culture area – region in which groups of people have a similar way of life Terms and People (continued) • adobe – sun-dried brick • clans – groups of families that were related to one another • sachem – tribal chief How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? In North America, groups of people developed unique cultures. Around 3,000 years ago, various groups began to emerge in an area stretching from the Appalachian Mountains to the Mississippi Valley. These people are called Mound Builders because they constructed large piles of earth as burial places or as the foundations of buildings. One group of Mound Builders, the Mississippians, built the first cities in North America. Scholars classify Native Americans into several culture areas. Ways of Life Hunting and Gathering • In many culture areas, women gathered plants and roots, and men hunted and fished. Farming • In other culture areas, Native Americans grew crops suited to the climate in which they lived. • Populations were much larger in farming areas than in non-farming areas. Trading • Trade was common in all culture areas. • Seashells or beads were used as currency in some areas. Well before 10,000 B.C., Native American s had spread across the North American continent. Native American tribes built different kinds of homes. The types of houses they built depended on the climate and the geography in the region where they lived. People of the Arctic, Subarctic, and Pacific Northwest People of the Arctic • They lived in a bitterly cold land. People of the Subarctic • They lived in dense forests in a land too cold for farming. • They ate fish, shellfish, and birds and hunted marine mammals from kayaks. • They hunted caribou, moose, and bear. People of the Pacific Northwest • There were plenty of animals and plants where they lived, so they could live in permanent settlements even though they were not farmers. The Pueblo people, such as the Hopis and Zunis, had stable towns with houses made of adobe. The towns lasted for hundreds of years. People of the Eastern Woodlands Early People of the Eastern Woodlands • The earliest woodlands people hunted, fished, and gathered nuts and berries. • By about A.D. 1000, some woodlands people had begun farming. Algonquian • These people spoke Algonquian languages People and lived in southern Canada, the Great Lakes area, and along the Atlantic coast to Virginia. Iroquois People • These groups of people spoke Iroquoian languages and lived in what is now New York. The Iroquois were made up of five distinct nations, and each nation was made up of clans. Women had great influence in Iroquois society: Membership in a clan was passed from a mother to her children. Women owned all the property that belonged to a clan and chose the clan’s sachem. During the 1500s, the five Iroquois nations went through a period of constant warfare. When the nations finally stopped fighting, they established the League of the Iroquois, a council that made laws to keep the peace. The Iroquois wrote their own constitution. Objectives • Learn about the role played by Muslims in world trade. • Discover how great trading states rose in East Africa and West Africa. • Find out how China dominated an important trade route across Asia. Terms and People • Muhammad – the prophet and founder of Islam • Mansa Musa – a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height • navigation – the science of locating the position and plotting the course of ships • Zheng He – a Chinese explorer who made several voyages to trade with nations in Asia and Africa How did trade link Europe, Africa, and Asia? From the earliest times, trade linked groups who lived at great distances from one another. Merchants carried their cultures with them as they traveled along their established trade routes. The Silk Road, one of the great trade routes of ancient times, stretched 5,000 miles from China to Persia. Merchants on the Silk Road brought silk, jade, pottery, spices, and bronze goods from China to Middle Eastern and European markets. Along the way, they traded in the Middle East for spices and other products. Trade in Africa began with Egypt in 3100 B.C. In about A.D. 1000, trade centers began to appear in eastern Africa. The growth in trade was also linked to the rise of the religion of Islam. In the 600s, Islam was founded on the Arabian Peninsula by the prophet Muhammad. Muslims believe in one God, and their sacred book is called the Quran. Islam spread rapidly when Arab armies swept across North Africa and into Spain. Muslim merchants also spread their religion far into Africa, and from Persia to India. Millions of people across Europe, Asia, and Africa became Muslims. By the 1500s, a global trading network linked the civilizations of Europe, Africa, and Asia. The Silk Road became less important when alternative sea routes were discovered. Objectives • Understand the importance of the JudeoChristian tradition. • Learn how Greece and Rome shaped ideas about government and law. • Discover the impact of the Crusades and the Renaissance on Europe. • Find out why Europeans began to look beyond their borders. What major influences shaped European civilization? European beliefs and values were influenced by Judaism and Christianity, collectively referred to as the JudeoChristian tradition. The political traditions of Greece and Rome also influenced Europe. Christianity Christian Beliefs • The religion is based on the belief that Jesus was God in human form and that he came to Earth to save the world. Teachings of Jesus • His teachings emphasized love, mercy, and forgiveness. • He taught that all people have an equal chance for salvation. Spread of Christianity • Jesus’ teachings appealed to the poor and the oppressed. • This helped the religion spread from the Middle East across Europe. The Renaissance Time Period The Renaissance, a rebirth of learning in Europe, began in the 1300s. Philosophy and Art European scholars and artists rediscovered classical Greek and Roman texts and art. Science and Inventions Johann Gutenberg’s printing press made more books available and boosted literacy rates. Powerful New NationStates The new nations—Spain, Portugal, France, and England—shifted important trade routes from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic Ocean. Beginning of the Age of Exploration Center for Exploration • In the 1400s, Prince Henry the Navigator set up a center for exploration at Sagres, Portugal. • There, sailors learned to use the magnetic compass and the astrolabe. Water Route Around Africa • By 1498, Portuguese sailor Vasco da Gama passed the southern tip of Africa on his way to India. • His course became an important trade route and helped boost Portuguese wealth and power. Hip Hop History Long ago, much of the world was covered by ice layers These thick sheets of ice are called glaciers As the water froze, the ocean level dropped Revealing dry land on which people could walk Watering crops by channeling water from other places Like rivers and streams is a method called irrigation Advanced cultures with cities, science, and industries We name them with the term civilizations People developed unique ways of life they were known for The way of life of a people is called their culture The Pueblo people like the Zunis and Hopis Made their homes from brick called adobe In the Arctic, the land was harsh and vast People hunted in small boats called kayaks Across the ocean, major trade started This helped to spread Islam founded by Muhammad The West African Kingdom of Mali’s ruler Was a Muslim king named Mansa Musa The Chinese made advancements in location And plotting ship’s courses it’s called navigation The idea that one God exists is A belief called monotheism Christianity was started by a Jewish teacher Who began to preach; his name was Jesus Ordinary citizens make decisions in an assembly This form of government is direct democracy People choose representatives to govern This type of government is called a republic