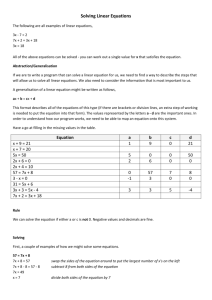
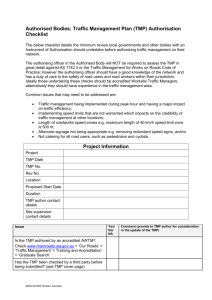
Work Zone Impacts
advertisement

Work Zone Impacts Module 5 What is a WZ Impact Assessment? WZ Impact Assessment is the process of understanding the safety and mobility impacts of a road construction or maintenance project Basic Concept Determine impacts of project? Acceptable? If yes, no problem Unacceptable? (Significant project) Can strategy be found to mitigate impacts to acceptable level? Yes – develop TMP No – determine best strategy Advise stakeholders of possible problems WZ Impacts Considerations Maximizing Safety Road Users Workers Maximizing mobility and accessibility Road user costs Emergency services Businesses Constructability Building projects effectively and efficiently Benefits of Assessing Impacts Identify and understand all impacts of the project Identify “significant projects” and determine suitable TMP Aid in identifying and evaluating alternative strategies Monitor and manage WZ impacts during construction Mobility Impacts Mobility Issues Delay Reduced quality of life issues Significant Projects – agency definition Reduced Speeds Queues and complete stoppages Freight Interference Travel time reliability – biggest concern Delayed deliveries Unanticipated costs Emergency response Causes of Recurring Congestion Non-recurring Congestion Safety Impacts Road user exposure to hazards Will staging create safety hazards greater than existing? Worker exposure to traffic Staging allow for positive protection? Geometrics during phases Availability of law enforcement Speed reduction necessary/considered? Business Impacts Access Temporary Signing Pavement Advance entrances notification of phase changes Keep owners informed Work Schedules Christmas Weekends shopping season Residential Access Impacts Keep residents informed as project begins and progresses Neighborhood association meetings, newsletters, mailings, etc. Maintain access if possible Incident Response Impacts Ensure access to all areas for emergency vehicles Hospitals nearby? Trauma centers? Plan to provide access within work site Identify alternate routes Pre-sign for use during incidents? Transit Impacts Transit route through project? Bus stops Alternate routes available Include in PR information Pedestrian Impacts MUTCD Part 6D: If project affects the movement of pedestrians, adequate pedestrian access and walkways shall be provided. Impact Assessment Proactive versus reactive Use early in the TMP Development process to identify and estimate the magnitude of the impacts Assess impacts on regional basis Use assessment to help evaluate various strategies for mitigating impacts Possibly use assessments to justify TCP revisions after award of project Goal A good impact assessment process should keep agency from being surprised after project is underway – when it is too late to consider strategies to reduce impacts. Mobility Impact Assessment Tools Historical knowledge – “Lane closures do not cause backups on this segment of road…” Various levels of tools for more detailed analysis Sketch Planning Tools Travel Demand Models Traffic Signal Optimization Tools Macroscopic Simulation Models Mesoscopic Simulation Models Microscopic Simulation Models WZ Analysis Tool Model Spectrum Transportation Model Approaches macro meso micro Macroscopic Delay Estimation Tools Basic Concept macro Strengths Special-purpose delay estimators for work zones Examples: QuickZone, DELAYE, QUEWZ-98 Relatively easy-to-use, rapid analysis Weaknesses Limited capability beyond modeling simple “pipeline” analyses High-level analysis Macroscopic Regional Planning Models macro Basic Concept Strengths Steady-state liquid flow Examples: TRANPLAN, EMME/2, TransCAD, others Can handle very large networks (metro areas) Weaknesses Not time sensitive Complex models, relatively expensive to build and maintain Mesoscopic Basic Concept Examples: DYNASMART-P, DYNAMEQ Strengths Particle Flow Vehicles are located on roadways but not specific lanes Can model sub-regional areas in major metropolitan areas Weaknesses Not detailed enough for some operational strategies (e.g., complex signal control) Model complexity is high, data and calibration resources are significant Microscopic CORSIM, VISSIM, and others Model individual vehicle movements Requires extensive resources to establish and calibrate Usually reserved for large and complex projects unless existing model can be utilized Work Zone Analysis Primer Aid in selection of the correct tool to use in the analysis Provide guidance to reviewer to ensure appropriate tool was selected for project Work Zone Modeling and Simulation Volume IX Case studies Aid for analysts How Should Results of Assessment Be Utilized? Formulate policies Identify strategies that will minimize impacts Identify critical issues to address in development of TMP Alternate route availability Effects on businesses and residents Results Used to Formulate Policy Ohio DOT MOT/PLC Policy TMP Development Process Identify Early in Process Analyzing Strategies MNDOT Specific – Fig. 1 Impacts Assessment at Project Level Consider WZ impacts in the assessments that are performed during alternatives evaluations. Allocate sufficient funds Address impacts of multiple projects Work Zone Impacts Assessment During Preliminary Engineering 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Compile project /WZ Scope Information for Alternatives Assess WZ Impacts of Alternatives at a Screening Level Analyze Potential Impacts (optional) Identify WZ Management Strategies Perform Plan/Program Level WZ Impacts Assessment Compile Planning-Level Work Zone Strategy Compile project /WZ Scope Information for the Alternatives The major categories of information that may be needed include the following: Project Scope Roadway/Traffic Characteristics Other Influencing Factors Identify WZ Management Strategies Issues To Be Addressed In Identifying WZ Management Strategies: TTC Strategies TO and PI Strategies. Coordination Strategies with Other Projects. Costs for the Management Strategies How to Incorporate WZ Impacts Assessments During Design Compile Preliminary Engineering Materials Reassess WZ Impacts Develop/Recommend Final Construction Staging and TMP Advertise and Award Contract Work Zone Impacts Assessment During Construction Assess the impact of any proposed changes prior to the start of work Implement the TMP. Actively monitor and manage work zone impacts during construction. Revise the TMP and implement appropriate revisions, if necessary. Document any findings or lessons for use in performance assessments. Example Checklist DDOT Example Checklist DDOT Guide Example Checklist DDOT Guide Example Checklist DDOT Guide Michigan TMP Template Michigan TMP Template http://www.ops.fhwa.dot.gov/wz/resources/final_rule/mdot_tmp_templ ate/mdot_tmp_template.pdf Review and Discussion When should the Impacts Assessment take place in the TMP process? Does your state have a procedure in place to assure impacts are factored in to the project planning and design?