Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
advertisement

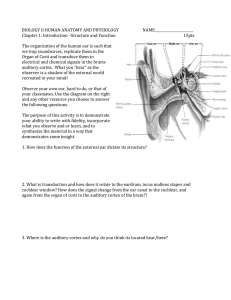
The “Ear” is housed within the TEMPORAL BONE The Outer Ear Consists of: The Pinna External Auditory cartilaginous, highly Canal (or external variable in appearance, auditory meatus) - 2.5 some landmarks. cm tube. Pinna Landmarks Helix Antihelix Concha Tragus Intertragal Notch Antitragus External Auditory Canal lateral portion-cartilage medial portion-osseous lined with epidermal (skin) tissue hairs in lateral part cerumen (ear wax) secreted in lateral part. Outer Ear Functions Amplification / Filtering Protection Localization The Middle Ear: A cleft within the temporal bone Lining is mucous membrane Tympanic Membrane separates it from EAC Eustachian tube connects it to nasopharynx Also Connected to Mastoid Air Cells Middle Ear Structures 1- Malleus 2- Incus --Ossicles 3- Stapes 4- Tympanic Membrane (Eardrum) 5- Round Window 6- Eustachian Tube Middle Ear Muscles 1. The Stapedius Attaches to Stapes,Contracts in Response to Loud sounds, chewing, speaking; Facial (VIIth cranial) nerve 2. The Tensor Tympani Helps open Eustachian tube Middle Ear Functions Impedance Matching Filtering Acoustic Reflex These sounds get through the middle ear most readily INNER EAR Two Halves: Vestibular--transduces motion and pull of gravity Cochlear--transduces sound energy (Both use Hair Cells) Within S. Media is the Organ of Corti The Stereocilia on IHCs and OHCs OHCs (at top) V or W shaped ranks IHC (at bottom) straight line ranks Cochlear Functions Transduction- Converting acousticalmechanical energy into electro-chemical energy. Frequency Analysis-Breaking sound up into its component frequencies Bekesy’s Traveling Wave Active Tuning from OHCs Afferent & Efferent Neurons IHC activation alters firing rate Afferent neurons have their cell bodies in the Spiral Ganglion (4) Major Components of the Central Auditory Nervous System (CANS) VIIIth cranial nerve Cochlear Nucleus <Trapezoid Body> Superior Olivary Complex Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculus Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex Brainstem Mid-brain Thalamus Temporal Lobe AUDITORY CORTEX MEDIAL GENICULATE BODY INFERIOR COLLICULUS LATERAL LEMNISCUS SUPERIOR OLIVARY COMPLEX COCHLEAR NUCLEUS Mid-Saggital View of Brain 4th Ventricle Corpus Callosum Cerebellum Thalamus Pons Cortical Processing Pattern Recognition Duration Discrimination Localization of Sounds Selective Attention Cerebral Dominance/Laterality Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli