Question 1
advertisement
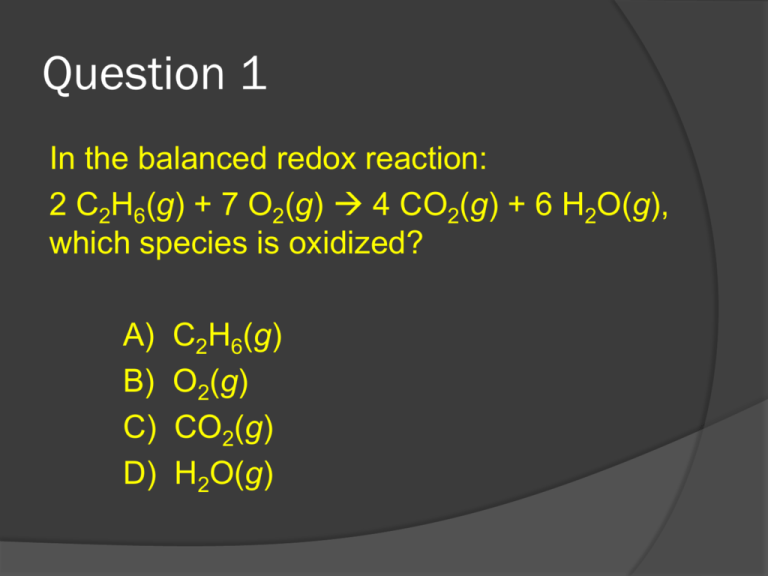
Question 1 In the balanced redox reaction: 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g), which species is oxidized? A) B) C) D) C2H6(g) O2(g) CO2(g) H2O(g) Question 1 In the balanced redox reaction: 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g), which species is oxidized? A) B) C) D) C2H6(g) O2(g) CO2(g) H2O(g) Question 2 The expression for the equilibrium constant, K, for the general reaction: a A + b B c C + d D is: K = [C][D] [A][B] TRUE or FALSE? Question 2 The expression for the equilibrium constant, K, for the general reaction: a A + b B c C + d D is: K = [C][D] [A][B] TRUE or FALSE? Question 3 Which species can be a Brønsted–Lowry base? A) CO32– B) HBr C) H2CO3 D) NH4+ Question 3 Which species can be a Brønsted–Lowry base? A) CO32– B) HBr C) H2CO3 D) NH4+ Question 4 Which species is the conjugate base of NH3? A) NH4+ D) H2O B) NH2 E) NH4OH C) NH2– Question 4 Which species is the conjugate base of NH3? A) NH4+ D) H2O B) NH2 E) NH4OH C) NH2– Question 5 Phosphorous-32 is used for organ imaging. How many neutrons are in this radioisotope? A) 15 B) 17 C) 32 D) 47 Question 5 Phosphorous-32 is used for organ imaging. How many neutrons are in this radioisotope? A) 15 B) 17 C) 32 D) 47 Question 6 The half-life (t1/2) of a radioactive isotope depends on: A) the amount of the radioisotope present. B) the isotope. C) the temperature. D) the pressure. E) All of the factors listed above. Question 6 The half-life (t1/2) of a radioactive isotope depends on: A) the amount of the radioisotope present. B) the isotope. C) the temperature. D) the pressure. E) All of the factors listed above. 1 0 e Question 7 In the galvanic cell created using zinc and copper placed in zinc sulfate and copper (II) sulfate solutions respectively, what is the standard potential of the cell? A) B) C) D) -0.76 V +0.34 V 1.10 V -0.42 V Reduction Reaction Zn2+ (aq) + 2e- Zn (s) E0 (v) -0.76 Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- Cu (s) +0.34 1 0 e Question 7 In the galvanic cell created using zinc and copper placed in zinc sulfate and copper (II) sulfate solutions respectively, what is the standard potential of the cell? A) B) C) D) -0.76 V +0.34 V 1.10 V -0.42 V Reduction Reaction Zn2+ (aq) + 2e- Zn (s) E0 (v) -0.76 Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- Cu (s) +0.34 1 0 e Question 8 In the galvanic cell created using zinc and copper placed in zinc sulfate and copper (II) sulfate solutions respectively, what substance coukd act as the salt bridge? A) B) C) D) Zinc sulfate Potassium chloride Copper sulfate Zinc metal 1 0 e Question 8 In the galvanic cell created using zinc and copper placed in zinc sulfate and copper (II) sulfate solutions respectively, what substance coukd act as the salt bridge? A) B) C) D) Zinc sulfate Potassium chloride Copper sulfate Zinc metal 1 0 e Question 9 Which species is a diprotic acid? A) Mg(OH)2 B) CH3COOH C) H2 D) H2CO3 1 0 e Question 9 Which species is a diprotic acid? A) Mg(OH)2 B) CH3COOH C) H2 D) H2CO3 1 0 e Question 10 Which compound is a weak acid? A) HNO3 B) HBr C) CH3COOH D) H2SO4 1 0 e Question 10 Which compound is a weak acid? A) HNO3 B) HBr C) CH3COOH D) H2SO4 1 0 e Question 11 What completes this nuclear equation: 65Cu 65Fe + 25 26 A) Alpha particle C) Positron B) Beta particle D) Gamma ray 1 0 e Question 11 What completes this nuclear equation: 65Cu 65Fe + 25 26 A) Alpha particle C) Positron B) Beta particle D) Gamma ray 1 0 e Question 12 Which has the greatest penetrating power? A) B) C) D) an alpha particle a gamma ray a beta particle All of the above have the same penetrating power. 1 0 e Question 12 Which has the greatest penetrating power? A) B) C) D) an alpha particle a gamma ray a beta particle All of the above have the same penetrating power. 1 0 e Question 13 When reactants can come together and form products, and products can come together to reform reactants the reaction is called a _____ reaction. 1 0 e Question 13 When reactants can come together and form products, and products can come together to reform reactants the reaction is called a _____ reaction. REVERSIBLE 1 0 e Question 14 What is the pH of a cleaning solution with a [H3O+] = 8.2 x 10–9 M H3O+? A) 5.9 C) 11.5 B) 8.1 D) 2.5 1 0 e Question 14 What is the pH of a cleaning solution with a [H3O+] = 8.2 x 10–9 M H3O+? A) 5.9 C) 11.5 B) 8.1 D) 2.5 1 0 e Question 15 Which solution has the highest pH? A) B) C) D) 1.9 x 10–8 M [H3O+] 1.0 x 10–7 M [H3O+] 1.0 x 10–2 M [H3O+] 5.1 x 10–4 M [H3O+] 1 0 e Question 15 Which solution has the highest pH? A) B) C) D) 1.9 x 10–8 M [H3O+] 1.0 x 10–7 M [H3O+] 1.0 x 10–2 M [H3O+] 5.1 x 10–4 M [H3O+]









