Electrical Potential Energy
advertisement

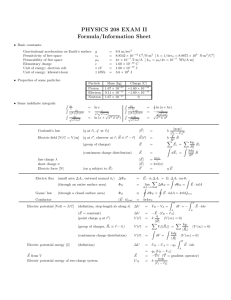
Electrical Energy and Capacitance Physics - Chapter 18 Ch. 18-1 (Pages 666-669) I. Electrical Energy & Electric Force Electrical potential energy - PE associated with an object due to position relative to an electric force. Results from interactions of 2 objects’ charges ΔPE electric change in electric potential energy (final minus initial) Factors determining PE electric 1. Charge 2. Strength of electric field 3. Position in the direction of the field PE = -q E d d = displacement from ref. point q = charge E = electric field strength electric PE electric= Kc (q1q2) r r = distance between charges in meters Kc=8.99 x 109 N(m2/C2) (pairs of charges) Reference point assumed to be infinity 18-2 Potential difference (p.670-675) Electric potential - electric potential energy of a charged particle in an electric field (divided by its charge) Electric potential (V) = electric potential energy charge of the particle V = PE electric q V is measured in volts 1 volt = 1 J/C Potential difference- change in electrical potential energy (V) *only changes in electric potential are significant and important ΔV = PE electric q ΔV Measured in volts (V) = 1 J/coulomb ΔV measures the change in energy per unit of charge A potential difference within a battery causes charge to move ex. 12 Volt car battery -positive terminal has electric potential of 12 V -negative terminal has electric potential of 0 V positive terminal has a higher electric potential then the negative terminal As 1 coulomb of charge moves from negative to the positive terminal the battery does work on the charge to increase the PE electric of the charge to 12 J of electric potential energy Each coulomb of charge that leaves the battery would have 12 J of energy This energy is given up to the parts of the device which is run from the battery 18-3 Capacitance Capacitor - a device used in electrical circuits to store charge A storehouse of charge Stores positive and negative charges separately Parallel-plate-capacitor-two metal plates separated by a small distance Connected to the 2 terminals of a battery (once charged, battery removed) Charge is removed from one plate and accumulates on another Capacitance- the ability of a conductor to store energy in the form of electrically separated charges Ratio of net charge on each plate to potential difference SI unit is the farad (F) = coulomb/volt Capacitance depends on the size, shape, and materials of the capacitor Larger plates = more storage of energy Materials between plates can change capacitance Charged capacitors release energy rapidly Ex. – camera flash, computer keyboard