The British Isles, Benelux States, and France
advertisement
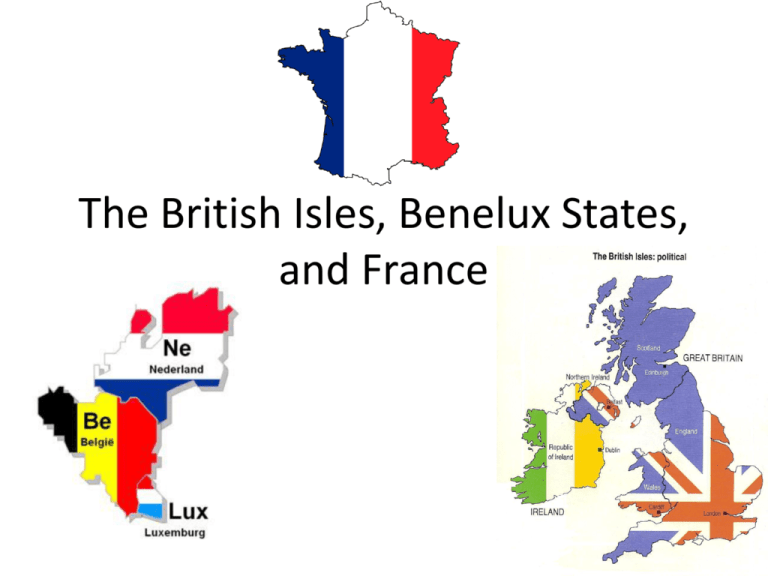
The British Isles, Benelux States, and France WARM UP 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Byzantine Empire M.A.I.N. Imperialism Romans Reparations Renaissance Alexander the Great a. humanism, the enlightenment b. Spread of Greek culture c. Spread of Christianity d. Republican form of Government e. Causes of WWI f. $$$ for war damages g. Taking over for raw resources and markets British Isles: History • Sequent Occupanceprocess of settlement by successive groups of people, each group creating its own, distinctive cultural landscape – – – – – Celts (Celtic) Romans Angles and Saxons Vikings William of Normandy British Isles: History British Isles: Culture Use pages 307-308 to create a double bubble map comparing and contrasting Ireland and Great Britain. IRELAND Great Britain British Isles: Economy • Industrial Revolutiontransition to machine based manufacturing (begins in 1800s) – 1st railroads & subways – Textile industry – G.B. dominates trade until 1900s • G.B.-oil, gas, service industries, tourism • Ireland- banking, computers, electronics The British Isles: • Read page 297, “The North Atlantic Drift.” • What climate factors allow farming in places as far north as Sweden and Iceland? France: History & Culture • Influenced by Gauls, Romans, Franks, and Vikings • 90% Roman Catholic • Paris is a primate city France: Economy • Read the “Economy” section on page 313. How has France’s physical geography influenced its economy today? The Benelux States • What is the European Union? • How did the relative location of the Benelux States lead to its creation? (315) The Benelux States • Belgium – Brussels • HQ for NATO • HQ for EU • Netherlands – The Hague • International Court of Justice • Luxembourg – High GDP per capita The Benelux States • Read “Polders” on page 293. • Define polder and dike. • In what other areas of the world might the Dutch techniques for creating polders be useful?