First Derivative Test
advertisement

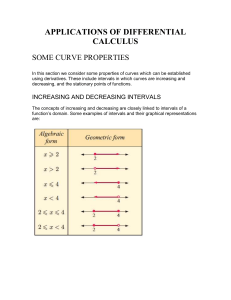
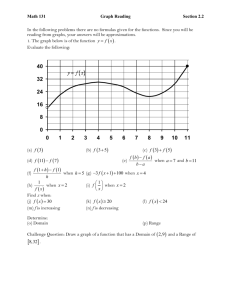
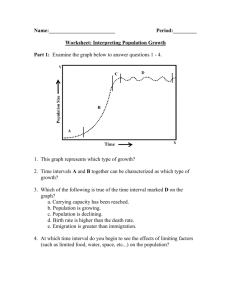
Increasing & Decreasing Functions and 1st Derivative Test Lesson 4.3 Increasing/Decreasing Functions • Consider the following function f(x) a • For all x < a we note that x1<x2 guarantees that f(x1) < f(x2) The function is said to be strictly increasing Increasing/Decreasing Functions • Similarly -- For all x > a we note that x1<x2 guarantees that f(x1) > f(x2) f(x) The function is said to be strictly decreasing a • If a function is either strictly decreasing or strictly increasing on an interval, it is said to be monotonic Test for Increasing and Decreasing Functions • If a function is differentiable and f ’(x) > 0 for all x on an interval, then it is strictly increasing • If a function is differentiable and f ’(x) < 0 for all x on an interval, then it is strictly decreasing • Consider how to find the intervals where the derivative is either negative or positive Test for Increasing and Decreasing Functions • Finding intervals where the derivative is negative or positive Find f ’(x) • f ‘(x) = 0 Determine where • f ‘(x) > 0 Critical numbers • f ‘(x) < 0 • f ‘(x) does not exist 1 3 f ( x) x 9 x 2 3 • Try for • Where is f(x) strictly increasing / decreasing Test for Increasing and Decreasing Functions • Determine f ‘(x) • Note graph of f’(x) • Where is it pos, neg f '( x) f ( x) f ‘(x) < 0 => f(x)f ‘(x) decreasing > 0 => f(x) increasing f ‘(x) > 0 => f(x) increasing • What does this tell us about f(x) First Derivative Test • Given that f ‘(x) = 0 at x = 3, x = -2, and x = 5.25 • How could we find whether these points are relative max or min? • Check f ‘(x) close to (left and right) the point in question • Thus, relative minf ‘(x) < 0 f ‘(x) > 0 on left on right First Derivative Test • Similarly, if f ‘(x) > 0 on left, f ‘(x) < 0 on right, • We have a relative maximum First Derivative Test • What if they are positive on both sides of the point in question? • This is called an inflection point Examples • Consider the following function f ( x) (2 x 1) ( x 9) 2 • Determine f ‘(x) • Set f ‘(x) = 0, solve • Find intervals 2 Assignment A • Lesson 4.3A • Page 226 • Exercises 1 – 57 EOO Application Problems • Consider the concentration of a medication in the bloodstream t hours after ingesting • Use different methods to determine when the concentration is greatest Table Graph Calculus 3t C (t ) 27 t 3 t0 Application Problems • A particle is moving along a line and its position is given by s(t ) t 2 7t 10 • What is the velocity of the particle at t = 1.5? • When is the particle moving in positive/negative direction? • When does the particle change direction? Application Problems • Consider bankruptcies (in 1000's) since 1988 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 594.6 643.0 725.5 880.4 845.3 1042.1 835.2 • Use calculator regression for a 4th degree polynomial Plot the data, plot the model Compare the maximum of the model, the maximum of the data Assignment B • Lesson 4.3 B • Page 227 • Exercises 95 – 101 all