File - Ms. halty's class
advertisement

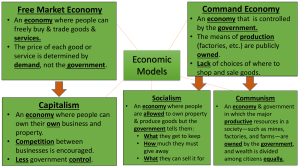
February 25, 2016 Get out reading-T Chart from yesterday Industrial Revolutions sparks new ways of thinking • Business leaders wanted less government intervention • Workers wanted more rights • Reformers wanted more government regulation Capitalism • Capitalism: – factors of production are privately owned – Goal is to make a profit – Don’t believe in helping poor workers because it would hurt the free market Capitalism • Based on laissez-faire economics – “let people do as they please” – Natural laws would promote economic growth • Adam Smith – Believed in free markets and free economy – Wrote “The Wealth of Nations” – Based beliefs on three natural laws Three Natural Laws • Law of self-interest – People work for their own good • Law of competition – Competition forces people to make a better product • Law of the “invisible hand” – Everyone working in own self interest will promote efficiency – Enough goods will be produced at the lowest price possible to meet demand in a market economy Socialism • Socialism: – factors of production are owned by the public – operate for the welfare of all – Believe it is the government and the wealthy people’s job to help out the poor members of society – Opposed to laissez-faire – Government should plan economy Marxism • Radical form of socialism • Coined by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in 1848 • Argued the Industrial Revolution had enriched the wealthy and impoverished the poor • Society was divided into “warring classes” of “haves” and “have nots” Communist Manifesto • Pamphlet written by Marx and Engels • Wealthy controlled the means of production while workers performed the labor • They argued the workers will unite and overthrow the wealth factory owners Communist Manifesto • Capitalism would destroy itself – Large corporations would buy up small factories and control all the wealth – Workers would revolt, seize factories, and produce necessary goods – Workers would spread wealth equally – Workers would control the government – Government would slowly diminish – The country would be ruled by a classless society – Finally, communism Communism • Communism: a complete form of socialism where all the land, mines, factories, railroads, and businesses are owned by all the people • Private property does not exist • All goods and services shared equally • Examples of Communism – Soviet Union, Cuba, China, Vietnam, North Korea Unions and Reforms • Union: voluntary labor associations formed by workers with the intent of fighting for workers rights – Shorter hours, better pay, better working conditions, job stability – Strike: refusal to work Reform Laws • Laws aimed at improving industrialization’s negative effects – Child labor, unsafe conditions, long workdays, poor pay • Factory Act of 1833: illegal to hire children under the age of 9 • The Ten Hours Act of 1847: limited the workday to 10 hours for women and children Reform Spreads • Abolition of Slavery: fight to end slave trade and slavery • Women’s rights: fought for suffrage and equal pay • Public Education: free public school for all children in the US