Anything new in Airway Management?
advertisement

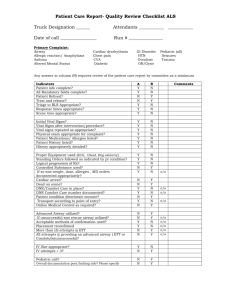
Anything new in Airway Management? Dr Adrian Burger Emergency Medicine Senior Registrar UCT/US So what do we do? • A,B,C’s…… • A is for clearing, opening and or securing the airway • Clearing - turn on side - suction - no more blind finger sweeps! Opening • Jaw thrust • Head Tilt Chin lift • Combined • Remember : C-spine stabilization Opening or securing the Airway • BMV • OPA/NPA • LMA • Combitube® • ETT Mask • Most basic piece of “airway” kit • Different types - clear, black - cushion around edge • Won’t maintain airway by self • Needs head tilt/chin lift or jaw thrust • Also needs Positive Pressure Ventilation Mask Positive Pressure Ventilation • Rescuer’s breathing efforts and one-way valve • Bag Mask Ventilation (BMV) Mask with one-way valve Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • Different colours = SIZE different sizes • Neonate to large adult 000 OO O 1 2 3 4 5 COLOUR Violet Blue Black White Green Orange Red Yellow Oropharyngeal Airways Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • Features: - single use - rounded edges - bite block - colour coding - airway path in centre Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • How to size it???? The size of the Guedel airway is the distance between the center of the incisors and the angle of the jaw (on the same side!) Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • How to put it in: Depress tongue Slip over spatula with curve caudal direction Place bite block between teeth • NO TWISTING MOVEMENT Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • Indications: To open and maintain an airway in a patient with a depressed level of consciousness With FMO2 or BMV Oropharyngeal Airway/Guedel • Contra indications: Patient won’t accept it LOC Risk of vomiting & aspiration Nasopharyngeal Airway • For maintaining airway in “more awake” patients • Sits in nasopharynx and opens airway • Does NOT protect against aspiration Nasopharyngeal Airway Nasopharyngeal Airway • How to size it? Estimate by comparing to patients little finger • How to insert it? Lubricate Gently push posteriorly towards ear on same side Fix with a safety pin Nasopharyngeal Airway • Contra-indications: Base of skull fracture Serious midline facial fractures When definitive airway needed LMA • Advanced airway • Useful alternative for “difficult intubation” • Easy to use • Sits on larynx - Protects lungs? LMA LMA • Have a range in unit • Re-use ?20 times • Part of kit • Formula for Children: The combined widths of the patient's index, middle and ring fingers SIZE 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 4 5 6 PATIENT <5 kg 5-10kg 10-20kg 20-30kg 30-50kg 50-70kg 70-100kg >100kg LMA in Emergency Medicine • Indications: Unconscious or anaesthetized patients AHA Guidelines for adults: BLS: alternative to BMV ACLS: Optional/alternative to BMV, failed ETT • Aspiration? • Paediatrics? LMA in Emergency Medicine • Aspiration? Less than with BMV Supraglottic device Aspirated from CPR or post LMA? Cricoid pressure during CPR LMA Use in Emergency Paediatrics • Little Data “Despite widespread use LMA, there is little data on its effectiveness during positive pressure ventilation in infants and young children “ • Obstruction The LMA appears more likely to cause partial airway obstruction in infants ( < 10kg) than in older children. • PALS®: Class Indeterminate • Neonates: “Can’t intubate can’t ventilate” LMA in Emergency Medicine • Benefits: Ineffective BMV with failed ETT AHA: Alternative to ETT or BMV in CPR Blind ETT, by passing ETT through LMA Drugs - 27% efficacy LMA in Emergency Medicine • Disadvantages: Needs adequate training Risk of aspiration Limited Paediatric use Not always successful LMA Insertion LMA Insertion Combitube® Combitube® • Advantages: Protect airway from aspiration Easy to use AHA: alternative to ETT for CPR • Disadvantages: Trauma to soft tissues Not available here in SA Combitube® • Head neutral or slightly flexed • Hold tongue and jaw between thumb & forefinger and lift • Gently insert Combitube® in a curved back and downward movement until black markers aligned with teeth • Inflate (proximal) pharyngeal balloon • Inflate (distal) tracheal balloon • Confirm which one of #1 or #2 tube is in lungs by using bag ventilator Combitube® Insertion ETT Equipment for ETT • • • • • • • • Mask and bag ventilator with O2 ETT - checked, lubricated, tape ready Laryngoscope Drugs: Induction agent & muscle relaxant McGills forceps, Bougie Primary detection tools Other advanced airways Surgical airway capability ETT • Advantages: Airway patent and protected Secretions suction O2 Medication Known tidal volume ETT • Disadvantages: Training Skill lost Interrupted CPR Why ETT? • For above benefits • Inability to BMV or ineffective BMV • Secure threatened airway • Certain thoracic injuries Anatomy endotracheal tubes • cuffed tubes • uncuffed tubes placement of ETT • length of tube at the larynx (cm) = internal diameter of correct ETT for size railroad techniques for changing tubes • getting the curves right Tube Placement Confirmation • Clinical - visual - auscultation - laryngoscopy • Detection devices - CO2 (2a) - EDD Detection Devices • Always clinical + device • No single device specific or sensitive • CO2 detector: 33%-100% sensitive : 97%-100% specific : only studied on ETT • EDD: bulb compressed or syringe pulled : High sensitivity : Poor specificity • CXR Secure the ETT • • • • Record depth at front teeth Evidence is commercial=tape Re-evaluate 3 Rules - verify placement - asynchronous CPR - avoid excessive ventilation BMV • • • • • Best for last! Easy to master First line in CPR Every unit has one Effective BMV BMV • OLD: ETT ventilation adjunct of choice for CPR • ETT complications - misplaced - displaced - interrupted CPR • AHA: BMV or advanced airway for CPR • Prehospital: BMV=LMA & Combitube® Failed Intubation • Can’t intubate, Can Ventilate Don’t panic, call for help Reassess need to intubate Reposition patient, airway Cricoid pressure Bougie Consider other advanced airways Call for help Failed Intubation • Can’t intubate, Can’t Ventilate Call for help, don’t panic Reassess airway, positioning Reassess equipment Two person ventilation Other advanced airway Surgical airway CALL FOR HELP Remember • Check your equipment before you need it • Be prepared • Don’t panic Parting shot “Patients do not die from lack of intubation they die from lack of oxygenation” References • Currents, winter2005-2006 • JAMA, Feb 9, 2000-Vol 283, No6 p783-790 • www.aic.cuhk.edu.hk/web8/index • www.healthsystem.virginia.edu/Internet/AnesthesiologyElective/airway/anatomy • www.lmana.com/prod/components/products/lma_classic